prac6 - Nick Circosta Online
advertisement

ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
Lab Practice 6
1. (Design/Problem Solving 1)
Create an algorithm for a program that determines the state (solid,
liquid, gas) of a sample of water. The program should read in a
temperature value of the sample in Kelvin degrees and provide the
user a choice of whether to convert the value into ˚C (Celsius) or
˚F (Fahrenheit). The program should then display the state of the
water sample (gas, liquid, solid) and the converted temperature.
The program should read in values continuously until the user
wants to quit. Your algorithm should take a top down approach
whereby you identify a high-level algorithm and then take each
step in this and break it down into the necessary sub-steps.
Conversions: Kelvin to Celsius = Kelvin – 273
Kelvin to Fahrenheit = 9 x Celsius ÷ 5 + 32
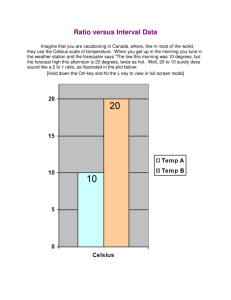
Gas
Liquid
solid
Temperature states of water
Celsius
Fahrenheit
100
212
1-99
33-211
0
32
You can check that your conversions are correct using the online
temperature conversion site at: http://www.convert-me.com/en/convert/temperature
Your solution must be implemented using at least 3 modules. It is
suggested to have at least 1 function for reading in the
temperature, 1 for the temperature conversion, and 1 to display
the state of the water sample.
ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
An example run of this program should look something like the
following: Welcome to the temperature conversion program
Please enter a the sample temperature in Degrees Kelvin:>345
Do you wish to convert the temperature to (c) for Celsius, or (f) for
Fahrenheit
:>c
The water is in a liquid state at 72.0 degrees celsius
Do you wish to enter another temperature? (Y for yes, N for no):>y
Please enter a the sample temperature in Degrees Kelvin:>234
Do you wish to convert the temperature to (c) for Celsius, or (f) for
Fahrenheit
:>F
The water is in a solid state at -38.2 degrees fahrenheit
Do you wish to enter another temperature? (Y for yes, N for
no):>N
2. (Design/Problem Solving 2)
Create a structure chart for the algorithm you have created in
question 1. See the notes and example at the end of the tutorial for
guidance in creating structure charts.
3.
(Programming exercise)
Implement the program from question 1 into a C program. The
solution must include at least 3 functions (additional to main) and
should be consistent with your algorithm.
ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
What to submit:
1.
Algorithm (this week).
2.
Structure Chart (this week).
3.
Program (next week).
Modular Programming Notes
See lecture notes Topic 6.
What is the structure chart used for:
Defining the fixed calling structure
Assist in defining dataflows
Assist in the first stage of incremental development of the
code
Also assist the division of labour on large projects.
After completing the algorithm the structure chart is merely a
formality. Each step in the algorithm should form a module in
the structure chart, and each of the sub-steps should be lower
levels in the structure chart. Also in this step you need to define
the inputs and outputs to each node in the structure chart.
A quick example
Given a simple algorithm:
Inputs:
number1 – an integer value holding the first number read.
number2– an integer value holding the second number read.
number3– an integer value holding the third number read.
Outputs:
sum – a long holding the sum of the 3 numbers.
The algorithm should start with a high level or top-level algorithm, which is
written in simple English and lists the major tasks to be performed.
ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
High-level algorithm
1. Read in first number.
2. Read in second number.
3. Read in third number.
4. Calculate the sum.
5. Display the result.
Step 1 Refinement
Function readNumber
Takes parameter nth where this represents the ordinal value of the number
being read. E.g., 2 for the second of the three numbers.
Print “Enter ”, nth, “ number: ”
Read num
Return num
End function readNumber
Step 4 Refinement
Function calculateSum
Takes all three numbers as parameters.
sum = number1 + number2 + number3
return sum
end function calculateSum
Step 5 Refinement
Function displayResult
Takes the calculated sum as a parameter.
Print “The sum is ”, sum
Print “Goodbye!”
end function displayResult
The Structure for this algorithm (using functions) is: -
main
nth
ReadNumber
nth
ReadNumber
nth
ReadNumber
sum
n1, n2, n3
CalculateSum
DisplayResult
ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
Things to Note: The top node is labeled main. As the high level part of the
algorithm is essentially our main function in the program when
using functions.
Each high-level step becomes a node in the structure chart.
Any sub-refinements would become nodes attached to the
node for the parent refinement as the tree is hierarchical.
Note how each node in the structure chart becomes a function
in the actual program.
The exception is that the ReadNumber routine is re-used twice
and this is indicated by the line through the corner of the box.
The parameters are shown on this diagram, although the return
values of the functions aren't in this case.
The code for this problem is: #include <stdio.h>
int ReadNumber(int nth)
{
int n;
printf("Please enter number %d: ", nth);
scanf("%d%*c", &n);
return(n);
}
int CalculateSum(int n1, int n2, int n3)
{
return(n1 + n2 + n3);
}
void DisplayResults(sum)
{
printf("The sum is %d\n", sum);
return;
}
int main()
{
int n1, n2, n3;
ICT102 Introduction to Computer Science
int sum;
n1 = ReadNumber(1);
n2 = ReadNumber(2);
n3 = ReadNumber(3);
sum = CalculateSum(n1, n2, n3);
DisplayResults(sum);
return(0);
}
![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)