Chapter 3
advertisement

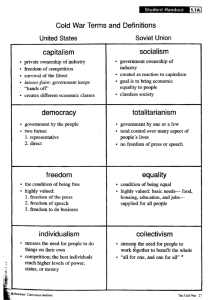
Chapter 3 Engines of Change—Karl Marx Chapter Objectives: After reading and understanding this chapter, a student should be able to Explain human nature through the idea of species-being and apply the idea to understanding his or her own social world Describe dialectical processes and analyze the structural dialectics of capitalism Explain Marx’s theory of class bi-polarization Explain how the value of exchange is creating in commodities Apply the idea of exploitation to current economic relations, including the globalization of exploitation Explain how industrialization, markets, and commodification are intrinsically expansive in capitalism and apply this dynamic to understanding contemporary capitalism Explain how alienation and commodity fetish are created and how they affect the lives of workers Describe false consciousness and explain how it is produced through dialectical elements within capitalism Explain why class consciousness has been slow to develop Describe how multinational capitalism and machines of reproduction have created a break in the chain of signification and produced free-floating signifiers and analyze her or his own world using the idea of free-floating signifiers Key Concepts (listed here and under each heading in the outline): species being; substructure and superstructure; the material dialectic; materialism and idealism; natural division of labor; primitive communism; class; means and relations of production; bourgeoisie and proletariat; capital accumulation; bi-polarization of conflict; labor theory of value; use-value and exchange-value; exploitation; necessary and surplus labor; absolute and relative surplus labor; industrialization; markets; commodification; money; globalization; alienation; private property; commodity fetish; misrecognition; false consciousness; ideology; religion; reification; division of labor; commodification of labor; class consciousness; market capitalism; monopoly capitalism; multinational capitalism; machines of reproduction; free-floating signifiers; simulacrum; biographic history Chapter Outline: I. Marx’s Perspective: Human Nature, History, and Reality Key concepts: species being; substructure and superstructure; the material dialectic; materialism and idealism; natural division of labor; primitive communism A. Species-being 1. Fundamental link between method of survival and defining features of an animal 2. Humans survive through production 1 3. Production and species-being provide a material base for human self consciousness 4. Idea of species-being is the core of such Marxian concepts as alienation, ideology, false consciousness, and class consciousness B. The material dialectic (Figures 3.1, 3.2) 1. Different elements that are naturally antagonistic or in tension to one another a. This antagonism is what energizes and brings change 2. Dialectics are cyclical in nature, with each new cycle bringing a different and generally unpredictable resolve II. The Basic Features of Capitalism Key concepts: class; means and relations of production; bourgeoisie and proletariat; capital accumulation; bi-polarization of conflict; labor theory of value; use-value and exchange-value; exploitation; necessary and surplus labor; absolute and relative surplus labor; industrialization; markets; commodification; money; globalization A. Class and class structure 1. Means and relations of production 2. Unique features of capitalist classes a. Capitalism lifts economic work out of all other institutional forms b. Bipolarization of classes i. Classes reduced to bourgeoisie and proletariat through Marxian business cycle (Figure 3.3) B. Value and exploitation 1. Two different values: use-value and exchange-value a. Value of exchange (price over and above its use) determined by investment of human labor 2. Capitalist profit dependent upon exploitation a. Difference between necessary labor and surplus labor (Figure 3.4) i. Absolute surplus and relative surplus labor C. Industrialization, markets, and commodification (Figure 3.5) 1. Industrialization: process through which work moves from being performed directly by human hands to having the intermediate presence of a machine a. Increases levels of relative surplus labor, exploitation, and alienation 2. Markets a. Intrinsically expansive in capitalism b. Rate of expansion dependent on money as abstract media of exchange i. Money comes to define all human relations because of its universality 3. Commodification 2 a. The process through which more and more of the human lifeworld is turned into something that can be bought or sold b. Production of new “needs” III. Ramifications of Capitalism Key concepts: alienation; private property; commodity fetish; misrecognition; false consciousness; ideology; religion; reification; division of labor; commodification of labor; class consciousness A. Alienation and commodity fetish 1. Alienation a. Founded in species-being b. Objective and subjective c. Four kinds of alienation i. From own human nature ii. From work process iii. From product iiii. From others 2. Commodity fetish a. Belief that commodity will fulfill human self and desire b. Misrecognition of exploitation and relations of production within product B. False consciousness and religion 1. False consciousness: awareness of world based on anything but speciesbeing 2. Ideology: false beliefs that legitimate unequal social relations 3. Religion a. As ideology i. Problem of reification ii. Preventing class consciousness C. False consciousness and the division of labor 1. Material and mental D. Creating class consciousness 1. Necessary for social change 2. Two kinds a. Class in itself b. Class for itself 3. Result of structural factors (Figure 3.6) a. Level of industrialization b. Level of ecological concentration of workers c. Level of worker education d. Level of communication and transportation technologies 4. Impediments to achieving class consciousness a. Dominant ideology (state) b. Worker concessions in core countries c. Exportation of exploitation d. Cultural diversity among workers 3 IV. Thinking About Modernity and Postmodernity Key Concepts: market capitalism; monopoly capitalism; multinational capitalism; machines of reproduction; free-floating signifiers; simulacrum; biographic history A. Three phases of capitalism 1. Early capitalism: market 2. Middle capitalism: monopoly 3. Late capitalism: multinational B. Machines of production and consciousness; 1. Consciousness based on material production 2. Industrialization led to false consciousness, but there was still a relationship that the worker had with production C. Machines of reproduction and schizophrenic culture 1. Machines of reproduction not linked to any material production at all: mass media, computer technologies 2. Break in signification chain a. free-floating signifiers b. simulacrum Chapter Summary: Marx’s perspective is created through two central ideas: species-being and the material dialectic. Species-being refers to the unique way in which humans survive as a species—we creatively produce all that we need. The material dialectic is the primary mechanism through which history progresses. There are internal contradictions within every economic system that push society to form new economic systems. The dialectic continues until communism is reached, a system that is in harmony with species-being. Every economic system is characterized by the means and relations of production. The means of production in capitalism is owned by the bourgeoisie and in the main consist of commodification, industrial production, private property, markets, and money. One of the unique features of capitalism is that it will swallow up all other classes save two: the bourgeoisie and proletariat. This bifurcation of class structure will, in turn, set the stage for class consciousness and economic revolution. Capitalism affects every area of human existence. Through it individuals are alienated from each aspect of species-being and creative production. The work process, the product, other people, and even their own inner being confront the worker as alien objects. As a result, humankind misrecognizes the truth and falls victim to commodity fetish, ideology, and false consciousness. However, because capitalism contains dialectical elements, it will also produce the necessary ingredient for economic revolution: class consciousness. Class consciousness is the result of workers becoming aware that their fate in life is determined primarily by class position. This awareness comes as alienation and exploitation reach high levels and as workers communicate one with another through increasing levels of education, worker concentration in the factory and city, and communication and transportation technologies. 4 Jameson’s argument concerning postmodernity is based on Marx’s theory of consciousness: human consciousness is materially based; that is, because of species being there is a direct relationship between the method of production and the ideas we have about ourselves and the way we perceive the world. In primitive communism we had direct and objective knowledge of the world and our selves. Under early capitalism we suffered from false consciousness and ideology, but this knowledge was still materially grounded in that we were connected to machines of production. In that state, we could have come to a real sense of alienation and class consciousness. However, in postmodernity the economy is shifting from machines of production to machines of reproduction. With machines of production, there was a connection between culture and the material world. With machines of reproduction, that connection is broken. As a result, cultural signs and symbols are cut loose from their mooring and loose any grounded sense of meaning or reality. 5