File - Mr.Nolan's Science Class's
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Kingdom Animalia
Characteristics of animals
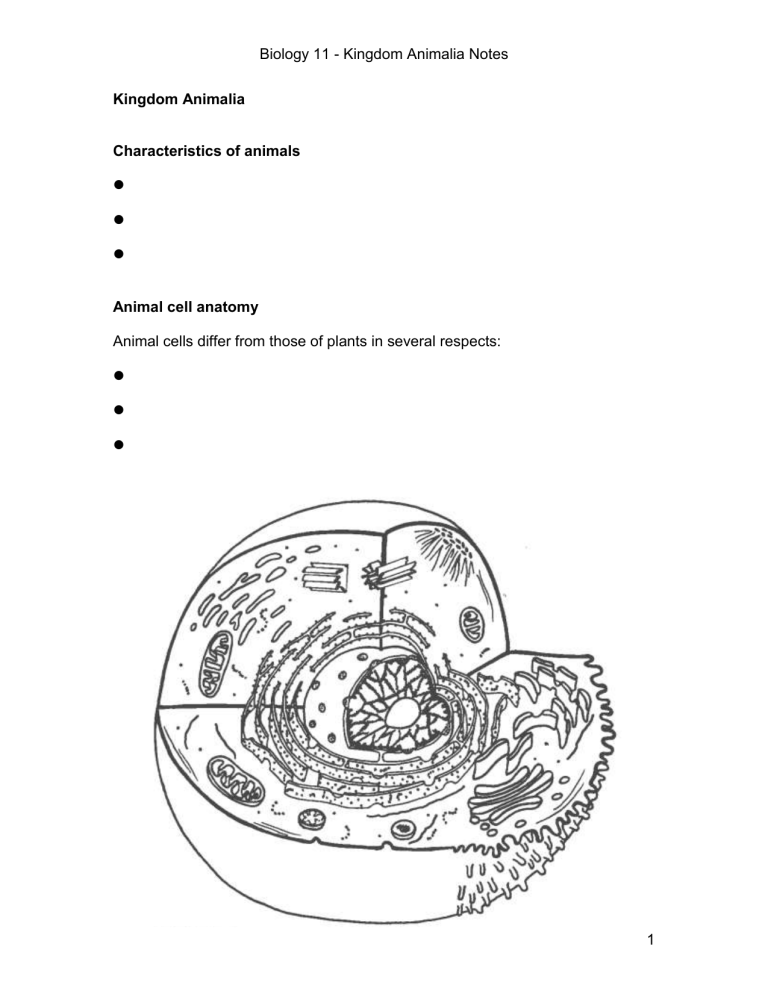
Animal cell anatomy
Animal cells differ from those of plants in several respects:
1
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Major trends in animal evolution
1.
2.
3.
4.
1. Body symmetry
There are three symmetries found in animals:
1. asymmetry –
2. radial symmetry –
3. bilateral symmetry
–
Evolution of body symmetry
cephalisation =
2
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
2. Embryonic germ layers
Each layer forms different adult tissues:
1. ectoderm =
2. mesoderm =
3. endoderm =
3. Body cavities
three types of body cavities are defined by the shape of the germ layers:
1. acoelom =
2. pseudocoelom =
3. coelom =
3
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
4. Organ Systems
in animals we see these systems evolve:
1. digestive –
2. excretory
–
3. circulatory –
4. nervous –
Animal phyla we will study:
Porifera -
Cnidaria -
Platyhelminthes -
Nematoda -
Annelida -
Arthropoda -
Mollusca -
Echinodermata -
Chordata -
4
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Porifera
Sponge anatomy
sponges have four different cells:
1. choanocytes =
2. porocytes =
3. pinacocytes =
4. amoebocytes =
5
Sponge feeding
1.
2.
3.
Sponge skeleton
Organ systems
The birth of animals
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
6
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Cnidaria
Cnidarian anatomy
Cnidarians come in two different forms:
1. polyp –
2. medusa –
Organ systems
7
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Feeding in cnidarians
gastrovascular cavity =
Anatomy of Obelia
there are two kinds of polyps:
1. feeding polyps –
2. medusa polyps –
8
Life cycle of Obelia
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
9
Cnidarian diversity
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Class Hydrozoa
Class Cubozoa
Class Anthozoa
Class Scyphozoa
10
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Platyhelminthes
– the flatworms
Digestive system
Nervous system
Flatworms are the first to show cephalisation:
eyespots = auricles =
11
Excretory system
flame cells =
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Flatworm reproduction
testes =
ovary =
uterus =
yolk gland =
genital pore =
12
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Flatworm diversity
Class Turbellaria
Class Trematoda – the flukes
divided into two groups:
1.
2.
Class Cestoda
– the tapeworms
13
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Tapeworm anatomy
The body of tapeworms is divided into:
scolex =
proglottids =
Life cycle of a tapeworm
14
Phylum Nematoda
Organ systems
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
15
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Roundworm reproduction
Parasitic roundworms
Importance of roundworms
16
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Annelida
Anatomy of annelids
Organ systems
nephridium =
17
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Feeding in segmented worms
Annelid reproduction
18
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Annelid diversity
There are three main groups of annelids:
Class Oligochaeta –
Class Polychaeta –
Class Hirudinea
–
Class Oligochaeta
19
Class Polychaeta
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Class Hirudinea
20
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Mollusca
Basic mollusc body plan
A typical mollusc has these 4 features:
1. shell =
2. mantle =
3. foot =
4. visceral mass =
21
Organ systems
Circulatory system
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Life cycle of molluscs
trochophore larva =
22
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Molluscan diversity
There are 3 main groups of living molluscs:
1. Class Bivalvia
–
2. Class Gastropoda –
3. Class Cephalopoda
–
Class Bivalvia
Class Gastropoda
23
Class Cephalopoda
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
24
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Arthropoda
Basic arthropod body plan
The body is made of 3 main parts:
1. head –
2. thorax –
3. abdomen –
25
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Digestive system
The gut contains, in order from mouth to anus, the following organs:
1. pharynx =
2. crop =
3. caeca =
4. stomach =
5. intestine =
6. rectum =
Excretory system
Malphigian tubules =
Nervous system
26
Circulatory system
Exoskeleton
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Arthropod diversity
We will look at three groups of arthropods:
1. Crustaceans –
2. Arachnids –
3. Insects
–
27
Crustaceans
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Diversity of crustaceans barnacles = krill = sea lice =
28
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Arachnids
Diversity of arachnids spiders = scorpions = mites =
29
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
The insects
Diversity of insects
About 85% of insects are found in 4 Orders:
1. Coleoptera –
2. Lepidoptera –
3. Diptera –
4. Hymenoptera
–
30
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Invertebrate evolution
Phylum Echinodermata
Water vascular system
madreporite =
31
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Echinoderm anatomy
Echinoderm diversity
There several important groups of living echinoderms:
1. asteroids –
2. ophiuroids –
3. echinoids –
4. holothuroids
–
5. crinoids –
32
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Phylum Chordata
Basic chordate body plan
All chordates have, at some time in their life, these three characteristics:
1. notochord –
2. pharynx with slits
–
3. dorsal hollow nerve cord (DHNC) –
33
Organ systems
1. digestive system =
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
2. excretory system =
3. circulatory system =
4. nervous system =
Invertebrate chordates
34
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Vertebrate chordates
Vertebrate diversity
There are 7 Classes of living vertebrates:
1. Agnatha
–
2. Chondrichthyes
–
3. Osteichthyes
–
4. Amphibia
–
5. Reptilia –
6. Mammalia –
7. Aves –
Class Agnatha
35
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Class Chondrichthyes
Class Osteichthyes
36
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
Terrestrial vertebrates
swim bladder = lung =
Class Amphibia
37
Class Aves
Class Reptilia
Class Mammalia
Biology 11 - Kingdom Animalia Notes
38







