2nd GP
advertisement

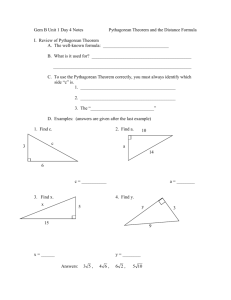
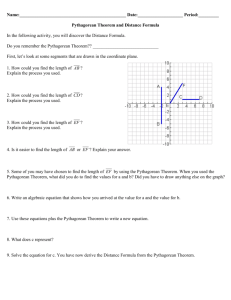
Geometry Unit 4: Right Triangles and Polygon Properties Second Grading Period – Weeks 1- 4 (18 days) Enduring Understandings (Big Ideas) Properties of right triangles, Pythagorean theorem and triples, special right triangles, and similarity will be analyzed. Areas and perimeters of regular polygons will be expressed numerically and analytically. Essential Questions CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Unit Rationale Using constructions, Geometer’s Sketchpad and modeling will enhance student learning on applications of right triangles and regular polygons. Guiding Questions √How do you determine if a triangle is a right triangle? √How do you determine the sides of special right triangles? √How do you apply special right triangles to determine the area and Why are right triangles important? How are right triangles useful? perimeter of a regular polygon? √How do you prove the Pythagorean Theorem on the coordinate plane? √How do you visually represent the Pythagorean Theorem? TEKS (Standards) TEKS Specificity - Intended Outcome (G.03.A) The student is expected to determine the validity of a conditional statement, its converse, inverse, and contrapositive. (G.03.B) The student is expected to construct and justify statements about geometric figures and their properties. (G.03.C) The student is expected to use logical reasoning to prove statements are true and find counter examples to disprove statements that are false. (G.5.A) use numeric and geometric patterns to develop algebraic expressions representing geometric properties; (G.5.B) use numeric and geometric patterns to make generalizations about geometric properties, including properties of polygons, ratios in similar figures and solids, and angle relationships in polygons and circles; (G.5.D) identify and apply patterns from right triangles to solve meaningful problems, including special right triangles (45-45-90 and 30-60-90) and triangles whose sides are Pythagorean triples. ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. I can : use numeric and geometric patterns to develop algebraic expressions representing geometric properties (G.5.A) use numeric patterns and apply them to regular polygons (G.5.B) identify right triangles and apply their properties where needed to solve problems(G.5.D) determine the sides of a special right triangle using its properties(G.5.D) represent geometric figures on the coordinate plane(G.7.A) determine the areas of regular polygons using special right triangles(G.8.A) derive and model the Pythagorean theorem on the coordinate plane(G.8.C) apply similarity properties to right triangles(G.11.C (G.7.A) use one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to represent points, lines, rays, line segments, and figures. (G.8.A) find areas of regular polygons, circles, and composite figures; SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 1 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. (G.8.C) derive, extend, and use the Pythagorean Theorem. (G.09.B) The student is expected to formulate and test conjectures about the properties and attributes of polygons and their component parts based on explorations and concrete models. (G.11.A) The student is expected to use and extend similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures about geometric figures. (G.11.B) The student is expected to use ratios to solve problems involving similar figures. (G.11.C) develop, apply, and justify triangle similarity relationships, such as right triangle ratios, trigonometric ratios, and Pythagorean triples using a variety of methods. ELPS 1E – Internalize new basic and academic language by using and reusing it in meaningful ways in speaking and writing activities that build concept and language attainment. 2C – Learn new language structures, expressions, and basic and academic vocabulary heard during classroom instruction and interactions 2D – Monitor understanding of spoken language during classroom instruction and interactions and seek clarification as needed 3D – speak using grade-level content area vocabulary in context to internalize new English words and build academic language proficiency 3E – Share information in cooperative learning interactions 4F – Use visual and contextual support and support from peers and teachers to read grade-appropriate content area text, enhance and confirm understanding, and develop vocabulary, grasp of language structures, and background knowledge needed to comprehend increasingly challenging language. 5B – Write using newly acquired basic vocabulary and content-based grade-level vocabulary College and Career Readiness Standards III.A.3 Recognize and apply right triangle relationships including basic geometry III.C.1 Make connections between Geometry and Algebra III.C.3 Make connections between Geometry and Measurement IV.C.1 Find the perimeter and area of two-dimensional figures IV.C.3 Determine indirect measurements of figures using scale drawings, similar figures, the Pythagorean theorem, and basic trigonometry X.B.2 Understand and use appropriate mathematical models in the natural, physical, and social sciences Given a range of geometric properties, students will use numeric and geometric patterns to develop algebraic expressions for the properties at least 80% of the time. Given a range of geometric properties, students will use numeric and geometric patterns to make generalizations about the properties at least 80% of the time. Given an appropriate problem, students will identify and use patterns from right triangles to solve it at least 80% of the time. Given geometric figures, students will use one- and two-dimensional coordinates systems to represent them at least 80% of the time. Given a regular polygon, circle or composite figure, students will calculate the area at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate its properties at least 80% of the time. Given triangle similarity relationships, students will develop, apply and justify them through a variety of methods at least 80% of the time. Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 2 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Geometry Unit 4: Right Triangles and Polygon Properties CURRICULUM GUIDE Second Grading Period – Weeks 1- 4 (18 days) Essential Pre-requisite Skills Grade 8 estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percents and other proportional relationships such as similarity an rates (8.3B) use pictures or models to demonstrate the Pythagorean Theorem (8.7C) find lateral and total surface areas of prisms, pyramids, and cylinders using concrete models and nets (two-dimensional models) (8.8A) use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-life problems (8.9A) use proportional relationships in similar two-dimensional figures or similar three-dimensional figures to find missing measurements (8.9B) Algebra 1 look for patterns and represent generalizations algebraically (A.3B) The Teaching and Learning Plan Instructional Model & Teacher Directions The teacher will… So students can…. Agile Mind Instructional Hints Make sure and read the Prepare Instruction for the given Topic. This area contains Goals and Objectives, Topic at a Glance, Prerequisite Skills, Resources and Language support for the given Topic. Also make sure and read Delivering Instruction for the given Topic and block. This area contains Agile Mind materials, opening the lesson, framing questions, lesson activities, and further questions for the given block. Both Prepare Instruction and Delivering Instruction can be found in the Advice for Instruction area. You can find the Advice for Instruction area by clicking Show Professional Support under the View tab. It is also a good idea to make copies of Student Activity sheets the day before in case the internet goes down. Also remember Agile Assessment has more TAKS formatted problems if needed. Days 1 -2 Days 1 -2 Modeling Right Triangles Modeling Right Triangles Engage Engage Provide the students with Pythagorean Models Draw squares with the given sides of a right triangle Determine the areas of the squares previously drawn (G.8.A) Post questions about the areas of given squares Explore Explore Record the areas of the squares around the given right triangles on the activity sheet Part 1.(G.5.A) Explain Divide the class in groups or individually allow the students to perform calculations Finish the part 1, part 2 and part 3 activity sheets. of areas of the squares around a right triangle Model the use of equations to represent the Pythagorean theorem Determine the difference between models that demonstrate the Explain Pythagorean Theorem vs. others and explain them in your journal. (G.5.B) Elaborate In their groups have the students finish the part 1, part 2 and part 3 activity sheets. Complete the Pythagorean Theorem Models – CW and HW activity sheets. Have students explain the Pythagorean Theorem in their journals in heir own words. Evaluate Student groups present their solutions to the rest of the class. Elaborate Have the students Complete the Pythagorean Theorem Models – CW and HW activity sheets (Gradable Activity). Evaluate Have the student groups choose three of the problems and put the solutions on chart paper. Have the student groups present their solutions to the rest of the class SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 3 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Days 3-4 Proving Pythagorean Theorem Agile Mind Unit 13 Days 3-4 Proving Pythagorean Theorem Agile Mind Unit 13 Day 3 Block 1 Overview, Exploring a Patty paper proof Day 4 Block 2 Exploring Extending the Pythagorean Theorem Day 3 Block 1 Overview, Exploring a Patty paper proof Day 4 Block 2 Exploring Extending the Pythagorean Theorem Days 5-6 - Section 7.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem Days 5-6 - Section 7.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem McDougal Littel Geometry Section 7.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem pg 435 Key Concept – Pythagorean Triples pp436/7 Skills Practice 1-16 Explain Determine Pythagorean Triples Do the skills practice in pairs.(G.11.C) Explain Use p435 to explain Pythagorean Triples In pairs have the students do the skills practice problems. (Gradable Activity) Evaluate Have each group do a class presentation of at least 2 of the problems In your journal write at least 4 Pythagorean Triples and explain why Pythagorean Triples they are important Evaluate Do a class presentation on 2 of your problems Days 7-8 Real World Applications Days 7-8 Real World Applications Similarity Pythagorean Theorem Similarity Pythagorean Theorem HW Elaborate Have the students do the activity sheets. (Gradable Activity) Apply Pythagorean theorem to real world applications Elaborate Do the activity sheets(G.8C, G.11C) Place the teacher assigned on chart paper Do a Rotating Review Evaluate Assign each group 2-3 problems and have them place the solutions to these problems on chart paper. Evaluate Students should display their solutions and do a rotating review. Day 9 Review of TAKS Geometry Questions Evaluate Use TAKS samples Develop a Pythagorean assessment Write the about the geometric representation of the theorem in your journal (G.8C, G.11C) Day 9 Review of TAKS Geometry Questions Evaluate Work TAKS example problems to gain familiarity with content and format Present your solutions to another pair of students. Have the students work through the problems in pairs Have the students discuss their problems to another pair Days 10-11 Agile Mind Unit 16 Special Right Triangles SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Days 10-11 Agile Mind Unit 16 Special Right Triangles Mathematics- Geometry Page 4 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 10 Block 1 Overview, Extending a Patty Paper Proof Day 11 Block 2 Extending the Pythagorean Theorem Day 10 Block 1 Overview, Extending a Patty Paper Proof Day 11 Block 2 Extending the Pythagorean Theorem Days 12 Section 7.4 Special Right Triangles Days 12 Section 7.4 Special Right Triangles McDougal Littel Geometry Section 7.4 Practice A, B C, 49-54 Elaborate Provide detailed notes on how organize the measurement of x, x, x 2 and Elaborate Group the 45-45-90 and 30-60-90 exercises on MDL 7.4 practice A and B Regroup the exercises by the given measurement of its side i.e. those given the hypotenuse in one group, those given the smallest side in other, and so on (G.5.B) x, x 3, 2 x with its corresponding angles Provide detailed notes on how to determine the measure of missing sides beginning with small side or hypotenuse or medium side Evaluate Evaluate Compare their solution with different groups Justify the answers verbally and algebraically Set up class in small groups Observe and note mistakes made Have students present their solutions with justifications(Gradable Activity) Analyze some wrong solutions Day 13 Problem Soving Agile Mind Unit 16 Mars Task Hopewell Geometry (Skip problem 2) Days 14-17 Agile Mind Unit 17 Day 13 Problem Soving Agile Mind Unit 16 Mars Task Hopewell Geometry (Skip problem 2) Days 14-17 Agile Mind Unit 17 Day 14 Block 1 Overview and the first part of the Exploring "Interior and exterior angles of a polygon Day 15 Block 2 Exploring " Interior and exterior angles of a polygon Day 16 Block 3 Exploring “Special quadrilaterals” Day 17 Block 4 Exploring “Special quadrilaterals” Days 18 Review and Test Searching for student problem areas, have the students scan pages 493-497 to remind them of what has been covered. In a whole class context, ask the students to list the problem areas. Address the problem areas first conceptually, then by working appropriate problems from page 498. Consider grouping students with common challenges with peer tutors, Evaluate Time allowing, assign problems to individuals to be posted during class period – one from each section that has not yet been discussed. Wrap up with one last call for questions. SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Cross-reference their solutions with their notes Day 14 Block 1 Overview and the first part of the Exploring "Interior and exterior angles of a polygon Day 15 Block 2 Exploring " Interior and exterior angles of a polygon Day 16 Block 3 Exploring “Special quadrilaterals” Day 17 Block 4 Exploring “Special quadrilaterals” Days 18 Review and Test Engage review pages 493-497 to see what has been covered in this unit and to determine where questions might still exist contribute challenges to the class list Evaluate ensure that his/her problem area(s) is (are) addressed participate in peer tutor groupings work problems as assigned from page 498 take assessment(Gradable Activity) Mathematics- Geometry Page 5 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Administer assessment ensuring alignment with guiding TEKS Ensure that assessment questions are aligned with the guiding TEKS Have the following materials on hand graphing calculators paper pencils Vocabulary: (Pertinent to the learning – specific) Pythagorean theorem hypotenuse Pythagorean triple Right triangle Special right triangle Angle of elevation Angle of depression Solving the right triangle Ratio Regular polygon Area Perimeter Pentagon Hexagon Radius Diagonal similarity TAKS Vocabulary use develop represent generalization identify apply solve understands determine extends find derive applies justify Resources Resources: Days 1-2 Activity: Pythagorean Models Day 3-4 Agile Mind Unit 13 Proving Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Geometry with The Geometer’s Sketchpad • pp 163-164 The Square Root Spiral Days 5-6 McDougal Littel Geometry • Section 7.1 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem • pg 435 Key Concept – Pythagorean Triples • pp436/7 Skills Practice 1-16 Days 7-8 Activity: Similarity vs Pythagorean Theorem Activity: Similarity vs Pythagorean Theorem HW Day 9 TEA Website Days 10-11 Agile Mind Unit 16 Special Right Triangles McDougal Littel Geometry pg 461 Skill Practice – Special Right Triangles 11,12 Days 12-13 McDougal Littel Geometry Section 7.4 Practice A, B C, 49-54 Days 14-17 Agile Mind Unit 17 Days 18 McDougal Littel Geometry pp 493-498 Chapter Summary, Chapter Review, Chapter Test SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 6 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) Formative Mini Assessments TAKS 15 The drawing below shows how 3 squares can be joined at their vertices to form a right triangle. College-Readiness i.e., Anticipated Skills for SAT/ACT/College Board/Career/Life 42 To estimate the height of her school’s gym, Nicole sights the top of the gym wall in a mirror that she has placed on the ground. The mirror is 3.6 meters from the base of the gym wall. November 2008 FMA Which is closest to the area in square inches of the largest square? May 2009 FMA in 2 2 B 233 in 2 C 210 in 2 D 1073 in A 1914 Nicole is standing 0.5 meter from the mirror, and her height is about 1.8 meters. What is the height of the gym wall? F1m G 5.9 m H 7.2 m J 12.96 m May 2009 FMA SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 7 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Geometry Unit 5: Coordinate Geometry CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Second Grading Period – Weeks 5 – 7 (11 days) Enduring Understandings (Big Ideas) Unit Rationale Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and other representational systems (NCTM Geometry standard) Students should understand that: The distance formula is an application of the Pythagorean theorem. The midpoint formula is easily derived and has useful applications. Quadrilaterals have unique and defining properties. Essential Questions Guiding Questions √How can you find the midpoint of a segment? √How can you find the distance between two points or the length of a segment? √What properties define a square? √What properties define a rectangle? √What properties define a rhombus? Why is Coordinate Geometry important? How is Coordinate Geometry useful? How do you find the midpoint or distance of a line? TEKS (Standards) TEKS Specificity - Intended Outcome G.2(A) use constructions to explore attributes of geometric figures and to make conjectures about geometric relationships (G.03.A) The student is expected to determine the validity of a conditional statement, its converse, inverse, and contrapositive. ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. I can: (G.03.B) The student is expected to construct and justify statements about geometric figures and their properties. (G.03.C) The student is expected to use logical reasoning to prove statements are true and find counter examples to disprove statements that are false. G.7(A) use one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to represent points, lines, rays, line segments, and figures; use constructions to explore lengths of segments and properties of midpoints.(G.2A) use one and two-dimensional coordinate systems to represent points and line segments(G.7A) use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships.(G.7B) derive and use formulas involving length, slope and midpoint.(G.7C) use the Pythagorean theorem to find the distance between two points.(G.8C) formulate and test statements made about geometric figures based on experimentation or models (G.9B) G.7(B) use slopes and equations of lines to investigate geometric relationships, including parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and special segments of triangles and other polygons G.7(C) derive and use formulas involving length, slope, and midpoint (G.08.A) The student is expected to find areas of regular polygons, circles, and composite figures. SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 8 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. G.8(C) derive, extend, and use the Pythagorean Theorem G.9(B) formulate and test conjectures about the properties and attributes of polygons and their component parts based on explorations and concrete models ELPS 1E – Internalize new basic and academic language by using and reusing it in meaningful ways in speaking and writing activities that build concept and language attainment. 2C – Learn new language structures, expressions, and basic and academic vocabulary heard during classroom instruction and interactions 2D – Monitor understanding of spoken language during classroom instruction and interactions and seek clarification as needed 3D – speak using grade-level content area vocabulary in context to internalize new English words and build academic language proficiency 3E – Share information in cooperative learning interactions 4F – Use visual and contextual support and support from peers and teachers to read grade-appropriate content area text, enhance and confirm understanding, and develop vocabulary, grasp of language structures, and background knowledge needed to comprehend increasingly challenging language. 5B – Write using newly acquired basic vocabulary and content-based grade-level vocabulary College and Career Readiness Standards III.A.3 Recognize and apply right triangle relationships including basic geometry III.C.1 Make connections between Geometry and Algebra III.C.3 Make connections between Geometry and Measurement IV.C.1 Find the perimeter and area of two-dimensional figures IV.C.3 Determine indirect measurements of figures using scale drawings, similar figures, the Pythagorean theorem, and basic trigonometry X.B.2 Understand and use appropriate mathematical models in the natural, physical, and social sciences Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) Given a geometric figure, students will use constructions to explore the relationships between its properties at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use either a one-or two-dimensional coordinate system to represent its parts at least 80% of the time Given a geometric figure, students will use slopes and equations to investigate relationships at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will derive and use formulas for length, slope and midpoint at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use the Pythagorean Theorem to determine measurements as appropriate at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, student will formulate and test conjectures regarding its properties and attributes based on investigation of concrete models at least 80% of the time. SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 9 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Geometry Unit 5: Coordinate Geometry CURRICULUM GUIDE Second Grading Period – Weeks 5 – 7 (11 days) Essential Pre-requisite Skills Grade 8 Use the Pythagorean theorem to solve real-life problems (8.9A) Locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers(8.7D) Use geometric concepts and properties to solve problems(8.7B) The Teaching and Learning Plan Instructional Model & Teacher Directions The teacher will… So students can…. Agile Mind Instructional Hints Make sure and read the Prepare Instruction for the given Topic. This area contains Goals and Objectives, Topic at a Glance, Prerequisite Skills, Resources and Language support for the given Topic. Also make sure and read Delivering Instruction for the given Topic and block. This area contains Agile Mind materials, opening the lesson, framing questions, lesson activities, and further questions for the given block. Both Prepare Instruction and Delivering Instruction can be found in the Advice for Instruction area. You can find the Advice for Instruction area by clicking Show Professional Support under the View tab. It is also a good idea to make copies of Student Activity sheets the day before in case the internet goes down. Also remember Agile Assessment has more TAKS formatted problems if needed. Day 1-3 Day 1-3 Distance and Midpoint Formula Distance and Midpoint Formula Agile Mind Unit 13 Agile Mind Unit 13 Day 1 Block 3 Exploring "The distance and midpoint formulas" Day 1 Block 3 Exploring "The distance and midpoint formulas" Day 2 Block 4 Exploring "The distance and midpoint formulas," the Summary Day 2 Block 4 Exploring "The distance and midpoint formulas," the Summary Day 3 Block 5 topic level assessment Day 3 Block 5 topic level assessment Day 4 Elaborate Have students work on “Problem Solving with Distance and Midpoint Formula handout” in pairs. Have the pair present their solutions to another pair. Day 5 Elaborate Have students work on Problem Solving with Midpoint Formula handout in pairs. Have the pair present their solutions to another pair. Evaluate Have the students explain the use of the midpoint and distance formula in their journals. SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Day 4 Elaborate Practice using the midpoint formula by working on assigned handout in their groups. (Gradable Activity) Problem Solving with Distance and Midpoint Formula.(G.7C) In their journals have the students explain in detail how the distance and midpoint formula are used. Day 5 Elaborate Work on Problem Solving with midpoint Formula (G.7C) Evaluate Mathematics- Geometry Demonstrate and explain the use of the midpoint and distance formula in your journal. (Gradable Activity) Page 10 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 6-8 Agile Mind Unit 21 Day 6-8 Agile Mind Unit 21 Day 6 Block 1 Overview, the Exploring “Shear mathematical magic Day 7 Block 2 Exploring “More area formulas” Day 8 Block 3 Exploring “More area formulas” Day 6 Block 1 Overview, the Exploring “Shear mathematical magic Day 7 Block 2 Exploring “More area formulas” Day 8 Block 3 Exploring “More area formulas” Day 9 Investigating Quadrilaterals Teacher Notes Day 9 Activity 1 :Squares Activity 1: Squares Engage: Draw a square, either on the whiteboard or on GSP. Ask them what it is. Once students respond, ask them how they know it is a square. Explore: Have students work on #1 and #2 in pairs while you walk around facilitating if necessary. Explain: Have students work on # 3. Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures they wrote. Elaborate/Evaluate: Have students work on #4 creating a square that satisfies the condition given: (Gradable Activity) Engage: Respond to teacher’s questions and participate in discussion. Explore: Work on problems #1 and #2, asking the teacher for help if necessary.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Explain: Work on # 3. Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures found.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Elaborate/Evaluate: Work on #4 creating a square that satisfies the condition given: Day 10 Activity 2 : Rectangles Day 10 Activity 2 :Rectangles Engage: Draw a rectangle, either on the whiteboard or on GSP. Ask them what it is. Once students respond, ask them how they know it is a rectangle. Explore: Have students work on #1 and #2 in pairs while you walk around facilitating if necessary. Explain: Have students work on # 3 . Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures they wrote. Elaborate/Evaluate: Have students work on #4 creating a rectangles that satisfies the condition given: SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Explain the properties of a square in your journal. Engage: Respond to teacher’s questions and participate actively in discussion. Explore: Work on problems #1 and #2, asking the teacher for help if necessary.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Explain: Work on # 3 . Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures found.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Elaborate/Evaluate: Work on #4 creating a rectangle that satisfies the condition given( G.7A, G.7B, G.9B). Mathematics- Geometry Page 11 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. (Gradable Activity) Day 11 Activity 3 : Rhombi Day 11 Activity 3 Rhombi Engage: Draw a rhombus, either on the whiteboard or on GSP. Ask them what it is. Some students may answer a parallelogram, which is correct but not specific enough. Explain that this is a rhombus. Explore: Have students work on #1 and #2 in pairs while you walk around facilitating if necessary. Explain: Have students work on # 3. Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures they wrote. Elaborate/Evaluate: Have students work on #4 and #5. (Gradable Activity) Vocabulary: (Pertinent to the learning – specific) distance length midpoint Pythagorean Theorem midpoint formula distance formula parallel perpendicular congruent rhombus congruence conjecture construction attributes SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Explain the properties of a rectangle in your journal. Engage: Respond to teacher’s questions and participate actively in discussion. Explore: Work on problems #1 and #2, asking the teacher for help if necessary.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Explain: Work on # 3 . Then, as a class, discuss some of the conjectures found.(G.7A, G.7B, G.9B) Elaborate/Evaluate: Work on #4 and #5 ( G.7A, G.7B, G.9B). TAKS Vocabulary analyzes make verify understands represent investigate derive use determine extend find formulate test Explain the properties of a square in your journal. Resources Day 1-3 Agile Mind Unit 13 Day 4 Problem Solving with Distance and Midpoint Formula handout Day 5 Problem Solving with Midpoint Formula handout Day 6-8 Agile Mind Unit 21 Day 9-11 Investigating Quadrilateral Properties 2.0 Teacher Notes Day 9 Activity 1: Squares Day 10 Activity 2 : Rectangles Day 11 Activity 3 : Rhombi Mathematics- Geometry Page 12 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) Formative Mini Assessments TAKS College-Readiness i.e., Anticipated Skills for SAT/ACT/College Board/Career/Life TAKS April 2006 # 25 (G.7C) November 2008 FMA SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 13 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Geometry Unit 5: Transformations CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Second Grading Period – Weeks 7 – 9 (9 days) Enduring Understandings (Big Ideas) Unit Rationale Students should understand: and represent translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations of objects in the plane by using sketches, coordinates, and vectors; to use various representations to help understand the effects of simple transformations and their compositions. Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations (NCTM) Essential Questions Guiding Questions √How does a translation change the coordinates of a figure? √How does a reflection affect the coordinates of a figure? √How does a center of dilation affect where the dilated figure is located? What are the different transformations? How are the different transformations the same and different? What is a tessellation? TEKS (Standards) TEKS Specificity - Intended Outcome (G.02.B) The student is expected to make and verify conjectures about angles, lines, polygons, circles, and three-dimensional figures and determine the validity of the conjectures, choosing from a variety of approaches such as coordinate, transformational, or axiomatic. ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. I can: (G.5C) use properties of transformations and their compositions to make connections between mathematics and the real world, such as tessellations. ( G.7A) use one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to represent points, lines, rays, line segments, and figures. (G.08.A) The student is expected to find areas of regular polygons, circles, and composite figures. use properties of transformations and their compositions to make connections between mathematics and the real world. (G.5C) use one- and two- dimensional coordinate systems to represent points, lines, rays, line segments and figures. (G.7A) use congruence transformations to make conjectures. (G.10A) justify properties of geometric figures including figures represented on a coordinate plane. (G.10A) use and extend similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures about geometric figures. (G.11A) (G.10A) use congruence transformations to make conjectures and justify properties of geometric figures including figures represented on a coordinate plane. (G.11A) use and extend similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures about geometric figures. ELPS 1E – Internalize new basic and academic language by using and reusing it in meaningful ways in speaking and writing activities that build concept and language attainment. 2C – Learn new language structures, expressions, and basic and academic vocabulary heard during classroom instruction and interactions 2D – Monitor understanding of spoken language during classroom instruction and interactions and seek clarification as needed 3D – speak using grade-level content area vocabulary in context to internalize new English words and build academic language proficiency 3E – Share information in cooperative learning interactions 4F – Use visual and contextual support and support from peers and teachers to read grade-appropriate content area text, enhance and confirm understanding, and develop vocabulary, grasp of language structures, and background knowledge needed to comprehend increasingly challenging language. 5B – Write using newly acquired basic vocabulary and content-based grade-level vocabulary SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 14 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. College and Career Readiness Standards III.A.3 Recognize and apply right triangle relationships including basic geometry III.C.1 Make connections between Geometry and Algebra III.C.3 Make connections between Geometry and Measurement IV.C.1 Find the perimeter and area of two-dimensional figures IV.C.3 Determine indirect measurements of figures using scale drawings, similar figures, the Pythagorean theorem, and basic trigonometry X.B.2 Understand and use appropriate mathematical models in the natural, physical, and social sciences Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) Given a geometric relationship, students will use the properties of transformations and their compositions to make connections to the real world at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use one-and two-dimensional coordinate systems to represent its parts or properties at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use congruence transformations to make conjectures about and justify its properties at least 80% of the time. Given a geometric figure, students will use similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures at least 80% of the time. SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 15 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Geometry Unit 5: Transformations CURRICULUM GUIDE Second Grading Period – Weeks 7 – 9 (9 days) Essential Pre-requisite Skills Grade 8 generate similar figures using dilations including enlargements and reductions (8.6A) graph dilations, reflections, and translations on a coordinate plane (8.6B) locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers (8.7D) Algebra 1 develop the concept of a slope as a rate of change and determine slopes from graphs, tables, and algebraic representations (A.6A) The Teaching and Learning Plan Instructional Model & Teacher Directions The teacher will… So students can…. Agile Mind Instructional Hints Make sure and read the Prepare Instruction for the given Topic. This area contains Goals and Objectives, Topic at a Glance, Prerequisite Skills, Resources and Language support for the given Topic. Also make sure and read Delivering Instruction for the given Topic and block. This area contains Agile Mind materials, opening the lesson, framing questions, lesson activities, and further questions for the given block. Both Prepare Instruction and Delivering Instruction can be found in the Advice for Instruction area. You can find the Advice for Instruction area by clicking Show Professional Support under the View tab. It is also a good idea to make copies of Student Activity sheets the day before in case the internet goes down. Also remember Agile Assessment has more TAKS formatted problems if needed. Day 1 – 5 Day 1 – 5 Transformations Transformations Agile Mind Unit 3 Agile Mind Unit 3 Day 1 Block 1 Overview, the Exploring "Translations and reflections" Day 2 Block 2 Exploring "Translations and reflections" Day 3 Block 3 Exploring "Reflections and rotations" Day 4 Block 4 Exploring "Applications of rigid transformations" Day 5 Block 5 Exploring “Applications of rigid transformations,” “Symmetry in polygons” Day 1 Block 1 Overview, the Exploring "Translations and reflections" Day 2 Block 2 Exploring "Translations and reflections" Day 3 Block 3 Exploring "Reflections and rotations" Day 4 Block 4 Exploring "Applications of rigid transformations" Day 5 Block 5 Exploring “Applications of rigid transformations,” “Symmetry in polygons” Day 6 - 9 Agile Mind Unit 14 Dilations and Similarity in Polygons Day 6 Block 1 Overview and the Exploring “Are these shapes similar?” Day 7 Block 2 Exploring “Are these shapes similar?” Day 8 Block 4 Exploring “Dilations” Day 9 Block 5 Exploring “Dilations,” and the Constructed response SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Day 6 -9 Agile Mind Unit 14 Dilations and Similarity in Polygons Day 6 Block 1 Overview and the Exploring “Are these shapes similar?” Day 7 Block 2 Exploring “Are these shapes similar?” Day 8 Block 4 Exploring “Dilations” Day 9 Block 5 Exploring “Dilations,” and the Constructed response Mathematics- Geometry Page 16 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Vocabulary: (Pertinent to the learning – specific) Transformation Dilation Rotation Reflection Scale factor Tessellation Rotational symmetry isometric Translation SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period TAKS Vocabulary Describe Use Understands Represents Apply Justify Solve Make Extend Mathematics- Geometry Resources Agile Mind Unit 3 Agile Mind Unit 14 Page 17 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Evidence of Learning (Summative Assessment) Formative Mini Assessments None Available TAKS College-Readiness i.e., Anticipated Skills for SAT/ACT/College Board/Career/Life Grade 10 2006 released test Item #4 None available Grade 10 2006 released test Item #34 SAISD © 2010-11 – Second Grading Period Mathematics- Geometry Page 18 of 18 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards.