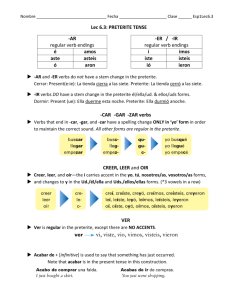
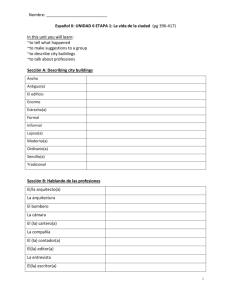
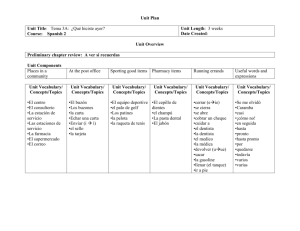
PRETERITE NOTES text
advertisement
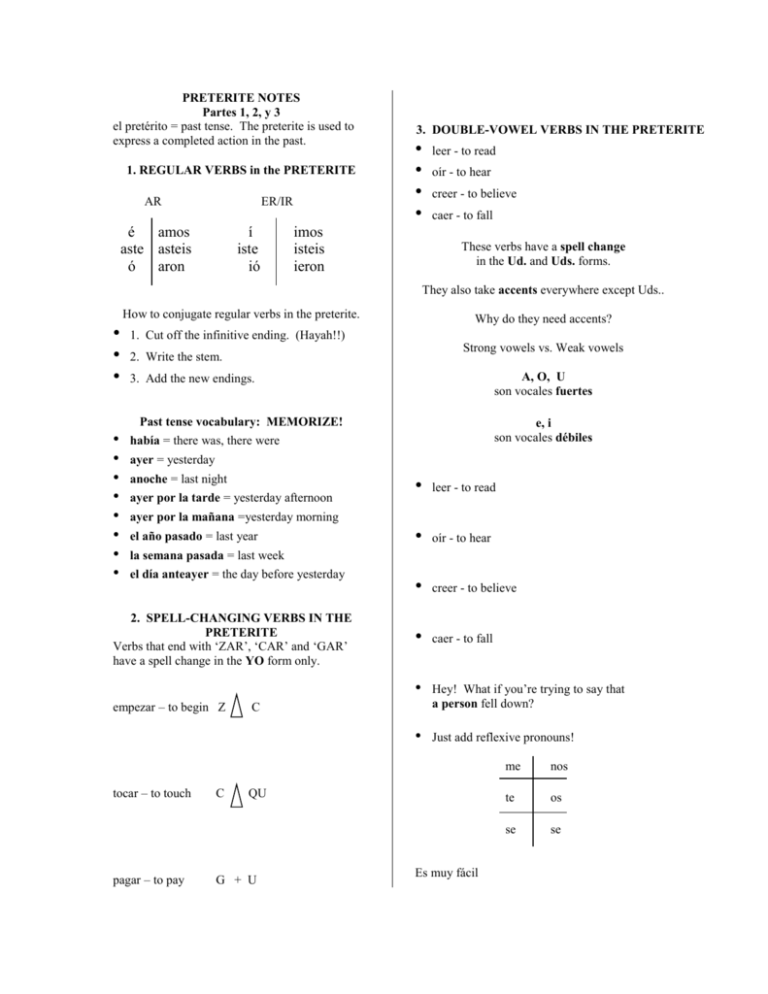
PRETERITE NOTES Partes 1, 2, y 3 el pretérito = past tense. The preterite is used to express a completed action in the past. 1. REGULAR VERBS in the PRETERITE AR ER/IR é amos aste asteis ó aron í iste ió imos isteis ieron 3. DOUBLE-VOWEL VERBS IN THE PRETERITE • • • • leer - to read oír - to hear creer - to believe caer - to fall These verbs have a spell change in the Ud. and Uds. forms. They also take accents everywhere except Uds.. How to conjugate regular verbs in the preterite. • • • Why do they need accents? 1. Cut off the infinitive ending. (Hayah!!) Strong vowels vs. Weak vowels 2. Write the stem. A, O, U son vocales fuertes 3. Add the new endings. Past tense vocabulary: MEMORIZE! • • • • • • • • e, i son vocales débiles había = there was, there were ayer = yesterday anoche = last night ayer por la tarde = yesterday afternoon • leer - to read • oír - to hear • creer - to believe • caer - to fall ayer por la mañana =yesterday morning el año pasado = last year la semana pasada = last week el día anteayer = the day before yesterday 2. SPELL-CHANGING VERBS IN THE PRETERITE Verbs that end with ‘ZAR’, ‘CAR’ and ‘GAR’ have a spell change in the YO form only. • empezar – to begin Z C • tocar – to touch pagar – to pay C Hey! What if you’re trying to say that a person fell down? Just add reflexive pronouns! QU G + U Es muy fácil me nos te os se se