EDCP373a-Pythagorean Theorem Lesson Plan
advertisement

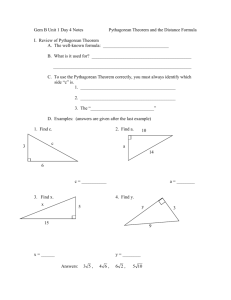
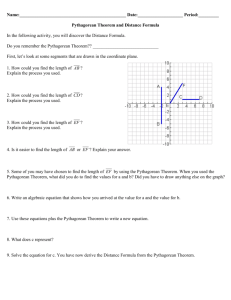
Teacher Candidate Name: Grade & Subject: Date + Time of demo/class: Gary Ma Faculty Advisor: Math 9 Pythagorean Theorem School Advisor: Oct.22.2012 Block + Classroom: SCRF1106 The Pythagorean theorem Topic: -What the theorem states Subject matter -When should it be used Explain about the material/technology to be taught/demonstrated C1: Develop and apply the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems Goals: Aims/Outcomes BC IRPs Objectives: Performance/ Behavioural Indicators What will students be able to do/ know by the end of the lesson? Instructional Materials: Aids/AV/Technology List the necessary materials: After the completion of today’s class, students should be able to -Know the formula for Pythagorean theorem -Understand the situations in which it can be used, and when it cannot. -Solve for the unknown length of a right angle triangle given the lengths of the other two sides Math 9 textbook Powerpoint slides Computer that is able to play the powerpoint slide Whiteboard markers For Teacher / For Students Introduction: Pose the introduction problem. Should students choose the blue or the red side? Hook: Focus student attention Pre-test / starter: Activate and diagnose prior knowledge New Terms: Vocabulary/ List and define new terms Show the class the introduction problem. Ask them how they go about making the choice they made. Check to see if this choice is based on the Pythagorean theorem, or if they are just eyeing the problem. Pythagorean theorem, right angled triangle, perpendicular, hypotenuse. 1. 2. 3. 5 minutes (to be used as micro teaching) 5. 6. Procedure: How much time will you spend on individual parts of the lesson? List steps necessary for using or applying the tool or process. Modeling/Explanation Demonstration 10 minute cushion time (in real lecture) 10 minutes 7. Show the class the proof of the Pythagorean theorem 8. Show the 4 triangles, with side lengths a, b, and c, each rotated 0, 90, 180, and 270 degrees 9. Place the triangles together to create a square 10. Label the sides in the square, demonstrating the sides a-b in the central square. Show how the area of each triangle is a*b/2. The area of the square is then (a-b)^2+2ab 15minutes 11. Allow class to work in partners, to attempt to finish the proof. Give them the hint of the area of the square being c^2. 12. Reveal how the proof is done by showing the algebraic steps 20-25 minutes 13. Show the class two sample problems on the next slide. These problems are to be turned in as exit slips 14. Assign homework from the textbook. The remaining class time is allowed for students to complete the homework. N/A Special Safety: Any special safety precautions 4. Show the class the introduction problem on the power point Allow 1 minute of discussion between partners Ask the class what they have chosen, and reveal the correct answer Show the powerpoint slides. Show the class Mathematically how the squares are equal in size Introduce the Pythagorean theorem Allow the class 2 minutes or so to work on the two sample problems on the slides. They may do it in partners Guided Practice: -Introduction problem -Basic Pythagorean theorem problem in partners -Completing the proof for the Pythagorean theorem in partners -Exit slip problems Guided/Monitored Activity. Application of knowledge, classroom activities for students, problem to solve, etc. Accommodations: Students can work in partners or in groups in various points of the lecture Differentiated Instruction Check For Understanding (Questions): Exit slips Assessment/Feedback Evaluation/Assessment: -Formative assessment while the class is working on the problems -Exit slips Measures of Progress How does this lesson relate to assignments/homework/readings. -Restate the Pythagorean theorem, how it can only be used on right angled triangles. Closure: Wrapping it up/ Recap Key Concepts Teacher Reflections: To be completed after lesson! Notes for yourself