Math 115 Practice Test 2
advertisement

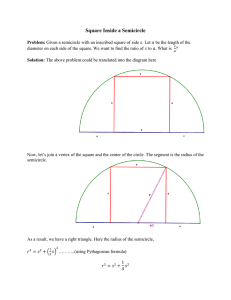
1 Math 115 Practice Test 2 TOTAL = 37 Note: All working leading to a solution must be shown for full marks to be awarded! Answers only will result in no marks being assigned. f x f [3] 1. If f x 5 x and g x x 3 find x , and give its domain in interval notation. g x g [3] 2.If f x 2x2 8x 4 and g x 3x2 12x 5 , find the solution set for: f x g x . . [3] 3. For the function f x [3] 4. Given the graph of a x 2 , find and simplify the difference quotient y f x f x h f x h . [3] shown below, show and explain all transformations you use to obtain the 1 graph of y f 2 x 2 3 2 x 5 x 3 f x x 7 3 x 5 . x5 3 2 [3] 5. Graph the piecewise relation defined by: Identify the domain and range and determine whether or not this relation is a function and justify your answer. [3] 6. For the function whose equation is f x 5 x4 : a) Find the average rate of change from ( 1, f(1)) to (2, f(2)). b) The equation of the secant line passing through those two points. [4] 7. Analyze the function 1 2 x 1 p x 2 x 6 3 x 3 x 2 2 x 3 . x3 Find the following: a) Domain and range. b) Maximum and minimum values. c) The intervals where the function is increasing or decreasing. d) The intervals where p x 0 and p x 0 . e) The symmetry. [2] 8. Let P = (x , y) be a point on the graph of y x . Express the distance from P to the point (1 , 0 ) as a function of x. [3] 9. Alan is building a garden shaped like a rectangle with a semicircle attached to one side. If he has 40 feet of fencing to go around it, what dimensions will give him maximum area in the garden? [3] 10. For the function g x 3 2 x 1 , find the difference quotient answer. [3] 11. If f x x 3 and g x x 2 a) Find f g x , b) Domain of : f x g x. g x h g x h and simplify your 2 [4] 12. Graph the function whose equation is f x 3 2 , x 1 by starting with its basic function and show and explain each transformation you use to obtain your final graph. ANSWERS f x f 5 x 1. f x 5 x and g x x 3 find x , domain of f(x) is: 5 x 0 x 5, domain of g x x3 g g(x) is: x 3 0 x 3 , therefore the domain of x 3 0 x 3 is x 5 and x 3 , which gives the final domain as 3,5 or 3 x 5 . 2. f x 2 x 2 8 x 4 and g x 3x 2 12 x 5 , find the solution set for: f x g x 2 x 2 8x 4 3x 2 12 x 5 5x 1 x 1 0 5x 2 4 x 1 0 critical values are: x 0.2,1 3. a f x a x 2 DQ f x h f x 4. From y f x h y x h 2 a x2 = h 1 f 2x , 2 ax 2 a x h x h 2 2 2 x h = ax 2 ax 2 2ahx ah2 x h 2 2 x h is A vertical compression and flip by a factor of 1 2 , horizontal compression and flip by a factor of 1 2 , this gives new x 4 2 coordinates 0 2 4 6 y 0 3 0 2 2 0 then 2 right and 3 down. to x 2 1 0 -1 -2 -3 y 0 -1.5 0 1 1 0 = 2ahx ah2 x h 2 x 2 h = 2ax ah x h 2 x 2 3 y then to x 4 3 2 1 0 -1 1 f 2 x 2 3 2 y -3 -4.5 -3 2 2 -3 f x x 5 5. x 3 5 6 7 Domain: , , 2 x -3 y 4 open 0 1 4 f x 3 3 x 5 y 4 5 7 2 x 5 6 7 range: , 0 , not a function, does not pass vertical line test 6. a) average rate of change is: 1 6 f x = x 7 x 3 2 0 5 x5 y 3 3 3 5 3 and 5 2 . 5 1 y y2 y1 f x2 f x1 f 2 f 1 6 1 Avg rate of change x x2 x1 x2 x1 2 1 1 6 1 6 b) Msec , choose point 1,1 , point-slope form: y y1 m x x1 y 1 x 1 y 1 7 x 6 6 4 7. p x x 2 4 1 x-1 x -2 2 y 0 open 1 p x =-2 x +6 x 2 0 3 a) Domain: , , range; decreasing on , 2 0, p x 3 x 3 2 x3 y x 2 closed 6 0 closed y 3 4 7 x3 0 open 3 6 b) max at ( 0, 6 ), min at ( 3, 0 ), c) Increasing on: 2, 0 0,3 d) p x 0, x Reals, x 0, p x 0, no solution , symmetry because of the restricted domains of this piecewise function, if 3, 0 , e) symmetry: there is no p x 2 x 6 , was restricted from x = -2 to x = 2, then we would have symmetry over those x values, but this is not the case. 8. The graph looks like: The distance formula is; D x2 x1 2 y2 y1 2 , since the equation of the graph is y x , we can sub this in for y : D x 12 x 0 x 2 2 x 1 x x 2 x 1 2 9. The diagram looks like a Norman window, a rectangle surmounted by a semicircle. If the radius of the circle is denoted by r , then the width is 2r , the circumference of the semicircle is r , then the length is given by; L 40 2r r 20 r r 2 2 . Then the area is given by: 5 L=20-r-r(π/2) 2r C=2πr r 1 1 1 A rectangle + semicircle 2r 20 r r r 2 40r 2r 2 r 2 r 2 2r 2 r 2 40r 2 2 2 2 1 A 2 r 2 40r this is a quadratic equation and since "a" is negative the parabola opens down and we have a maximum which occurs at the vertex. 2 We know the r value at the vertex is: r b 40 40 40 ~ 5.600991535, and L 20 ~ 5.6, 1 4 2a 4 2 2 2 2 therefore the dimensions of the rectangle are 11.2 feet by 5.6 feet and the radius of the semicircle is 5.6 feet. 10. g x h g x 2 g x 3 x 1 h 2 x 1 2 x h 1 x h 1 x 1 h 1 3 2 2 3 x h 1 x 1 h 2 x 2 2 x 2h 2 1 2h x h 1 x 1 h x h 1 x 1 h 2 x h 1 x 1 11. a) b) f x g x x 3 x 2 Domain: domain of f x g x , domain of f x : x 3 0 domain of g x : x 2 0 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 2 2, 12. I Basic: y x 1 y 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 x y x 1 2 1 y 1 2 1 2 2 2 asymptotes: x 0, y 0 2 vertical stretch & flip by factor of 2. x x y x y 1 1 4 4 2 2 1 2 1 2 2 1 2 1 asymptotes; x 0, y 0 2 3 1 left, 3 up x 1 x y x y y 1.5 7 0.5 1 2 5 0 1 3 4 1 2 asymptotes: x 1, y 3 6