Lab Final
advertisement

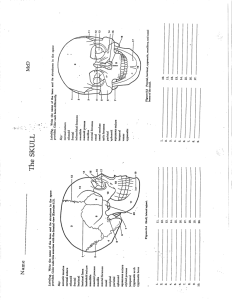
Biology 1 – Study Guide for Lab Final Lab 8 – DNA, Protein Synthesis, and Biotechnology Be able to read a DNA fingerprint. What do the bands represent? Be able to build a complimentary strand, mRNA, tRNA and proteins from a strand of DNA. Whey is shape important for proteins? Know the effects of radiation on the germinated seedlings. Are they somatic or sex cell mutations? How can you tell if the radiation affected the sex cells? Lab 9 – Genetics Know the following terms: haploid, diploid, chromosomes, homozygous, heterozygous, recessive, dominant, and genotype. Be able to calculate the % deviation of a sample from the expected. Know how to read a karyotype. Know how to read a pedigree. Be able to do a genetic problem (monohybrid, sex-linked, incomplete dominance, test cross). Lab 10 – Macroevolution and Homologous Structures Know the bones of the skull and skeleton. What bone forms the forehead? Contains the external auditory meatus? Bears the foramen magnum? What is another name for the collar bone? Shoulder blade? Shin bone? Knee cap? Know why ribs are attached by cartilage. How many ribs do males and females have? Why are more injuries seen in the cervical or lumbar regions? What teeth are absent in horses and sheep? Why do birds and mammals have a hard palate? How can you tell if an animal is bipedal? What does the position of the orbit tell you about an animal’s lifestyle? Lab 11 – Microevolution and Interactions Between Organisms and Their Environment Know the following terms: biotic, abiotic, habitat, niche. What is a trophic level? (producers, primary consumer, secondary consumer, decomposer). Be able to explain the Natural selection experiment with predators and beans. Be able to calculate predator efficiency. Know the notes on the Predator Movie Lab 12 – Population Growth and Diseases Know the following terms: natality, mortality, immigration, emigration, biotic potential, carrying capacity. What is ZPG? Know the four categories of diseases: genetic, deficiency, degenerative, communicable. Know the following terms: pathogen, transmission, incubation period, asymptomatic carriers, and communicable period. STD pathogens are three types: viral, bacterial, and others. Know the STD activity. Know the example of the earth (apple). How much of the “apple” do we depend on? Lab 13 – Human Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Know the following terms: tidal volume, respiratory rate, apnea, Know how to calculate pulmonary ventilation and alveolar ventilation. Know the experiments with breathing rates and apnea time. Know the components of blood (table on 238). Know what the chemicals do to heart rate. Know how to read blood pressures and what they mean. Know the parts of the heart. Lab 14 – Nervous System Know the difference between phasic and tonic receptors. What is two-point touch discrimination? Know where the types of tastebuds are found on the tongue. What is a blind spot? Know what the numbers mean for visual acuity. What is an astigmatism? Know the structure of the eye. What is the tapetum lucidum? What are proprioceptors. Lab 15 – Ecology Know the different habitats in the sanctuary. How large is it? Who is the director? Why was the corner given up and what was given in return? Why? What was the chemical spill in the sanctuary?