Chapter 11 Human Anatomy The Cardiovascular System
advertisement

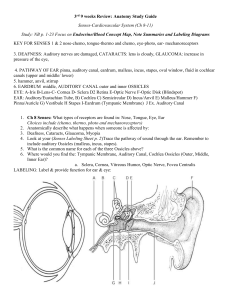
Chapter 11 Human Anatomy The Cardiovascular System Vocabulary Terms: Aorta Hypertension Vena Cava Atrium Systole Ventricle Diastole Capillaries Vein Artery The HEART …. Weighs about one pound Is about the size of a closed fist Found in the center of the thoracic cavity under the sternum Is slightly pointed toward the left hip Is covered by pericardium membranes and is surrounded by serous fluid Has three layers 1. Epicardium----outer membrane 2. Myocardium ----muscle 3. Endocardium---inner membrane Pumps 6000 liters of blood per day. Heart Anatomy Atria- the receiving chambers of the heart Ventricles- the sending chambers of the heart Septum- the dividing wall of the heart Vena Cava- veins that bring blood to the heart from the body Aorta- major artery that takes blood away from the heart Pulmonary Artery- carries blood from the heart to the lungs Pulmonary Vein- carries blood from the lungs to the heart. AV valves- (Tricuspid and Bicuspid valves)- connect the atria to the ventricles Semi-lunar Valves- (aortic and pulmonary) connect the ventricles to the aorta and pulmonary artery Coronary Artery- primary blood supply to the heart muscle itself SA Node- the Primary “Pacemaker” for the Atria AV Node- the pacemaker for the Ventricles Purkinje Fibers- network of nerves that run through the heart. Electrical Stimulation of the Heart- Although Cardiac Muscle can contract on its own, the coordinated contraction involves the stimulation of the heart by the Vagus Nerve. The SA Node causes the Atria to contract and that signal passes to the AV node to contract the ventricles. The characteristics heart sound of “Lubb-Dubb” is the sound of the heart valves closing as the heart contracts. Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that shows the electrical stimulation of the heart and the resulting ECG wave. (P-Q-R-S-T Wave) P- Atria contraction Q- Atria relaxes R-Ventricles contract S- Ventricles relax T- Rest Cardiac Cycle- The heart collects blood from the body and lungs and transfer’s it from the atria to the ventricles. The ventricles pump blood to the body and lungs. Systole occurs when the heart is contracted and Diastole occurs when the heart is at rest. Cardiac Output- is measured by multiplying the Stroke Volume times the Heart Rate Example CO = 70ml. X 75 bpm CO= 5250 ml/min Factors that can affect heart rate Resting heart rate- 1. Decreased stroke volume 2. Physical exertion and stress 3. Hormones (like adrenalin) 4. Age 5. Gender 6. Temperature 7. Physical fitness Measured when the person is at complete rest. For Males 64-72 bpm For Females 72-80 bpm Blood Vessels- -Are the pathways of blood throughout the body. -Were determined by physician William Harvey in the late 1600’s -5 types including arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins. -Veins and Arteries have 3 “Tunics” Tunica Externa- connective tissue Tunica Media- smooth muscle Tunica Intima- squamous cell inner lining -Capillaries only have Tunica Intima Characteristics of Arteries -Thick Tunica Media -Very elastic -Subject to blood pressure -Carries blood away from the heart -Smaller Lumen (space blood travels through) Characteristics of Veins -Thin tunica media -Less elastic -Little if any blood pressure -Have internal valves to prevent back flow of blood -Larger lumen -Uses skeletal muscle contraction and breathing to push blood back to the Heart Characteristics of Capillaries -One cell in thickness -Nutrients, wastes and gasses are exchanged from blood to cells here -Sections are called capillary beds and can control the flow of blood though or around them. (important in directing blood flow to area of the body) Major Blood Vessels of the body Aorta- largest artery of the body, extends directly from the left ventricle, subject to the highest blood pressure, has four parts (ascending aorta, aortic arch, thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta). Carotid arteries- found in the neck, they serve the head and brain. Coronary arteries- supply the heart muscle. Axillary and Brachial arteries – serve the arms Illiac artery- serves the pelvis and branches to the legs Femoral artery- serves the upper leg. Mesentary artery- serves the intestines Renal artery- serves the kidneys Hepatic artery-serves the liver Pulmonary artery- carries blood from the heart to the lungs Superior and Inferior Vena Cava- largest veins of the body- carries blood directly back to the heart. Jugular veins- found in the neck they bring blood from the head and brain to the heart Brachial and Axillary veins- bring blood from the arms back to the heart Illiac veins- bring blood from the legs to the inferior vena cava Femoral veins- bring blood from the upper leg to the heart Mesentary veins- intestines Renal veins- kidneys Hepatic veins- liver Pulmonary veins- lungs Special Circulatory Patterns Brain- Hepatic Portal- Fetal Circulation- Vital Signs Pulse and Heart RateBlood PressureFactors that affect BP 1. Neural 2. Renal 3. Temperature 4. Chemical 5. Diet 6. Genetics (African-Americans have a higher risk) Diseases and Disorders of the cardiovascular system Pericarditis- an inflammation of the lining of the heart Heart Murmur- sound produced by faulty heart valves allowing backflow of blood. Angina Pectoris- Chest pains produced by lack of Oxygen to the heart Myocardial Infarction- Proper name for a heart attack. Usually caused by lack of O2 to the heart. Heart Block- Failure of the nerve signal to contract to get to the AV node. Ischemia- lack of blood to a body part, including the heart. Fibrillation- rapid shuttering or misfire of the heart Congestive heart failure- inefficient heart that causes fluid to build up in the lungs and the kidneys to shut down due to low blood pressure. Hypotension- Low Blood Pressure Hypertension- High Blood Pressure Atherosclerosis- narrowing of a blood vessel to due buildup of cholesterol and plaque. Aneurism- a weakened blood vessel that bulges and enlarges. Tachycardia- rapid Heart rate Brachycardia- slow Heart rate Varicose Veins-swollen blood vessels in which blood pools or collects on its way back to the heart. Faulty valves in large veins.