What is Science/Metric Notes
advertisement

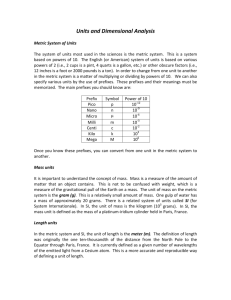
What is Science? Science is Name some of the Sciences you are familiar with and what they study. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. What is Earth Science? Earth Science is Four major branches of Earth Science 1. 2. 3. 4. Worksheet: “What is Earth Science?” begin in class and finish as homework “How Many Earth Sciences are There?” homework Go over definitions – what makes a good definition Technology – define Is every technology, therefore, inherently good? Does it always stay that way? Think about all of the technological advances that have ever happened. Write a list of some of the important past technologies that you can think of. Technology timeline activity Why did this activity end at 1957? -All space exploration technology has occurred in Mr. Dichraff’s lifetime. Sputnik Other satellites Mercury Gemini Apollo Space Shuttles Space Telescopes Space Stations Mars Rovers Other planetary explorers Now think about your lifetime. What technological advances have occurred since you were born? Assignment: “My Life in 2057” – handout Safety in the laboratory Much of the safety information is just ____________________. If you think someone may get hurt if you do something, ________ _____________________! Safety rules handout. Discussion of basic safety rules with examples. The most important safety rule to remember is: Metric System: Notes Developed by the ____________ Original distance used for the meter = Base Units: Lengths = Liquid volumes = Mass = Temperature = Celsius is based on Kelvin is different because of its Prefixes: kilo- hecto- deka- base deci- centi- milli- Each change in this order is a __________________. So, for conversions you will then just ________________. Count the spaces from where you start to where you want to end and ______ ____________________________________________________. Examples: 456.7890123 km = _______________________ mm 543210.9876 cg = ________________________ dkg 19283.74650 mL = _______________________ L 1234.567890 m = _________________________ hm Accuracy: Places after the decimal point indicate the accuracy of the measurement. Therefore, a number like 2.0 mm _______________________ than 2 mm. Using the metric measuring devices I expect you to estimate between the smallest markings to achieve the greatest accuracy. Demonstrate using the meter stick. Estimate between the mm markings to get an accuracy of 0.1 mm. When converting to other meter based units, do not drop the number after the decimal, even if it is a zero. Hand out measurement activity worksheets Length measurement activity: With a partner you will measure and record the items listed. Make sure you record your initial measurements to the 0.1 mm accuracy that is in the directions. Volume: define: Liquids: _____________ Use a _________ container to measure volumes When measuring water in a glass container the upper surface of the water will form a depression called a ___________. This occurs because ______________________________. To be accurate in your measurement, read the volume ___ __________________________________________. Solids: m3, cm3, etc. Regular: Regular rectangular solid – L x W x H Units must be the same on all dimensions Cylinder – л r2 h Sphere – 4/3 л r3 Irregular: Water displacement method Metric System continued: Mass: ___________________________________ _________________________________________ Do not confuse this with weight. Weight ________ __________________________________________ __________________________________________ Mass Activity: Use of balances Double pan – Use known masses with the beam/rider to determine the mass of the object Triple beam – Use the beams/riders to determine the mass of the object – make sure the riders on the top two beams are in the slots on the beams Measure the items on the Mass activity sheet. Three different cubes and three different cylinders are listed. You must do all three. Record your masses accurate to 0.01 grams (estimate between the tenth of a gram markings) Density: the calculation of the amount of matter in a given volume of material Density is calculated by taking the mass divided by the volume of the object. The units used are generally ______. Calculate the densities of the items on the density activity worksheet. Make sure to put the proper units with your numbers. You will need the volume and mass numbers previously obtained to do this portion. The volumes of the three cubes are the same and the volumes of the three cylinders are the same. Metric System continued: Specific Gravity: The comparison between the density of a substance and the density of water Water has a density of 1 g/cm3. Therefore when you divide the density of your substance by the density of water you are dividing by 1 so the number stays the same. But, the units will cancel out so you are left with a number without units that tells you relationship to the density of water. (If I request the density of a substance on a worksheet or test there must be units with it. If I ask for specific gravity, it is the same number but will have no units) Buoyancy: shaping an object correctly to allow it to displace its weight in water and therefore float. Generally if a material is less dense than water it will float in water. But, if you take a more dense object it can still be made to float if you shape it correctly. That is how we are able to make boats out of aluminum and ships out of steel even though these materials are more dense than water. Temperature: a measurement of the amount of kinetic energy in the molecules of a substance Metric scales for temperature are degrees Celsius, named after Andres Celsius, and Kelvins, named after Lord Kelvin. The only difference between these scales is the starting point. Lord Kelvin used the same size units as Celsius did, he just decided to start his scale at what is believed to be the lowest possible temperature, absolute zero. On this scale there are no negative numbers – no temperatures below zero.
![Temperature Notes [9/22/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006907012_1-3fc2d93efdacd086a05519765259a482-300x300.png)