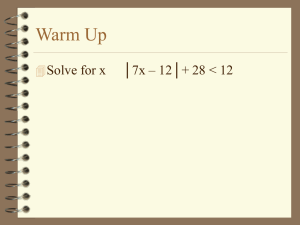Practice for Test 3
advertisement

Mac 1140 Chapter 4 Practice for Test 3 NON-CALCULATOR, Part A 1 2. Write in exponential form: log 2 3 8 36 6 1. Write in logarithmic form: Evaluate: 4. 5 log5 8 3. log 10 5. log44 3 Rewrite as a single logarithm. Simplify final answer if possible. 6. log x + 1 log( x 2) - 3log(x+4) 2 7. ln(x2 – 9) – ln (x - 3) + ln(x) Rewrite as a sum or difference of logarithms. x2 y 8. log t 9. ln (3 2 x ) 10. Solve by addition. x + 2y = 6 2x - y = -8 11. Solve by substitution. 2x2 – y = 8 y = -7x – 4 12. Solve. 2x2 – y2 = 1 x2 – 2y2 = -1 Graph: 13. x2 + y2 > 9 14a. x + 2y 4 y x 3 14b. y > x2 - 4 -x + y < 2 NONCALCULATOR, Part B: Sketch the graph. Identify the asymptotes, the coordinates of the translated x-intercept, and domain and range for each graph. . (You may check the graph on your calculator) 1. y = log (x) 2. y = -3 + log3(x) 3. y = log (x – 3) 4. y =-2 + log4 (x-3) 5. y = 4 + ln (x + 2) Evaluate: 6. log 100 7. log 1017 8. ln e43 9. log 2 8 11. log 4 2 12. log 50 + log 2 13. log 3 54 – log 3 2 15. eln 17 16. 10log 17 14. 2log 7 10. log 2 (1/4) 7 Solve: 17. 23x-5 = 16 18. 82x-5 = 16x 21. log 2 (x) + log 2 (x + 6) = 4 19. 3x = 19 20. log 3 (x + 2) = 4 22. log (x – 3) – log (x + 2) = log (5) 23. ln x = 7 24. ln (x – 2) = 7 26. 3x = 5(x – 1) 25. eln 17 = 2x 3x 9 27. logx64 = 3 2 28. 4x-3 = 8 29. 30. 25x + 1 = 6 31. ex = 25 32. 5x+4 = 52 Graph by filling in a table and graphing points in the table (see tables in answers; check graphs on calculator.). 33. f(x) = 3x 34. f(x) = log3x (Replace f(x) with y & rewrite in exponential form first. Then select y-values and evaluate for x.) 35. Which of the following functions has an inverse? (Graph & use one-to-one, horizontal line test.) a. f(x) = x2 – 3x - 4 b. f(x) = x3 36. Determine the inverse of: a. f(x) = 3x - 5 (Procedure is on page 138.) 2x 3 b. f(x) = 3x 5 A CALCULATOR MAY BE USED ON THE REMAINDER OF THE PROBLEMS. SET THE MODE TO FOUR DECIMAL PLACES. Evaluate 1. ln 924 Solve: 4. e3x - 2 = 10 2. log 924 3. log 7 924 5. -3x = 5 6. log (2x + 7) = -3 7. 3 – ln(x) = 2x – 5 9. y = x2 y = -x2 + 4 8. ex = ln (x) 10. y = x + 2 xy = 7 ANSWERS Non-calculator portion, Part A: 1 1 1. log366 = 2. 2-3 = 2 8 8. 2log(x) + log (y) - 1 log(t) 2 3. 1 4. 8 9. ln 3 + xln2 13. 14a. x x2 7. ln (x2 + 3x) 6. log 3 ( x 4) 1 15 10. (-2,4) 11. , , , (-4, 24) 12. (1, 1 ), (-1, 1 ) 2 2 14b. 5. 3 Non-calculator portion, Part B: 1. x=0, (1, 0), D = (0, ), R = (- , ) or all reals 2. x=0, (1, -3), D =(0, ), R = (- , ) or all reals 3. x = 3, (4, 0), D = (3, ), R = all reals 4. x = 3, (4, -2), D = (4, ), R = all reals 5. x =-2, (-1, 4), D = (-2, ) , R= all reals 6) 2 7) 17 8) 43 9) 3 10) –2 11) 1/2 12) 2 13) 3 14) 1 15) 17 16) 17 17) 3 18) 15/2 19) log3 19 20) 79 21) 2 (throw away –8) 22) No solution (throw away-13/4) 23) e7 24) e7 + 2 25) 17/2 26) –ln5/(ln3 – ln5) or ln 5/(ln5 – ln3) 9 1 27)4 28) 29) 2 30) 31) x = ln 25 32) –4 + log552 2 2 33) x y -1 1/3 0 1 1 3 2 9 34) x y 1/3 -1 1 0 3 1 9 2 34) exponential form 3y = x 35) b, because this function is one-to-one; each y is paired with exactly one x. 36a) f-1(x) = x 5 3 36b) f-1(x) = 5x 3 2x 2 Calculator portion: 1) 6.8287 2) 2.9657 3) 3.5093 4).8283 5) no solution 6) –3.4995 7) 3.3896 8) no solution 9) ( 1.4142, 2) 10) (1.8284, 3.8284), (-3.8284, -1.8284)