Review sheet
advertisement

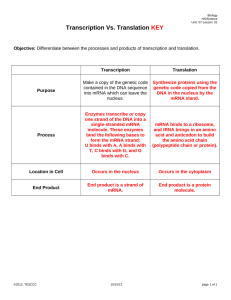
Chapter 13 Review sheet Protein Synthesis Part I. Short answer 1. Fill in the chart below comparing DNA and RNA. Sugar Phosphate group Bases Number of strands Shape Location in cell 2. DNA Deoxyribose Yes A, T, C, & G 2 Double helix Nucleus only RNA Yes Fill in the chart below comparing transcription with replication. Location in cell Produces Copies Use the enzyme Replication Nucleus DNA Both sides of DNA molecule DNA polymerase Transcription 3. Why does the process of transcription need to occur in order to make a protein? 4. Name two ways that mutations can affect the making of proteins in the organism. 5. The process of __________________________ makes mRNA from DNA. 6. The process of ________________________ makes a protein based on the instructions on the mRNA. 7. Transcription takes place in the _________________ of the cell. 8. Translation takes place in the __________________ of the cell. 9. If the codon is GUA, the anticodon that would pair with it would be __________. Part II. Protein synthesis. Examine the diagram below. Then, answer the questions that follow. 10. Label the nucleus in the picture above. 11. Label the ribosome in the picture above. 12. Label the DNA in the diagram above. 13. The mRNA will be divided into groups of three bases (labeled “A” above) called _____________ once it arrives at the ribosome. 14. Label a tRNA molecule in the diagram on the previous page. 15. The group of three bases attached to the tRNA molecule is called a(n) ______________. 16. Label an amino acid in the picture on the previous page. 17. Amino acids will be joined together to build what larger molecules? 18. Label a peptide bond in the picture on the previous page. Part III. Translating the genetic code. 19. If the DNA sequence is CGC TAC CGC TTA ATT, what would the mRNA made from it look like? (5 points) 20. Use the genetic code chart from your packet to translate the sequence of mRNA below into its corresponding amino acids. List the amino acids in order on your answer sheet. Be sure to write the entire name of each amino acid; do not abbreviate them. mRNA: CCU CUC GAG AAU Amino acid sequence: 21. Use the chart on the last page to explain why each sequence of mRNA ends with either UAG, UAA, or UGA. Part IV. Gene mutations. Compare each mRNA sequence to the original sequence shown below. Identify the type of mutation (frameshift or point). If it is a point mutation, identify the type (silent, nonsense, or missense). Original sequence: CCU GUU AAC GGG 22. CCUGUUACGGG 23. CCAGUUAACGGG 24. CCUGUUAACGAG 25. CCUGUUAACUGA