Review sheet for Midterm exam 1
advertisement
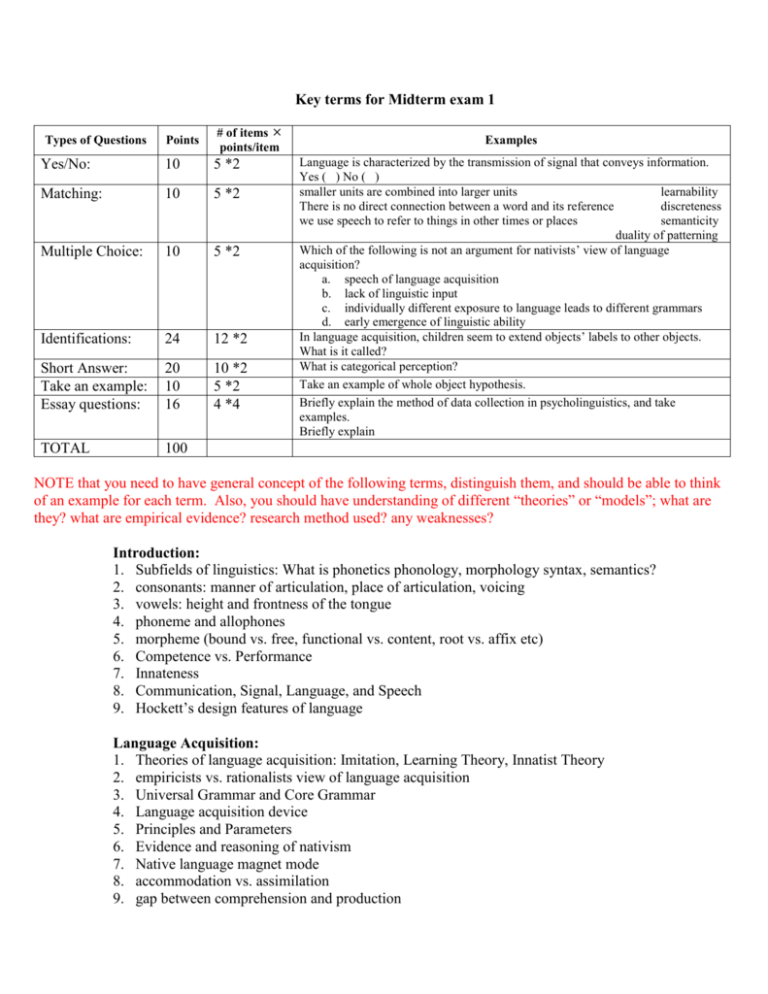
Key terms for Midterm exam 1 Points # of items points/item Yes/No: 10 5 *2 Matching: 10 5 *2 Multiple Choice: 10 5 *2 Identifications: 24 12 *2 Short Answer: Take an example: Essay questions: 20 10 16 10 *2 5 *2 4 *4 TOTAL 100 Types of Questions Examples Language is characterized by the transmission of signal that conveys information. Yes ( ) No ( ) smaller units are combined into larger units learnability There is no direct connection between a word and its reference discreteness we use speech to refer to things in other times or places semanticity duality of patterning Which of the following is not an argument for nativists’ view of language acquisition? a. speech of language acquisition b. lack of linguistic input c. individually different exposure to language leads to different grammars d. early emergence of linguistic ability In language acquisition, children seem to extend objects’ labels to other objects. What is it called? What is categorical perception? Take an example of whole object hypothesis. Briefly explain the method of data collection in psycholinguistics, and take examples. Briefly explain NOTE that you need to have general concept of the following terms, distinguish them, and should be able to think of an example for each term. Also, you should have understanding of different “theories” or “models”; what are they? what are empirical evidence? research method used? any weaknesses? Introduction: 1. Subfields of linguistics: What is phonetics phonology, morphology syntax, semantics? 2. consonants: manner of articulation, place of articulation, voicing 3. vowels: height and frontness of the tongue 4. phoneme and allophones 5. morpheme (bound vs. free, functional vs. content, root vs. affix etc) 6. Competence vs. Performance 7. Innateness 8. Communication, Signal, Language, and Speech 9. Hockett’s design features of language Language Acquisition: 1. Theories of language acquisition: Imitation, Learning Theory, Innatist Theory 2. empiricists vs. rationalists view of language acquisition 3. Universal Grammar and Core Grammar 4. Language acquisition device 5. Principles and Parameters 6. Evidence and reasoning of nativism 7. Native language magnet mode 8. accommodation vs. assimilation 9. gap between comprehension and production 10. Mapping problem in semantic development 11. Whole-object hypothesis 12. Taxonomic constraint 13. Mutual exclusivity assumption 14. Over-extensions 15. Under-extensions 16. Syntactic Bootstrapping and Semantic Bootstrapping 17. MLU 18. Holophrases 19. Telegraphic stage 20. U-shaped development 21. Productivity in morphological development 22. statistical learning of language and research Speech Perception: 1. Invariance problem 2. Segmentation problem 3. Categorical perception 4. identification task vs. discrimination task 5. VOT 6. Bottom-up processing vs. Top-down processing 7. pre-lexical vs. post-lexical 8. Phoneme Monitoring Task 9. Phoneme Restoration 10. prototype vs. storage of examplars 11. Motor Theory 12. Cohort Model 13. Three stages of word recognition 14. Trace 15. Frequency Effect 16. Phonological neighborhood effect 17. Context effect 18. Familiarity effects 19. McGurk Effect Research Methods: 1. observational vs. experimental 2. quantitative vs. qualitative 3. theory-driven vs. data-driven 4. sucking habituation paradigm 5. head-turning procedures 6. inter-modal preferential looking task 7. production elicitation 8. identification task vs. discrimination task (in categorical perception) 9. shadowing – fluent restorations 10. cross-modal priming 11. Phoneme Monitoring Task










