Chapter Four Notes - Sociology101summer2010
advertisement
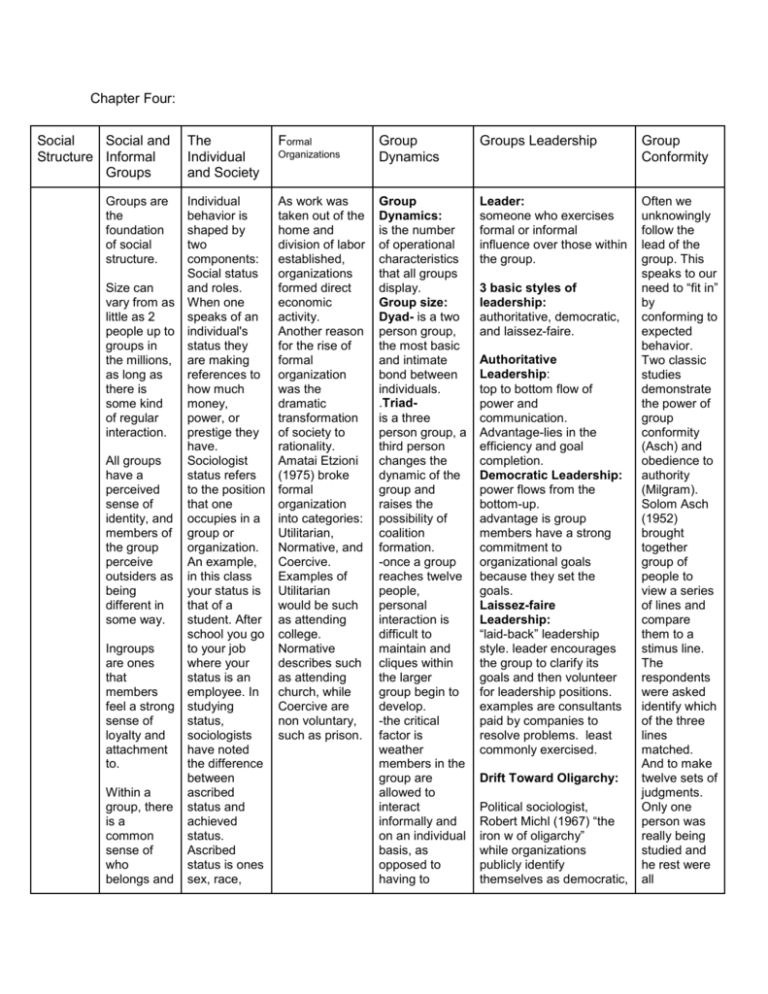
Chapter Four: Social Social and Structure Informal Groups Groups are the foundation of social structure. Size can vary from as little as 2 people up to groups in the millions, as long as there is some kind of regular interaction. All groups have a perceived sense of identity, and members of the group perceive outsiders as being different in some way. Ingroups are ones that members feel a strong sense of loyalty and attachment to. Within a group, there is a common sense of who belongs and The Individual and Society Formal Individual behavior is shaped by two components: Social status and roles. When one speaks of an individual's status they are making references to how much money, power, or prestige they have. Sociologist status refers to the position that one occupies in a group or organization. An example, in this class your status is that of a student. After school you go to your job where your status is an employee. In studying status, sociologists have noted the difference between ascribed status and achieved status. Ascribed status is ones sex, race, As work was taken out of the home and division of labor established, organizations formed direct economic activity. Another reason for the rise of formal organization was the dramatic transformation of society to rationality. Amatai Etzioni (1975) broke formal organization into categories: Utilitarian, Normative, and Coercive. Examples of Utilitarian would be such as attending college. Normative describes such as attending church, while Coercive are non voluntary, such as prison. Organizations Group Dynamics Groups Leadership Group Conformity Group Dynamics: is the number of operational characteristics that all groups display. Group size: Dyad- is a two person group, the most basic and intimate bond between individuals. .Triadis a three person group, a third person changes the dynamic of the group and raises the possibility of coalition formation. -once a group reaches twelve people, personal interaction is difficult to maintain and cliques within the larger group begin to develop. -the critical factor is weather members in the group are allowed to interact informally and on an individual basis, as opposed to having to Leader: someone who exercises formal or informal influence over those within the group. Often we unknowingly follow the lead of the group. This speaks to our need to “fit in” by conforming to expected behavior. Two classic studies demonstrate the power of group conformity (Asch) and obedience to authority (Milgram). Solom Asch (1952) brought together group of people to view a series of lines and compare them to a stimus line. The respondents were asked identify which of the three lines matched. And to make twelve sets of judgments. Only one person was really being studied and he rest were all 3 basic styles of leadership: authoritative, democratic, and laissez-faire. Authoritative Leadership: top to bottom flow of power and communication. Advantage-lies in the efficiency and goal completion. Democratic Leadership: power flows from the bottom-up. advantage is group members have a strong commitment to organizational goals because they set the goals. Laissez-faire Leadership: “laid-back” leadership style. leader encourages the group to clarify its goals and then volunteer for leadership positions. examples are consultants paid by companies to resolve problems. least commonly exercised. Drift Toward Oligarchy: Political sociologist, Robert Michl (1967) “the iron w of oligarchy” while organizations publicly identify themselves as democratic, who doesn’t. Outgroups are ones that show resentment or hatred towards other groups. Group membership provides a sense of identity and security. According to Durkheim’s study which showed a correlation between lack of social interaction and suicide - people feel the need to belong to groups. It provides meaning to our existence. class, religion, and nationality. It came to us by birth or through some condition we have no control over. Achieved status is what we gain through our own efforts. Achieved status might be student, professional, father, carpenter, president. Another type of status is a master status. Race in the US qualifies as a master status. Black professionals often complain of being treated differently both inside and outside their organizations due to their race. On the other hand, for white females, master status would be of gender not race. Unfortunately, since in many cases it is not possible to change a master status, many in society find conform to group standards. Group Cohesion: there are a number of factors that affect group cohesion. - first is the frequency of interaction. -second is how the group perceives other members. - finally, new members can affect the cohesion. Group Thinkis the process where by a group arrives at a decision that they privately know is wrong, but feel that they cannot, as individuals cannot challenge. Group Polarization- a group moves to an extreme position, one arrived at in a group situation, that few individuals would favor apart from the group. a few if any, practice democracy. natural tendency for leadership to conl and almost all aspects of the organization. organization=oligarchies 3 reasons why organizations start out as being ommd to democracy drift into oligarchy: 1:leadership is in charge of day-t-day running of the organization’s business. 2: organizations do not have time to keep k of organizational affairs -life is complex; we belong to many organizations; often there are not enough hours e day to take care of things we are responsible for. 3: natural tendency for leadership to want to entrench itself in power. accomplices of the researcher with instructions on how to answer. The First six rounds all the respondents answered correctly. The following six rounds the accomplices all choose incorrect answers. The point of the experiment was to determine what effect this would have on the subject. Asch assumed that since the correct answer was so obvious, subject would not conform to the group by giving incorrect answers. Asch was wrong, over 75% of subjects studied agreed with incorrect answer at least once. About one third of all the answers from all subjects were incorrect even though the correct themselves unable to escape unjust treatment. Attached to each status is a role, or a set of expected behaviors. an example, you are a student are expected to go to class, take your seat and wait for for the professor to arrive. When she arrives you are expected to listen, take notes, and ask questions when appropriate. The professor as well has a role. She is expected to be to class on time, give out assignments and grades. Finally, we all bring to a role our different personalities. Some of us are outgoing, and others are more reserved. Some of us approach life with a grand sense of humor, whole others are more serious about life. These are the things that make us all answer was obvious. Stanley Milgram (1963) tested subjects on obedience to authority. The researcher explained to two individuals the purpose of he study was to determined punishment was an effective tool in learning. The individual who was to be the teacher was the one being studied on. The other individual was the student, who was a accomplice of the researcher. The teacher would ask the student questions. If the students answered wrong then the teacher would shock the student with volts from 15 to 450 volts. Of course the experiment was rigged. The student never feels an shocks, he is just individual. acting as if he was being shocked. The central question of the study was how much was the teacher willing to administer before refusing to continue? At first the student responded correctly. Soon after he continues to answer wrong. The teacher shocks the student even when the student has not been responding since 330 volts. At some point teachers asked to stop but, the researchers convince and tell them they have to finish no matter what. 65% of the participants (20 of 40) continued to administer shocks all the way to the en of the shock series. The importance of above studies is at they demonstrate how powerful the group is in shaping our opinions and behavior, and how strong our allegiance is to authority.











