Foglio Formule Fisica 331: Circuiti, Condensatori, Induttori, CA
advertisement

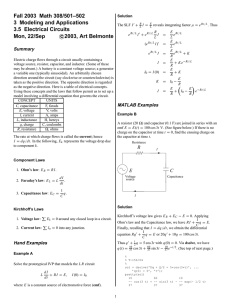
Physics 331 Final Exam Formula Sheet Ohm’s Law V=IR Power dissipated in a resistor in the form of heat P=VI=I2R=V2/R Resistors in Series RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + . . . Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law: The sum of the voltage drops around any closed loop equals the sum of the voltage rises around that loop. VRISE = VDROP (around any closed loop) Rx Voltage Divider Law: Vx V RT 1 1 1 1 ... Resistors in Parallel: R T R1 R 2 R 3 Kirchhoff’s Current Law: The sum of all current entering a junction, or any portion of a circuit, equals the sum of the current leaving the same. Ienter Iexit (any junction) Current Divider Rule: Capacitors: Q C= [F] (Farads) V Ix I RT Rx Capacitor in Series: 1 1 1 1 ..... C T C1 C 2 C 3 Capacitors in Parallel: C T C1 C 2 C 3 ..... Charging a Capacitor: t i(t) E - RC e R v R ( t) E e - t RC v C ( t) E(1 - e - t RC = RC ) Discharging a Capacitor: t i(t) Vo - e R v R ( t) Vo e - t - t v C ( t) Vo e ' = RTC Inductors and Inductance VL = L di dt Inductors in Series: LT = L1 + L2 + L3 +. . . . Inductor in Parallel: 1 1 1 1 ..... L T L1 L 2 L 3 Current build up (switch initially closed after having been opened) At v L ( t) E e - t t v R ( t) E(1 - e ) i(t) E R (1 e - t ) = L R Current decay (switch moved to a new position) - t i(t) I o e vR(t) = R i(t) Alternating Current f = 1/T =2f Complex Numbers: C=a+jb M a 2 b2 polar form: vL(t) = RT i(t) : ' = L RT C = M cos + j M sin b tan -1 a C=M Inductive Reactance: Capacitve Reactance: Resistance |XL| = L |XC| = 1 / ( C) R Impedance: ZR = R 0 ZL = XL 90 = L 90 ZC = XC -90 = 1 / (C) -90 Resistance: Inductance: Capacitance: Ohm’s Law for AC: V=IZ Time Domain: v(t) = Vm sin ( t ) Phasor Notation: V = Vrms (books notation) I = Irms V = Vm (also acceptable) I = Im Vrms = Vm/2 Vm = 2 Vrms Irms = Im/2 Im = 2 Irms i(t) = Im sin ( t ) Components in Series ZT = Z1 + Z2 + Z3 + . . Z Voltage Divider Rule: Vx VT x ZT 1 1 1 1 ... Components in Parallel: Z T Z1 Z 2 Z 3 Z Current Divider Rule: Ix IT T Zx ZZ Two impedance values in parallel: ZT 1 2 Z1 Z 2 In general the equivalent of Ohm’s Law is always satisfied e iT vR = iR R vC = iC XC vL = i L XL ZT magnitudes only