File
advertisement

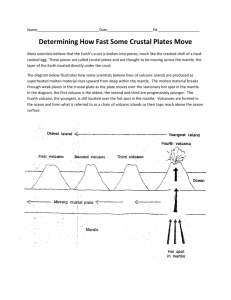
HOT SPOTS!! (Graphing Activity) Part One: Background on Hot Spots A mantle plume is an upwelling of abnormally hot rock within the Earth's mantle. As the heads of mantle plumes can partly melt when they reach shallow depths, they are thought to be the cause of volcanic centers known as hot spots. Fold this flap back using the line below as a guide. Then glue this side (tab) to your NOTEBOOK. Magma generated by the hot spot rises through the lithospheric plates and produces volcanoes on Earth’s surface. Some scientists think that plate tectonics cools the mantle, and the mantle plumes cool the core. The Hawaiian hot spot has been active at least 70 million years, producing a volcanic chain that extends 3,750 miles (6,000 km) across the northwest Pacific Ocean. Each island is made up of at least one primary volcano, although many islands are composites of more than one. The Hawaiian volcanoes were produced by the Hawaiian hot spot, which is presently under the Big Island of Hawaii. As the Pacific Plate moves towards the Northwest, the island of Hawaii will no longer be over the stationary hot spot, and will no longer have volcanic activity. As the Pacific Plate moves, a new section of ocean floor will be situated over the hot spot. Eventually magma will harden into igneous rock, accumulate, rise above sea level, and form a new island in the chain. If the magma does not reach sea level, a seamount is formed. A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean floor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level), and thus is not an island. Currently the big island of Hawaii is situated over the hot spot, producing volcanoes like Kilauea. Define the following terms: Mantle Plume – Hot Spot – Seamount – Part Two: Create a Line Graph The Northwest movement of the Pacific Plate can be seen by looking at the ages of volcanic islands in the Hawaiian Island Chain. To better understand the relationship between volcanic island ages, plate movements, and hot spots, use the information provided in Data Table 1 to create a line graph showing the relative ages of some of the Hawaiian Islands and outer seamounts. Data Table 1 – Ages of some of the Hawaiian Islands and outer seamounts Volcano Name (1) Kilauea (2) West Maui (3) Waianae (4) Kaula (5) Nihoa (6) Necker (7) La Perouse Pinnacles (8) Gardner Pinnacles (9) Laysan (10)Pearl and Hermes Reef Distance from Kilauea (km) 0 221 374 600 780 1,058 1,209 1,435 1,818 2,281 Age (Ma) 0 1.32 3.7 4.0 7.2 10.3 12.0 12.3 19.9 20.6 Did you create a GOOD graph? Create an appropriate title Label each axis with units Units have equal intervals Plot data points and connect Remember: D- Dependent R- Responding Y- Axis M- Manipulated I-Independent X-Axis Name: ____________________ Hot Spots - Analysis Question Describe the formation of the Hawaiian Islands and how they are formed differently from a volcano formed at a convergent boundary. Use evidence from your graph to explain the relationship between the age of the Hawaiian Islands and distance between them. Evidence = DATA (numbers) ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Name: ____________________ Hot Spots - Analysis Question: Describe the formation of the Hawaiian Islands and how they are formed differently from a volcano formed at a convergent boundary. Use evidence from your graph to explain the relationship between the age of the Hawaiian Islands and distance between them. Evidence = DATA (numbers) ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________