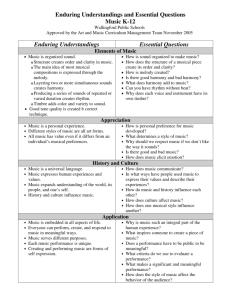
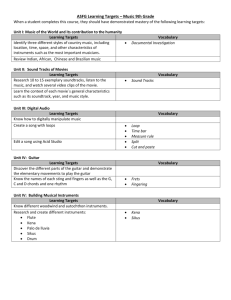
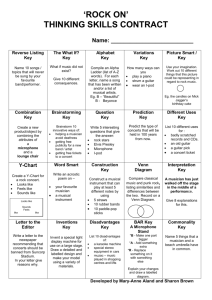
GLOSSARY | 1
GLOSSARY
45 RPM record: a seven-inch phonograph record played at 45 revolutions per minute (r.p.m.), especially a
popular music single; developed in 1949 by RCA and dominant in the United States through the 1970s
Amplifier: (short: amp) an electric device used to increase, enhance, and manipulate the sound of whatever
instrument is plugged into it, usually a guitar or piano
Arrangement: 1. in classical music, the adaptation of a composition for a medium different from that for which
it was originally written. 2. in popular music, the process of adding instrumentation to a songwriter’s basic
melody and harmony
Arranger: person who adapts compositions, often adding instrumentation to a composer’s original work or a
songwriter’s basic melody and harmony
Baby boomer: an individual born during the post-World War II baby boom
Baby boomer: generally considered to be the boom of 77 million babies born between 1945 and 1964 in the
United States
Backed with (b/w): refers to the “B-side” of a gramophone record; the B-side was often intended to be less
popular than the A-side but this was not always the case
Backing Vocalist: singer providing vocal harmony or counter melody to complement the melody
Bass guitar: the lowest-sounding guitar in rock and roll, often with only 4 strings
Blues: a kind of song often with verses of three-lines each and specific musical patterns and common form
(common chord progression, first two lines are repeated and the third is new lyrical information) from AfricanAmerican musical traditions
Brass: family of wind instruments made from brass or metal with a cup-shaped mouthpiece, including the
trumpet, trombone, tuba, and others
Bridge: short section of the song that alters the basic melody or harmony and works as a transition between a
verse and a chorus
Chorus: section of a song that repeats regularly in music often with the same musical accompaniment; also
known as a refrain and appears between verses and after the bridge
Civil rights: rights for a nation’s citizens as defined by law, often understood as freedoms or protections; in the
United States, particularly the rights guaranteed under the U. S. Constitution, including those known as the Bill
of Rights
Classical music: in day-to-day usage, music generally outside the field of “popular music,” often influenced by
Western European art music traditions
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.
GLOSSARY | 2
Cold War: a nuclear arms standoff between the U.S. and the Soviet Union following World War II that avoided
military battles; each nation opposed the political and economic tactics of the other
Color/timbre: the element of music that describes the quality or characteristics of a sound; used to talk about
the sound of different kinds of instruments (voice, piano, guitar, flute, etc.) and ways of describing them
(scratchy, sweet, piercing, floating); also known as timbre
Composition: 1. combining and organizing distinct parts or elements to form a whole; 2. the act of creating an
artistic work
Country: songs with special musical patterns from traditions in rural and mountain communities in the southern
and western United States, often featuring stringed instruments
Crossover: 1. music, track, or artist that spans more than one genre or style of music 2. music, track or artist that
spans more than one audience and is popular among different groups such as African-American listeners or
European-American listeners
Culture: a body of customary beliefs, behavior, social patterns, shared values and attitudes, styles for living and
creative products shared by a group of people
Disc Jockey (DJ): a person who presents comments on and/or select popular music recordings, most often on
the radio or in a dance club; in hip-hop, the DJ will often alter the sound of records played on a turntable by
scratching, playing the break, or looping
Disposable income: the amount of an individual’s income available for spending after essentials (food, clothing,
shelter, taxes) has been taken care of
Doo-wop: a vocal group harmony style loved by teens in northern cities, where backup singers sing repeated
words or nonsense syllables
Drum set: a collection of drums, cymbals and sometimes other percussion instruments arranged so that one
person can play all of them
Electric Organ: an instrument that uses electricity to make sound when keys and pedals are pressed; an electric
organ often has two rows of keys, called manuals, and a pedal board
Gospel: religious music of African-American Christians that emerged in urban centers during the early decades
of the twentieth century; gospel music informed a style often called “southern gospel” rooted in musical
traditions of predominantly white Protestants in the southeastern U.S.
Great Migration: historical term for mass migrations of African Americans from rural areas to cities from around
1915 to 1970
Guitar: a family of musical instruments that create sound when its strings are plucked or strummed
Hall of fame: a place that honors people for outstanding achievements in a profession
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.
GLOSSARY | 3
Harmony: two or more different pitches (or notes) that sound simultaneously in patterns to accompany the
melody (tune)
Instrument: an object or equipment that musicians use to make musical sounds
Instrumentation: the specific instruments and voices selected for particular sections, parts, textures, and roles
in an arrangement of a musical composition
Jukebox: a money-operated phonograph or compact disc player, equipped with pushbuttons for the selection of
particular recordings
Juvenile delinquency: conduct by a juvenile characterized by antisocial behavior that is beyond parental control
and subject to legal action; many linked juvenile delinquency to rock and roll and those who listened to it
Keyboard: a family of musical instruments that create sound when keys are pressed
Lyrics: the words of a song, often arranged in sections of verses and choruses
Mainstream: a dominating, widespread, or prevailing viewpoint or influence often projected to be an overall
“norm” for a community or society
Manager: individual responsible for the business affairs of a band or artist (booking tours, making travel
arrangements, negotiating contracts, etc.)
Melisma: more than one successive note sung on one syllable (ex: 5 successive notes sung on the word “do”)
Melody: pitches that are sounded in succession, or one after the other, as in a line of a song; the tune
Music Journalist: writer, reporter, and/or reviewer that writes, reviews, comments, and reports on music, the
music industry, music trends, and artists for websites, journals, or newspapers
Musical style: 1. the distinctive characteristics of the sound and organization of musical performances and
compositions; used to categorize music reflecting similar approaches to melody, harmony, form, and/or
performance techniques; 2. Musical patterns or trends in songs and performances of a number of artists, often
used to classify musical genres
Musician: a person who creates, performs, and studies music
Musicology: the study of music
Orchestra: a large ensemble of instruments, often divided into four main sections – or groups of instruments –
strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion
Percussion: a family of musical instruments that create sound when struck or hit, such as drums, cymbals,
shakers, among others
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.
GLOSSARY | 4
Performance Practice: standards for the total presentation of a performance, which may include styles of
artistic interpretation, dress, movement, and/or performer-audience interaction
Performer: singer or musician; some performers are involved in the business of music as well
Piano: a keyboard instrument that creates sound when a key is pressed and a hammer hits a string
Pitch: the element of music that describes the sound of notes from low to high; the frequency of sound waves
Point of view: the narrative element that describes who is telling a story and whether the storyteller talks about
events that happen to him/her or someone else
Popular music: in day-to-day usage, music generally outside the field of “classical music,” often reflecting the
mass tastes of a society, trends in traditional music-making, and commercial systems for producing and
distributing music
Producer: person who oversees the production of a band or artist’s music (creative direction, recording, mixing,
mastering, etc.); also the person or group who makes a good or provides a service
Racial segregation: separation of racial groups by law and custom, which restricted the access of black
Americans to jobs, schools, neighborhoods, stores, etc. and privileged white Americans; outlawed by the U.S.
Congress in 1964
Record/Music Executive: powerful decision maker at a record company who often oversees management,
production, marketing, etc.
Region: an area that includes smaller places, usually sharing similar features of land, weather, and/or customs
Rhythm and blues: a style of upbeat popular music blending big band swing and blues that attracted large
numbers of African American audiences after World War II, in the mid-1940s through the 1950s; a root of rock
and roll
Rhythm: ahe element of music that describes how we make patterns in time, such as pulses, beats, etc.
Rock and roll: African-American slang dating back to the early 20th Century. In the early 1950s, the term came
to be used to describe a new form of music, steeped in the blues, rhythm & blues, country and gospel. Today, it
refers to a wide variety of popular music.
Rock band: a group of musicians who perform rock and related amplified music, often with the core instruments
of drum set, electric guitar, bass guitar, keyboards, and vocalist
Rock Photographer: dedicated to photographing music, bands, artists, and related events often for newspapers
press releases, websites, and social media
Rural: of or relating to the country, farming, or people in farming communities
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.
GLOSSARY | 5
Sideman/Sidewoman: 1. musician or vocalist who performs and/or records with a group or independent artist
that he or she is not normally associated with; many side-artists specialize in one or more genres 2. backup or
supporting artist
Singer-songwriter: individual who is primarily a songwriter but also performs those songs; singer-songwriters
grew emerged in the early 1970s
Society: a term describing collective human networks, or organized groups of people who often share common
interests; what people do together in communities, institutions, and other groups
Song: a musical composition typically arranged for voice and accompaniment; contains melody, harmony, and
lyrics
Songwriter: a person who writes the words, music (or both) for a song
Songwriting: the art of composing the lyrics and/or music of a song
Sound Engineer: person who uses technology to alter or enhance sounds in the recording studio
Strings: family of instruments that produce sound as a stretched string is vibrated by bowing (violin, viola, cello)
or plucking (guitar, lute); the section of an orchestra that typically includes violin, viola, cello, and double bass
Suburb: a small residential community established outside of a city; post World War II, families often fled cities
to the safety and comfort of suburban areas. Neither urban nor rural, suburban towns were a compromise
between the two extremes.
Symbolism: A poetic device where words are used to stand for or represent something else by conveying both
literal and figurative meanings
Synthesizer: a keyboard instrument that uses electricity to imitate the sounds of many families of instruments
Teenager: an individual between the ages of 13 and 19 (also known as an adolescent); teenagers shaped
popular culture in the 1950s by rebelling against the tastes of the older generations
Tradition: customs, beliefs, or practices valued by one generation and taught to the next
Transistor radio: small, portable, affordable radio popular among teenagers in the 1950s that allowed them to
listen to whatever music that they wanted whenever they wanted
Tremolo as related to guitar especially, a controlled, pulsating change of pitch; on guitar, this is accomplished by
using the whammy bar
Turntables: the most common device for playing recorded sound of records from the 1870s through the 1980s;
turntables and vinyl records remain popular for “scratching” in hip-hop music, though for recording use it has
largely been replaced by the sampler or compact disc
Urban: of or relating to a city or heavily populated area
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.
GLOSSARY | 6
Verse: a section of lyrics that tells part of the song’s story and is similar to a verse in a poem
Vinyl: short for vinyl record; a musical medium to play music that is a vinyl disk with grooves; must be played on
a turntable or a record player
Vocalist: performer who uses the voice as an instrument; singer
Volume/Dynamics: the element of music that describes the loudness or quietness of a sound; the amplitude of
sound waves
Woodwinds: family of wind instruments with single or double reeds (clarinet, saxophone, oboe) or a mouth hole
(flute, piccolo)
©2014 Rock and Roll Hall of Fame and Museum, Inc. All rights reserved.