DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) **Long molecule made up of units
advertisement

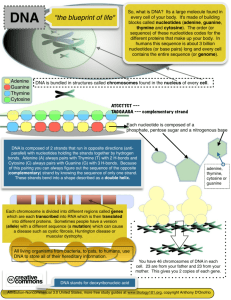
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid ) **Long molecule made up of units called nucleotides. *Nucleotide-- consists of: a.) 5-carbon sugar ( deoxyribose) b.) phosphate group c.) nitrogenous base * There are 4 different nitrogenous bases: 1. Purines—adenine(A) & guanine(G) *2 rings in their structure 2. Pyrimidines –cytosine(C) & thymine(T) *1 ring in their structure ***It is the order of the nitrogen bases that make up the genetic code*** DNA molecules are very long and must be folded into a space only one one-thousandth of its length. They are found in the nucleus of the cell. Example: ** The chromosome of a bacterial cell in the human colon contains 4,639,221 base pairs. **A human cell contains almost 1000 times as many base pairs of DNA as a bacterium. The DNA of a human cell is more than 1 meter in length and is found coiled up in the nucleus of a single cell. 1. Frederick Griffith (1928) did an experiment with bacteria and determined there was something in cells that transferred information and it could be a gene 2. Oswald Avery (1944) repeated Griffith’s experiments and determined that the nucleic acid DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation of an organism to the next. 3. Alfred Hershey & Martha Chase (1952) did an experiment with viruses that determined the genetic material of a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. 4. Erwin Chargaff discovered that percentages of guanine(G) and cytosine(C) were almost equal in all samples of DNA and the same was true for adenine(A) and thymine(T) 5. Rosalind Franklin (1950) used x-ray diffraction to get information about the structure of DNA. She discovered that strands in DNA are twisted around each other like coils of a spring. This shape is called a Helix. She also discovered that there might be two strands and that the nitrogenous bases might point towards the center. Therefore, making it a Double Helix. 6. James Watson & Francis Crick used the discoveries of all the previous scientists to develop a model of DNA. **Double Helix- 2 strands of DNA wound around each other in the shape of a spiral staircase. **Hydrogen bonds formed between 2 nitrogenous bases all the way up and down the strand to hold the two strands together. **Hydrogen bonds can only form between certain base pairs: This is called base pairing * Adenine(A) & Thymine(T) * Cytosine(C) & Guanine(G) DNA REPLICATION ** The process where a DNA molecule separates into 2 strands, then produces 2 new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template, or model, for the new strand. ** Carried out by the enzyme DNA polymerase ** This enzyme also “ proofreads” the new DNA strands to make sure that each Molecule is a perfect copy of the original DNA.