REVIEW SHEET FOR EXAM 3
advertisement

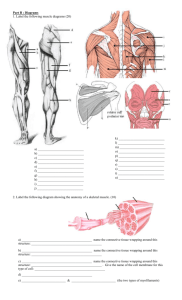
REVIEW SHEET FOR EXAM 3 Chapter 10 & 11 Muscle similarities/differences between cardiac, skeletal, smooth muscle Connective tissue coverings: all What is the sarcolemma and the sarcoplasm? Know definitions of origin, insertion, belly, which is more moveable? microscopic anatomy: sarcomere, myofibril, myofilament, what is found in the A band? the zone of overlap?, H zone?, I band? Be able to label a sarcomere. What is the muscle contraction theory? What are the steps involved? (as described in lecture.) What is the neuromuscular junction, the axon terminal or synaptic end bulb, and the motor end plate? Ach, what is it and what does it do? What about AChE? What is the role of Calcium? When is ATP used? Describe the movement of the action potential. What is the importance of the terminal cisternae? What does the triad complex do? What part of actin does myosin bind to? What is CP? Remember the basics of anaerobic and aerobic metabolism. What is depolarization? repolarization? What happens to the cell during contraction (Na+)....the all-or-none law? Know what a motor neuron is, how gradations of strength occur, what is a motor unit? What is a twitch? What are the 3 phases associated with one? What occurs during each phase? What is treppe, wave summation, and tetany? What causes decreases in muscle contraction strength? What causes muscle fatigue? Muscle fiber type - slow, intermediate, fast, by what other name are they called? What are the main characteristics of each? Any training effects of the muscle fibers? Types of contraction: isometric, concentric, eccentric, which causes the most muscle damage (soreness) when does muscle soreness peak? Muscle actions: prime movers, antagonists, synergists, and fixators What criteria used to name muscles: shape, size, attachments, action, number of divisions, location examples of each? Which muscles maintain posture: keep you upright? Which muscles medially rotate the shoulder? which muscles medially rotate the hip? Which muscles laterally rotate the shoulder and which laterally rotate the hip? Which flex the shoulder? and extend the shoulder? Which extend and flex at the elbow and shoulder? Which extend and flex at the hip, knee? What muscles cause trunk flexion and rotation? Which is designed for mainly abdominal compression? Homeostatic Imbalances What are some neurotoxins that block ACh? and AChase? what causes rigor mortis? What is muscular dystrophy? what is the cause? What is fibromylagia? Origins, insertions, and actions will be asked