UML record
advertisement
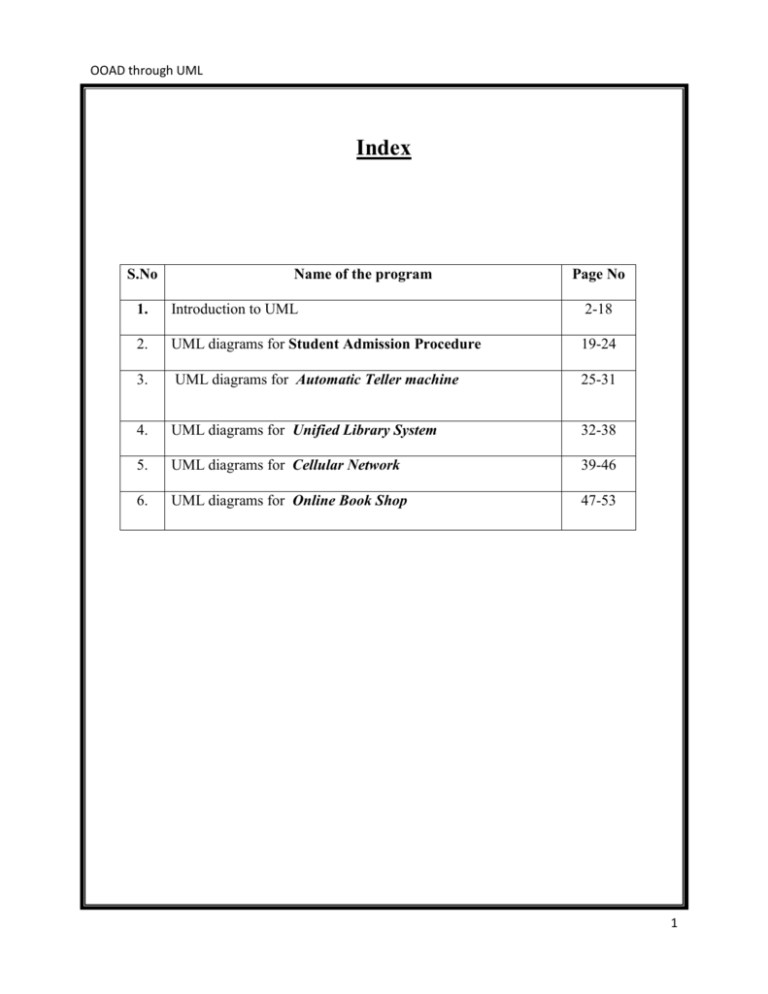
OOAD through UML Index S.No Name of the program Page No 1. Introduction to UML 2-18 2. UML diagrams for Student Admission Procedure 19-24 3. UML diagrams for Automatic Teller machine 25-31 4. UML diagrams for Unified Library System 32-38 5. UML diagrams for Cellular Network 39-46 6. UML diagrams for Online Book Shop 47-53 1 OOAD through UML WHAT IS UML? The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a standard language for writing software blueprints. The UML is a language for - Visualizing - Specifying - Constructing - Documenting the artifacts of a software-intensive system. The UML is appropriate for modeling systems ranging from enterprise information systems to distributed Web-based applications and even to hard real time embedded systems. IMPORTANCE OF MODELING 1) If we want to build a dog house, with a little planning, we’ll likely end up with a dog house that’s reasonably functional and we can do it with no one’s help. 2) If we want to build a house for a family, it’s going to take a lot longer. In this case we need some detailed planning; we’ll need to draw some blueprints, before we lay the foundation. 3) If we want to build a high-rise office building, we’ll have to do extensive planning; and we need all sorts of blueprints and models to communicate with one another. WHAT IS A MODEL A Model is a simplification of reality. We build models so that we can better understand the system we are developing. We build models of complex systems because we cannot comprehend such a system in its entirety. Through Modeling, we achieve four aims 1. Models help us to visualize a system as it is or as we want it to be. 2. Models permit us to specify the structure or behavior of a system. 3. Models give us a template that guides us in constructing a system. 4. Models document the decisions we have made. 2 OOAD through UML PRINCIPLES OF MODELING Four basic principles of modeling are 1) The choice of what models to create has a profound influence on how a 2) Problem is attacked and how a solution is shaped. 3) Every model may be expressed at different levels of precision. 4) The best models are connected to reality. 5) No single model is sufficient. CONCEPTUAL MODEL OF UML To understand UML, you need to form a conceptual model of the language. This requires learning three major elements: I. II. III. Basic Building Blocks Rules Common Mechanisms I) BASIC BUILDING BLOCKS There are 3 kinds of basic building blocks 1. Things 2. Relationships 3. Diagrams 1) THINGS in the UML There are 4 kinds of things in the UML i. Structural Things ii. Behavioral Things iii. Annotational Things iv. Grouping Things 3 OOAD through UML 1) Structural Things Structural Things are nouns of UML models. There are 7 kinds of Structural things a) Class A class is a set of objects that share the same attributes, operations, relationships and semantics. b) Interface An Interface is a collection of operations that specify a service of a class or component ISpelling c) Collaboration Collaboration describes co-operative work of an element. d) Use Case Use Case describes set of sequence of actions that a system performs that yields an observable result of value to a particular actor. UseCase Actor 4 OOAD through UML e) Active Class Active class is just like a class but its elements are connected to other class elements. f) Component Component represents physical packaging of logical elements like classes, interfaces and collaborations. Component g) Node A Node is physical element that exists at run-time and having at least some memory and processing capability. Node ii) Behavioral Things Behavioral Things are the verbs of UML representing behavior over time and space. There are 2 kinds of Behavioral things a) Interaction Interaction is used to show communication between two objects. 5 OOAD through UML b) State Machine State Machine specifies sequence of states of an object. iii) Annotational Things Annotational Things are explanatory parts of UML. Only 1 type. Note Note is used to give comments to an element or collection of elements. Note iv) Grouping Things Grouping Things are the organizational parts of the model. Only one type. Package Package is a general purpose mechanism for organizing elements or things into groups or packages. Package 6 OOAD through UML 2) RELATIONSHIPS There are 4 kinds of Relationships in the UML: a) Dependency: It is denoted by dashed line with an arrow. Dependency is a relationship between two things in which a change to one thing (Independent thing) may affect the other thing (Dependent thing). b) Association: It is denoted by a solid line. ____________________ Association is a structural relationship that describes a set of links, a link being a connection among objects. Aggregation is a special kind of association, representing a structural relationship between a whole and its parts. c) Generalization: It is denoted by a solid line with a hollow arrow head pointing to the parent 7 OOAD through UML Generalization is a relationship in which the child will share the behavior of the parent. d) Realization: It is denoted by dashed lines with a hollow arrow head. Realization is a relationship between classifiers, where one classifier specifies a contract that another classifier guarantees to carry out 3) DIAGRAMS There are 9 types of Diagrams in UML, which are classified into 2 types i) Structural Diagrams (static diagrams) These are of 4 types 8 OOAD through UML a) Class Diagram A Class diagram shows a set of classes, interfaces, and collaborations and their relationships. A class consists of class name, attributes, operations and responsibilities. b) Object Diagram An Object diagram shows a set of objects and their relationships. They represent snapshots of instances of the things found in class diagrams. 9 OOAD through UML c) Component Diagram A Component diagram shows the organizations and dependencies among a set of components. d) Deployment Diagram A Deployment diagram shows the configuration of run-time processing nodes and the components that are present in them. Component and Deployment diagrams are called as Physical Diagrams. ii) Behavioral Diagrams (Dynamic diagrams) These are of 5 types a) Use Case Diagram A Use Case diagram shows a set of use cases and actors and their relationships. An Actor can be a human or a system. The role of actor is written below. 10 OOAD through UML Interaction Diagrams An Interaction diagram shows an interaction, consisting of a set of objects and their relationships, including the messages they exchange among them. 2 types of Interaction diagrams are: b) Sequence Diagram A Sequence diagram is an interaction diagram that emphasizes the time-ordering of messages. To show interaction between objects we use 3 types of messages. Simple Messages: A Simple message shows how control is passed from one object to other without describing communication in detail i.e. without indicating whether it is synchronous or asynchronous message. Synchronous Messages: If sender object waits for a reply from receiver object from destination, such messages are called Synchronous messages. Here, only one object can send a message at a given instance of time. Asynchronous Messages: If sender object continues executing while target is processing the message then such messages are said to be Asynchronous messages. Here, multiple messages are executed at a time. Object Lifeline: An Object life line is vertical dashed lines that represent the existence of an object over a period of time. Focus of Control: It is represented by rectangle that shows the period of time during which an object performs some actions. 11 OOAD through UML c) Collaboration Diagram A Collaboration diagram is an interaction diagram that emphasizes the structural organization of the objects that send and receive messages. 3: fill form 5: check form 1: Request form 4: submit S: Student A: Admin 2: give form 6: eligible d) State chart Diagram A State chart diagram shows a state machine, consisting of states, transitions, events, and activities. 12 OOAD through UML Event: It refers to happening of an activity at a given time and place. e) Activity Diagram An activity diagram is a special kind of state chart diagram that shows the flow from activity to activity within a system, which are connected by a triggerless transition. We can check some conditions using decision box, which is denoted by a diamond. 13 OOAD through UML Activity: It is a major task that must take place in order to fulfill an operation contract. Initial Activity: This shows the starting point of the flow. It is denoted by solid circle Final Activity: This shows the end of the flow in the activity diagram. It is denoted by a solid circle nested in a circle. Decision Box: A point in an Activity diagram where a flow splits into several mutually exclusive guarded flows. It has one incoming transition and two outgoing transitions. Forking and Joining:-We use synchronization bar to specify the forking and joining of parallel flows of control. A synchronization bar is a thick horizontal or vertical line. A Fork may have one incoming transition and two or more outgoing transitions, each of which represents an independent flow of control. A Join may have two or more incoming transitions and one outgoing transition. Student synchronization bar Forking Listen Watch Joining Success 14 OOAD through UML Swimlanes: They are used to group related activities into one column. II) RULES There are 2 kinds of rules 1) Well formed rules 2) Less-well formed rules 1) Well formed rules: These are of 5 types: a) Names: What you call things, relationships, and diagrams b) Scope: The content that gives specific meaning to a name. c) Visibility: How these names can be seen and used by others. d) Integrity: How things properly and consistently relate to one another. e) Execution: To run a model. 2) Less-well formed rules: These are of 3 types a) Elided: Certain elements are hidden to simplify the view. b) Incomplete: Certain elements may be missing. c) Inconsistent: The integrity of the model is not guaranteed. III) Common Mechanism: To make our model simpler we have to follow the following 4 common mechanisms: a) Specification: Provides all the parts of the model that the system should contain. b) Adornments: Provides visual representation of most important aspects of the elements c) Common Divisions: Provides division between classes & objects and interface & implementation. 15 OOAD through UML d) Extensibility Mechanisms: It is possible to extend the UML in a controlled ways. There are 3 mechanisms: i) Stereotypes: Allows creating new kind of building blocks that are derived from the existing one. ii) Tagged Values: Used to extend the properties of UML building blocks. iii) Constraints: Allows adding new rules or modifying existing one. ARCHITECTURE OF UML Architecture is a set of decisions about 1) The organization of software system 2) The selection of structural elements 3) The behavior of these structural elements 4) The composition of these structural elements 5) The architectural style that guides the organization 16 OOAD through UML Architecture of UML can be described using 5 views 1) Use case view: It contains use cases that describe the behavior of the system as seen by the end user. The static aspects of this view are captured in Use case diagrams. 2) Design view: It contains classes, collaborations and interfaces. This view supports the functional requirements of the system. The static aspects of this view are captured in Class diagrams and Object diagrams. 3) Process view: It contains threads and processes that form the systems concurrency and synchronization mechanisms. This view focuses on the performance, scalability and throughput of the system. The static aspects of this view are captured in Class diagrams and Object diagrams. 4) Implementation view: It contains components and files that are used to assemble and release the physical system. This view focuses on the configuration management of the system. The static aspects of this view are captured in Component diagram. 5) Deployment view: It contains the nodes that form the system hardware topology. This view focuses on distribution, delivery and installation of the parts that make the physical system. The static aspects of this view are captured in Deployment diagram. The dynamic aspects of all the above mentioned vies are captured in Interaction, Activity and State chart diagrams. 17 OOAD through UML SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT LIFE CYCLE UML is a process independent language, meaning that it is not connected to any particular software development life cycle. To get the most benefit from the UML, we should consider a process that is - Use case driven - Architecture-centric - Iterative and incremental This use case driven, architecture-centric, and iterative and incremental process can be broken into phases. A Phase is the span of time between two major milestones of the process, when a well-defined set of objectives are met, artifacts are completed, and decisions are made whether to move into the next phase. There are four phases in the software development life cycle: Inception is the first phase of the process, when the seed idea for the development is brought up to the point of being—at least internally— sufficiently well-founded to warrant entering into the elaboration phase. Elaboration is the second phase of the process, when the product vision and its architecture are defined. In this phase, the system’s requirements are articulated, prioritized, and baselined. Construction is the third phase of the process, when the software is brought from an executable architectural baseline to being ready to be transitioned to the user community. Transition is the fourth phase of the process, when the software is turned into the hands of the user community. The process rarely ends here, because even during this phase, the system is continuously improved, bugs are eradicated, and features that didn’t make an earlier release are added. One element that distinguishes this process and that cuts across all 4 phases is iteration. Iteration is a distinct set of activities, with a baselined plan and evaluation criteria that result in a release, either internal or external. 18 OOAD through UML Name of the Project: Student Admission Procedure Project Statement: The given problem is to model the admission of a student in Padmasri Dr.B.V.Raju Institute of Technology. Functional Requirements: The College Provides admission for the Student by giving the application form The Administrator checks the application form which is filled by the students, tests whether he/she is eligible or not. After paying fee he/she issues admission card. The Cashier collects the fees from the students and gives their respective receipt. Use case Diagram: request the form give the form apply for admission administrator student check the application cashier collects it fill the fee give receipt collect admission card cashier from the administrator by showing receipt 19 OOAD through UML Documentation: Objective: In the above use case diagram we have three actors, student, administrator and cashier performing different operations, represented by the use cases for all the three actors. The use case diagram is initiated student by requesting the form. Flow of messages in response to which the administrator give the form, the student fills the form and submits it back to administrator; he then checks the form for eligibility. Then student pays the fee and takes the receipt. The use case diagram terminates with the student collecting the admission card. Alternative flows: if the student is not eligible then the use case stops. Class Diagram Documentation: Class name: Student Attributes :name, fname, address and dob Functions: fillform, reqform, payfee and coladmncard Relationships :association with administrator and cashier 20 OOAD through UML Class name : Administrator Attributes : name, id. Functions: giveform, checkappl, giveadmcard, update database. Class name : Cashier Attributes : name, id. Functions : Collectcash, givereceipt. 21 OOAD through UML Sequence Diagram s:Student a:Administrator c:Cashier request for form give the form submit application verify the application approved/rejected fill the fee issue receipt show the receipt give admission card 22 OOAD through UML Collaboration Diagram 4: verify the application a:Administr ator c:Cashier 1: request for form 3: submit application 8: show the receipt 7: issue receipt 6: fill the fee s:Student 2: give the form 5: approved/rejected 9: give admission card 23 OOAD through UML Activity Diagram request for the form issue the form fill the form check the eligibility eligible pay the amount and receive the reciept not eligible receive the admission card Documentation: The above activity diagram starts when the student requests for a form, the administrator issues one. Then he fills the form and submits it back to the administrator. The administrator checks the form for eligibility; if eligible the student then pays the fee to the cashier and then submits it to administrator to collect the admission card. In case if the student is not eligible then the activity diagram ends as there is no other activity takes place. 24 OOAD through UML Name of the Project : Automatic Teller machine Project Statement: The given project is to model automatic teller machine in which a customer uses his/her ATM card to draw money from ATM. Functional requirements: The ATM machine provides facilities like withdraw amount, check balance, change password, mini-statement, and transfer of amount etc to customers. Use case diagram: Insert card display pin no screen Enter pin no customer display options (menu) screen system Select option Enter amount withdraw money/change password/etc. issue cash Collect cash and card 25 OOAD through UML Documentation: Objective: In the above use case diagram we have two actors, customer and system performing different operations, represented by the use cases for the atm system. The use case diagram is initiated with the customer inserting the card Flow of messages: in response to which the system displays the pin no screen. The customer enters the pin no. The system verifies the pin no and displays an options menu. The customer selects the option he wants(withdraw money in this case).Further the customer enters the amount he would like to withdraw. The system issues cash. The use case diagram terminates with the user collecting the cash and the card. Alternative flows: In case the pin no entered by the customer is invalid, he is directed to reentering the pin no. In case the amount entered by the user is insufficient or out of limit, then the user is directed to re-enter the amount. Class Diagram: 26 OOAD through UML Documentation: Class name: System (ATM machine) Attributes: system id, location Functions: display pin no screen, display menu, issue cash and check balance Relationships: association with customer and database. Class name: Customer Attributes: name, addr, acct no, pin no Functions: insert card, enter pin num, select option, enter amt and collect cash Class name: Database Attributes: bank name, location Functions: maintain acct details, add customer, del customer. 27 OOAD through UML Sequence Diagram: u : Customer s : System d : database insert card send card details display pin no screen enter pin no request pin no details sending display options menu check select option enter amount request balance details sending check if balance is adequate issue cash collect cash update database reload data exit 28 OOAD through UML Collaboration Diagram: 7: check 13: check if balance is adequate 1: insert card 4: enter pin no 9: select option 10: enter amount 15: collect cash s : System u : Customer 3: display pin no screen 8: display options menu 14: issue cash 18: exit 6: sending 12: sending 17: reload data 2: send card details 5: request pin no details 11: request balance details 16: update database d : database 29 OOAD through UML Activity Diagram: start insert card enter the pin number Invalid Pin no valid select the account type select the options enter the amount insufficient balance Limit exceeds Sufficient balance available within limit collect the amount further transactions no more transactions collect card stop 30 OOAD through UML Documentation: The above activity diagram starts when the customer inserts his card. He enters the pin no on to the screen. The system then verifies whether the pin no is valid. In case it is not valid the customer is asked to re-enter the pin no. In case it is valid, the customer selects the account type he wants to use and the option (in this case withdrawing money).The customer then enters the amount he wants to withdraw. This is scrutinized first by checking if sufficient balance is present in the account and second if it is within limit. In case both satisfy, the cash is issued to the customer. The customer collects the cash. In case he wants to further select some options he is provided with the option to do so. If not, he collects his card and the activity diagram stops. 31 OOAD through UML Name of the Project: Unified Library System Project Statement: The given problem is to model the unified library system in Padmasri Dr. B.V.Raju Institute of Technology. Functional Requirements: 1. The Librarian will have a complete access to the system as listed below. Permits to login with unique register id. Can add new items to database, can delete damaged items from data base. Check on transactions of borrowers and ensure charges for overdue items, damaged and lost items are paid. Ensure delays in returning borrowed items are not repeated. 2. The Members (Staff and Students) have to login into the system and they can search for a particular book. They can borrow a book, renewal a book. Use case Diagram: login database search book <<include>> borrow book Member <<extend>> check id card of student <<include>> <<include>> get book from other dept. Student Staff return book add book librarian delete book 32 OOAD through UML Documentation: Objective: In the above use case diagram we have three actors, member (student, staff), librarian and database performing different operations, represented by the use cases for all the three actors. The use case diagram is initiated when the member log’s into his/her account. Flow of messages the database checks log in data and then the member searches for the required book (suppose if the book is available), borrows it, after a certain period of time he returns the book. The librarian checks the member’s ID card before issuing the book. He also adds or removes the book from the database. The use case diagram terminates with the returning the borrowed book. Alternative flows: if the required book is not available then the book is borrowed from the departmental library, where also the ID card is checked by the librarian. 33 OOAD through UML Class Diagram Documentation: Class name: Member (student,staff) Attributes : id, name, borrowlimit,address, fine amount Functions: borrowbooks, returnbooks, check availability, payfine. Relationships :associated with librarian class and base class for both Student and Staff. 34 OOAD through UML Class name : Librarian Attributes : name, id, address Functions: issuebook, renewbooks, collectfines, collectbooks, addmembers, add_newitems, delete members, remove item. Class name : Articles Attributes : issuedate,returndate, bookid, availability Relationships: dependent on Librarian class Class name: Titles Attributes: item_id, price, copies, title, edition, publications, author, reservedcopies, issued copies. Functions: newtitles, removetitles, additionalpurchases. Relationships: dependent on Librarian class. 35 OOAD through UML Sequence Diagram : Librarian :Lending Window : Titles : Aarticles : Member Lending details validate find borrowing limit Borrowing limit not exeeded Find availability Requested items available Update issue details issue details updated update book borrowed udated 36 OOAD through UML Collaboration Diagram 1: Lending details : Librarian 4: Find availability :Lending Window : Titles 5: Requested items available 3: Borrowing limit not exeeded 9: udated 6: Update issue details 7: issue details updated 2: validate find borrowing limit 8: update book borrowed : Member : Aarticles 37 OOAD through UML Activity Diagram log in select a book from the library if not available Search the book in the departmental library Available submit the library card Available Issue the book and return on the prescribed date Documentation: The above activity diagram starts when the member logs in for a book. The member then searches for a book. If the book is available he takes it, in case if not available then he takes the book from the departmental library. Then the he submits the library card to the librarian. He checks the card and then issues the book to the member. The member returns the book on the day specified by the librarian. 38 OOAD through UML Name of the Project: Cellular Network Project Statement: The given problem is to model the cellular network Functional Requirements: User can make a call, receive a call. User can also do additional actions while receiving a call like receive additional call and while making a call user can place a conference call etc. Network should support user to perform above mentioned actions. And it should check user Phone numbers and their balance amount. Tower receives signal from user and sends it to destination user. 39 OOAD through UML Use case Diagram <<extend>> accept the conference recieve the call <<extend>> Dial a number invite for conference request for connection verify number Network balance enquiry Customer request the destination tower Tower connect the destination tower Hears the ring Continues the conversation disconnect call 40 OOAD through UML Documentation: Objective:In the above use case diagram we have three actors, customer, Tower and Network performing different operations, represented by the use cases for the cellular network. The use case diagram is initiated when the customer receives call or dails a number to make a call. Flow of messages:in response to which the customer accepts the call or waits for the another user to accept the call. The user can check balance, send sms during the conversation. The network verifies the number and balance. The tower makes the connection between the two users. The use case diagram terminates when the call is disconnected by either one of the users. Alternative flows: In case the number dialed is wrong or busy, the customers have to redail or wait till the user is available. Suppose the balance is low or nil the networks verify it and then end the call. 41 OOAD through UML Class Diagram 42 OOAD through UML Documentation: Class name: User Attributes : user name, user number. Functions: dialing the number, waiting, receiving from the user, recharge, balance enquiry. Relationships: association with Tower, Options, Balance, Recharge. Class name : Tower Functions: receiving the request, requesting the destination, providing connection, Disconnecting the connection, provide balance enquiry, enter 18 digits Number. Relationships: associated with request for connection, depends on database. Class name : Database Attributes : user name, user number, bal Functions : valid number of sender, valid number of receiver, out going calls, balance. Class name: Options Attributes: op Functions: mms, sms, outgoing calls, business sms, internet. 43 OOAD through UML Sequence Diagram u:USER t:TOWER n:NETWORK dial the number request for connection request the destination provide the connection continue the conversation disconnect the connection balance enquiry update the balance exit 44 OOAD through UML Collaboration Diagram 1: dial the number 5: continue the conversation u:USER 4: provide the connection 9: exit 3: request the destination 2: request for connection 6: disconnect the connection t:TOWER 7: balance enquiry 8: update the balance n:NETWO RK 45 OOAD through UML Activity Diagram dial the no process the network give busy indication busy ringtone response no response till 30 secs indicate no balance balance out before 1 min increment the usage time and update the balance have balance disconnect the service Documentation: The activity diagram begins when the user dials the number; the network checks the number and balance. If user is busy wait, If not then wait for the user to accept the call. The network checks the balance frequently, if balance below the limit then, disconnect the service. In case if balance is available then wait for the user to complete conversation and end the call. 46 OOAD through UML Name of the Project: Online Book Shop Project Statement: The given problem is to model online book shop. Functional Requirements: Create an online bookshop where the user can register him/her self and can order for books and pay the bill during the delivery of the books. Book shop staff has to send ordered items to the customer. Use case Diagram: Login in the website Provide book information for user search for availability of required book confirm about selected book Internet User Collect info or money from the user Give your debit or credit card number Specify means for collecting book Collect book 47 OOAD through UML Documentation: Objective:In the above use case diagram we have two actors, user and internet performing different operations, represented by the use cases for the online book shopping system. The use case diagram is initiated with the user ‘logs in’ in the website. Flow of messages:in response to which the system displays the books available, the user searches for a book, checks its availability, then confirms the selection of the book. The system takes the information about the payment of money. Then the system gives the means by which the book can be collected The use case diagram terminates with the user collecting the book. Alternative flows: In case the required book is not available the use case terminates. Class Diagram: 48 OOAD through UML Documentation: Class name: User Attributes : Card no, name. Functions:Enter Url, select book, give credit cardno., collect book. Relationships : Depends on book dealer and internet. Class name : Internet Functions: open requested site, process user requests, gather user data and send to DB. Relationships: depends on Database Class name : BookDealer Functions : Book delivery. Relationships: Depends of Database. Class name: Database Attributes: Card no, name Functions: Update book info,update credit cardno, update user info. 49 OOAD through UML Sequence Diagram User Internet Database Book dealer Request URL Display request Page Select book Request for credit cardno Submit details and cardno Update user info view requests Collect book from book dealer 50 OOAD through UML Collaboration Diagram 1: Request URL 3: Select book 5: Submit details and cardno User Internet 2: Display request Page 4: Request for credit cardno 6: Update user info 8: Collect book from book dealer Book dealer Database 7: view requests 51 OOAD through UML Activity Diagram Display welcome message Display item information Found confirm book selection create order from shipping cart display order accepted rejected if required book not found ship to customer 52 OOAD through UML Documentation: The activity diagram begins with the user logging in his/her account. The system displays the list of available books, the user searches for the required book. In case the book is not found then the activity terminates. If found then the user places an order and then makes the payment using his/her credit card. Then the system confirms the order and the details about the means of collecting the books are specified to the user. 53