Introduction To Networking LANS and WANS
advertisement

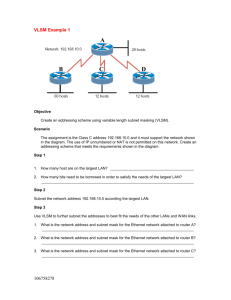
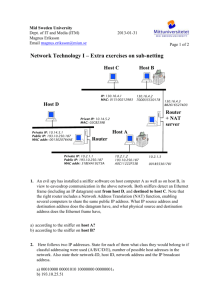
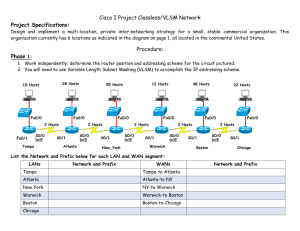
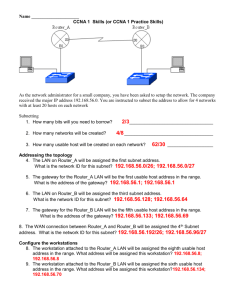
Introduction To Networking LANS and WANS Foundation Degree in IT for Business By: Ben Hampson Staffordshire University Date Issued: 23/02/09 Submission Date: 27/03/09 Recipient: Ivo Chakarov A Report On The Networking LANS and WANS case study. By Ben Hampson Recipient: Ivo Chakarov Abstract The evidence in this report will show how to configure a new network for the Warmingham Health authority. IP addressing will be shown and the steps that I took Inorder to make the subnets work for the networks. There will also be a section on pricing; this will include a list of prices from the computer to cables to labour. The cabling section will include a diagram where I have created the plan of where the cables are going to be place so that the computers can be linked to the network in the most cost effective way. The cabling diagram is for one floor of the building and is only for one building, although the plans for the pricing will include the prices for the whole project which will include all computers the cabling diagram will only be included for one floor. The report will explain how the system will be configured. It will explain how the simulation on packet tracer works. This will give the hospital a proposal of how this network is going to work for what the want it to do. The simulation will show a fully working design, which the hospitals network will be based on. Acknowledgements None Contents Abstract .......................................................................................................................... 2 Acknowledgements ........................................................................................................ 3 Contents ......................................................................................................................... 4 Terms Of Reference ....................................................................................................... 4 Forward ...................................................................................................................... 5 Aim ........................................................................................................................ 5 Objectives .............................................................................................................. 5 1.0 Method ..................................................................................................................... 5 1.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................. 6 2.0 Findings.................................................................................................................... 8 2.1 IP Addressing ........................................................................................................... 8 2.2 IP Address Configuration ........................................................................................ 9 2.3 IP Address Configuration table .............................................................................. 12 2.4 configuration of devices ......................................................................................... 14 2.5 Floor plan ............................................................................................................... 16 2.6 Costing ................................................................................................................... 18 3.0 Conclusion ............................................................................................................. 20 References/Bibliography.............................................................................................. 21 http://www.pcwb.co.uk/ec/basket.jtp [online] accessed 19/03/2009 .................. 21 Terms Of Reference Forward This report is going to look at the hospital network requirements that the three hospitals will be working on. The network is needed to be future proof and allow the three hospitals to work with the same records for its patients and also the same health server. Also in the network was needed to be the IP server allowing the network to use the internet. The report will explain how to work out the correct IP addresses for the given network address for the machines. A cabling diagram will be shown to explain how the machines are going to reach the two switches on one floor of one of the three sites. Also the way in which the network is going to be configured will be explained and what it has been done is this particular way. The main objective of the report is to show the hospital, which is described in the case study how the desired structure of the network is possible and how this may be completed so that all three sites have a fully working, future proof network. Aim 1. to explain to the IP addresses are found 2. To cost up the equipment that is needed to create the network and give the reasons for choosing these. 3. To provide a cabling diagram to show the layout of computers and how they are all connected to the server. 4. To write a report to show all my findings. Objectives 1. To understand process of subnetting 2. To find out the cost of putting the network together, 3. To find information using the internet regards to costs for the equipment. 4. To find out information on how cabling should be done. 1.0 Method The information within this report was collected from… The internet to investigate subnetting, VLSM and costing for the equipment to make the network useful. Packet tracer to show a simulation to show the hospital what their network is going to be like and to show that it is possible to get the network working. To find information from engineers or internet to find out how cabling should be completed 1.1 Introduction The following report is created to show the IP configuration that is produced for the three hospitals that will be using the same network. With each section and departments being in different subnets the calculation were needed to be made Inorder to make all the sections of the network can talk together. They need to be able to communicate with each other as the computers in the doctor’s surgery, used for the doctors and the administrators, will be used to retrieve patient records and talk to the health care server. The three places that are being used for the doctor’s surgery are Warmingham; this is going to be the main building where the main routers are going to be held. The first surgery is in Audley. This like the other surgery in Peover, both surgeries are to have 120 computers for the doctors and 90 computers for the admin teams. In the report I will also show on one floor of the doctor’s surgery how the cabling should be laid out so that all the cables are fitted safely and securely. This report will have a section where the costing to implement the charges. This will describe costing such as computers, switches, labour, cabling etc. 2.0 Findings 2.1 IP Addressing The following IP address was given for the hospital. 172.168.0.0. as this is a class B IP address this means that it has a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0, this information is going to be used to complete the table in the IP address configuration table section. The Case study required VLSM (variable length subnet mask) to be used to address the network. VLSM is a means of allocating IP addressing to subnets according to their individual need. VLSM is used so that the minimum amounts of subnets are used so that they can be used for future growth. 2.2 IP Address Configuration As the IP address has been obtained then from here we need to work out how to get 420 computers, 5 Switches, 3 Routers patient records and health care server onto the same IP address. The only way to complete this is to subnet the address. This is done by VLSM. VLSM allows you to change the subnet mask were needed so that minimum address are lost. We ARE allowed to use the zero subnet in this report as stated by the handout. The number below show the number of hosts that are required on each subnet. I have put these into numerical order so this order is what we need to work in. 120 – Doctors computers in Audley 120 – Doctors computers in Peover 90 – Administrators in Audley 90 – Administrators in Peover 25 – Warmingham network connected to the servers. The following is the process that is needed to complete the VLSM for 120 hosts. 1. Work out 120 in binary. 128 64 1 32 1 16 1 8 1 4 0 2 0 1 0 Now add up the totals in the totals of the boxes that are filled in, this gives you 7. Now from the right count left 7 spaces. The number on your left is the number in which the increments must go up on. This means that 128 is the number that you must go up in. As we have this information we can now work out the subnet mask. This is done by: 255.255.0.0 This is the default subnet mask for a class B. So starting from the right, write your subnet mask in binary 255.255.00000000.00000000 We know it takes seven bits to make 120 hosts. 0= hosts 1= Network bits Because we want 120 hosts and not networks, we need to make sure we have 7 host bits. So 255.255.11111111.10000000 As you can see we have added seven 0 (host bits) and so the remainder can now become network bits, so fill in the left over as 1’s. Now if we convert this from binary to decimal we know have our new subnet mask which is 255.255.255.128 Now we need to work out the ranges. To do this in your subnet mask take your lowest increment and find the equivalent in binary. So 255.255.11111111.10000000 The lowest increment is this 1. This 1 converted to binary = 128. So now we know using this subnet mask on the network address given that we add 128 to the address in the fourth octet (because the increment is in the last octet. So for example 172.168.0.0 This is start of the first range 172.168.0.128 this is start of the second Range 172.168.0.256 This is the start of the third range however each octet can only go up to 255 and so this is not a valid address. We now have two network ranges to allow us to support up to 120 hosts. To work out the end of the ranges you take 1 away from the next range. So 172.168.0.0 the end address will be 172.168.0.127 172.168.0.128 the end address will be 172.168.0.255 172.168.0.256 So the range of IP address in the first network will be 172.168.0.0 -172.168.0.127 and the next range 172.168.0.0 – 172.168.0.255 Now you have worked out the two 120 hosts you now start again on the 90 hosts. However you have used the 172.168.0.0 through to 172.168.0.255 for the 120 doctor machines so the next address will have to start from 172.168.1.0. Below is the IP address for subnet. IP Address Subnet Mask 172.168.0.0 /16 255.255.0.0 120 Hosts 172.168.0.0 – 127 172.168.0.128 – 255 /25 90 Hosts 172.168.1.0 – 127 172.168.1.128- 255 /25 /25 /25 25 Hosts 172.168.2.0 – 31 /27 172.168.2.32 – 35 /30 172.168.2.36 - 39 /30 The 2 hosts listed here are the host that are needed to complete the sub network from the Warmingham HQ Router to the Audley Hospital, and one fro Warmingham to Peover. Listed above shows that there are two 120 hosts, two 90 hosts, one 25 hosts and two 2 hosts. This can also be seen in the diagram below. 2 Hosts 2.3 IP Address Configuration table Host/ Interface IP address start Doctor Machine 172.168.0.1 Audley Admin Machine 172.168.1.1 Audley Doctor machine 172.168.0.129 peover Admin machine 172.168.1.129 Peover Audley router 172.168.0.126 Fa0/0 Peover router 172.168.0.254 Fa0/0 Audley router 172.168.1.126 Fa0/1 Peover router 172.168.1.254 Fa0/1 Audley router 172.168.2.34 serial 0/0 Peover router 172.168.2.37 serial 0/0 Warmingham 172.168.2.30 router Fa0/0 Warmingham 172.168.2.33 router serial 0/0 IP address end Mask DCT/DTE* N/A Default Gateway* 172.168.0.126 Broadcast address 172.168.0.127 Network Address 172.168.0.0 172.168.0.126 25 172.168.1.126 25 N/A 172.168.0.126 172.168.1.127 172.168.1.0 172.168.0.254 25 N/A 172.168.0.254 172.168.0.255 172.168.0.128 172.168.1.254 25 N/A 172.168.1.254 172.168.1.255 172.168.1.128 N/A 25 N/A N/A N/A 25 N/A N/A N/A 25 N/A N/A N/A 25 N/A N/A N/A 30 DTE N/A N/A 30 DTE N/A 172.168.2.31 172.168.2.0 N/A 27 N/A N/A 172.168.2.31 172.168.2.0 172.168.2.34 30 DCE N/A Warmingham router serial 0/1 Warmingham router serial 0/2 Patient records 172.168.2.37 172.168.2.38 30 DCE N/A 145.45.5.100 N/A N/A DTE N/A 172.168.2.1 172.168.2.30 27 N/A 172.168.2.30 Health care server 172.168.2.2 172.168.2.30 27 N/A 172.168.2.30 2.4 configuration of devices After completing the network diagram in packet tracer it was time that I needed to start configuring the devices so that they would be able to work. The case study needed me to configure the routers and also make sure that there were many other things completed with the configuration as well. I needed to set hostnames for routers I did this by the following. In the CLI tab on the router I got to the global configuration mode by typing; Enable Configure Terminal Then Hostname [xxxxxx] The hostname will now be used as the routers ID. I then had to give the interfaces the correct IP address and Subnet mask, Once again in the global configuration mode; Interface [interface],[IP address], [Subnet masks] No Shut this makes the interface shut down by default. I then had to set the clock rate on a number of the serial ports on the routers, and DCE are used the we have to set the clock rate. While in the same mode as above Clock [xxxxxx] I used 64000 Normally the clock rate is set by the ISP, however in the diagram we have leased lines between the sites and so we need to set the clock rate ourselves. The easy way to remember which side sets the clock is to remember is that the C in DCE stands for clocking. Once we had the PCS and routers interface set up with the correct IP address I tested the connectivity by issuing a ping command. This allows us to see if data can get across the network or not. After checking that all the sub networks were able to communicate with each other, I needed to complete the EIGRP which is the routing protocol. This allows routers to send information not just to networks on the router but also from other networks which are linked to other routers. The following steps are the ones I took to set up the EIGRP: From global configuration mode issue the router Router eigrp <Autonomous system number> Network <networks advertising> <wildcard mask> This allowed my network to set up neighbour relationships and start to exchange routes. From global configuration mode: Interface loopback <loopback number I used 10><IP address> <subnet mask> From global configuration mode Ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 <interface to send out on> Under the interface Description<description> To configure the message banner of the day I did the following: From global configuration mode Banner motd <message to type> Password set up !!!!!Note all the passwords are cisco From global configuration mode enter the following commands: Enable secret <password> Now I had to set a password on the console port. This is done from global configuration mode Line console 0 Password <password> Login (Most important command this specifies that the router needs to prompt for a password) Now if anyone try’s to connect to the console port they will be asked for a password. Next was to do the same but for the vty ports. These are terminal ports and are used for telnet. Line vty 0 4 (specifying 0-4 means it will support 5 separate terminal sessions) Password <password> Login The last thing to do was to set up a host table. This allows the user to just type the name of the device rather then “telnet <ip address of interface of router> To do this I issued the following command Ip host <hostname of router> <ip address of one of the interface> The last thing is to Write mem (this saves all the current configuration) Now I had configured all the devices the last thing to do was to issue a write memory on all devices so that the current configuration is saved to start-up. 2.5 Floor plan Below is a copy of the floor plan that I have indicated where the cables, PC, switch should go when they are on that floor. As it shows above the cables run from the computers into a cabling tray, this makes sure that the cables are neat and tidy and out of harms way for anyone. Also if any of the cables would need to be moved or replaced the engineer wouldn’t have to go looking for it they would know that it would in the cabling try. The doctors switch and the admin switch are in different locations because if something was to go wrong with one switch this can be repaired without danger of knocking into the other switch. 2.6 Costing the following section is regards to the costing of putting this network together. Computers HP DX2400MT CELERON 440 1GB 160GB OFFICE SBE INCLUDED VISTA BUSINESS/XP PRO Price per unit = £259.00 Total cost = £108,780.00 The reason for this choice is that the computer has very good memory and also a good speed ROM and RAM. Switches Trendware TRENDnet TEG S240TX 24-Port Ethernet Switch Price per unit = £197.90 Total price = £989.50 As this switch has the required speed and ports to complete this task. Routers Cisco 2621XM Router Price per unit $2538.99 (£1737.63) Total price $7614 – (£5212.90) The reason for choosing this is that this router has the needed amount of capacity and ports that are required to complete this network Engineer £250 per three hours. Six hours per day = £500 Five days are week = 2500 20 weeks = £50000 So two engineers total cost to complete work is £100000. Cabling Belkin 100 meter . Cat. 5 UTP Patch Cable This roll of straight through cable will link the computers to the routers to allow the connection. Price per unit £143.89 Total price £1143.89 Total Price £ 216,126.29 3.0 Conclusion After writing up this report and completing all the task that have been asked I have realised how hard to completely reform a layout is. From the first stage of knowing what you want up to the point of configuring everything, every last detail must be completely perfect for the network to run. This is the reason for the 20 weeks that I have given the two engineers to complete the work. I feel that the 2 engineers will be able to complete the transformation of the network within the 20 weeks, The total cost of the network is £216126.29 this is for al the equipment and for the labour. In conclusion I feel that the overall network has worked a lot better as all hospitals are able to gather the same information and have the same records. References/Bibliography http://www.pcwb.co.uk/ec/basket.jtp [online] accessed 19/03/2009 Computers Routers http://www.shopping.com/xPO-Cisco-2621XM-CISCO2621XM-DC-RF [online] accessed 19/03/2009 Switches http://www.shopping.com/xPO-Trendware [online] accessed 20/03/2009 Cabling http://www.shopping.com/xPO-cabeling [online] accessed 20/03/2009