Practice test 2
advertisement

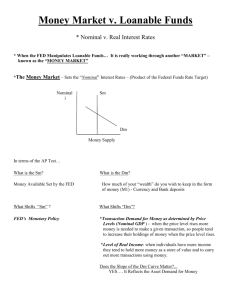
1. The best measure of the standard of living is A) nominal GDP B) real GDG C) nominal GDP per capita D) real GDP per capita 2. Suppose that real GDP for 2004 was $10,000 billion and real GDP for 2005 was $11,000 billion. What is the rate of growth of real GDP between 2004 and 2005? A) 10% B) 1% C) 5% D) 2% 3. If GDP grows at a rate of 3% per year, how long will it take for GDP to double in size? A) 21 years B) 12 years C) 23 years D) 35 years 4. Between 1997 and 2007, if the economy’s real GDP grew from $20 billion to $40 billion, what must the average annual growth rate in the economy have been? A) 3% B) 100% C) 20% D) 10% 5. Workers in _______ countries have ______ to work with than do workers in low income countries. A) high income; less physical capital B) high income; more physical capital C) high income; more labor D) low income; less labor 6. If, as economist Alwyn Young has suggested, high growth rates in Singapore are not a result of technological progress, how are growth rates in Singapore expected to change over time? A) Without technological progress, the high growth rates cannot be sustained B) As long as the labor force participation rate is rising, growth can still continue, despite a lack of technological progress C) As long as the amount of capital per hour worked continues to expand, the growth rate in Singapore will continue to rise at an increasing rate. D) Agricultural workers will continue to expand their productivity, thereby allowing Singapore to achieve growth rates above those of higher-income countries. 7. A financial intermediary’s main function is to match _______ with excess funds to ____ with a shortage of funds. A) savers; borrower B) borrower; savers C) governments; households D) firms; insurance companies 8. A country with no trade and no borrowing and lending relationships with other countries is known as a A) planned economy B) market economy C) open economy D) closed economy 9. Private savings is defined as A) Y + TR – C – T B) T + G + TR C) T – G + TR D) Y + TR + C – T 10. If real GDP in a closed economy is $40 billion, consumption is $20 billion, and government purchases are $10 billion, what is investment? A) $10 billion B) $70 billion C) $40 billion D) $30 billion 11. When the government runs a deficit, which of the following is true? A) T > TR – G B) G > T + TR C) G > TR – T D) T < G + TR 12. Which of the following would increase public savings? A) an increase in taxes B) an increase in transfers C) an increase in government purchases D) all of the above would increase public savings 13. If government purchases are $400 million, taxes are $700 million, and transfers are $200 million, which of the following is true? A) Public savings is $500 million B) The budget deficit is $100 million C) The budget deficit is $500 million D) Public savings is $100 million 14. The federal budget deficit can be reduced by A) raising taxes B) raising government spending C) raising transfer payments D) higher interest rates 15. The demand for loanable funds has a _____ slope because the lower the interest arte, the ______ number of investment projects are profitable, and the _____ the quantity of loanable funds demanded A) negative; greater; greater B) negative; greater; lesser C) negative; lesser; greater D) positive; lesser; lesser 16. An increase in the demand for loanable funds will occur if there is A) B) C) D) an increase in the real interest rate a decrease in the real interest rate an increase in expected profits from firm investment projects an increase in the nominal interest rate accompanied by an equal increase in inflation 17. If technological change increases the profitability of new investments for firms, then the _____ curve for loanable funds will shift to the ______. A) supply; right B) supply; left C) demand; right D) demand; left Use this graph to answer the following question 18. The loanable funds market is in equilibrium, as shown in the figure above. An increase in the supply of loanable funds could result in which of the following combinations of real interest arte and quantity of loanable funds at a new equilibrium? A) The real interest rate is 5 percent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million B) The real interest rate is 5 percent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million C) The real interest rate is 3 percent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million D) The real interest rate is 3 percent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million 19. The loanable funds market is in equilibrium, as shown in the figure above. As a result of an increase in the government budget deficit, the _____ for loanable funds will _______ , thereby ______ the equilibrium real interest rate and ______ the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds A) demand; rise; increasing; increasing B) supply; rise; decreasing; increasing C) demand; fall; decreasing; decreasing D) supply; fall; increasing; decreasing 20. A recession begins with a _____ in spending by firms on capital goods and a _____ in spending on durable goods by households A) increase; decrease B) increase; increase C) decrease; increase D) decrease; decrease 21. If a country’s real GDP is rising by 3% per year, while its population is rising at 5% per year, which of the following is true? A) the country’s standard of living is falling B) the country’s standard of living is rising C) growth in nominal GDP outweighs growth in the population D) growth in nominal GDP is less than the growth in the population 22. Which of the following is not a reason why the Industrial Revolution occurred when and where it did? A) The British government was committed to upholding private property rights B) The British government was able to eliminate arbitrary increases in taxes C) The British government was able to more easily seize wealth D) Institutional changes by the British government helped protect wealth. 23. GDP in a country grew from $10 billion to $14 billion over the span of 5 years. The average annual growth rate of GDP was A) 4% B) 40% C) 10% D) 8% 24. A small economy increased its capital per hour worked (K/L) from $40,000 to $50,000. As a result, real GDP per worker (Y/L) grew from $20,000 to $25,000. If the economy increases its capital per hour worked by another $10,000 to $60,000, but there is no change in technology, by how much more and in what direction will input per worker change? A) Output per worker will increase by exactly $5,000 B) Output per worker will increase by more than $5,000 C) Output per worker will increase by less than $5,000 D) Output per worker will fall by more than $5,000 25. In the long run, a country will experience an increasing standard of living only if it experiences A) a high rate of consumption B) continuous technological change C) a high rate of labor force growth D) a slow rate of population growth Answer: 1. D 2. A 3. C 4. D 5. B 6. A 7. A 8. D 9. A 10. A 11. D 12. A 13. D 14. A 15. A 16. C 17. C 18. C 19. D 20. D 21. A 22. C 23. D 24. C 25. B