1.1 Using Qualitative Graphs
advertisement

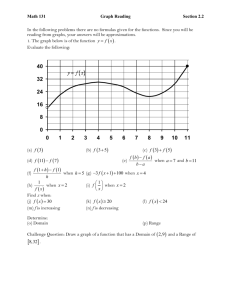
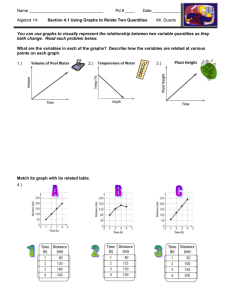
1.1 Using Qualitative Graphs to Describe Situations Objectives Use qualitative graphs to describe situations Identify independent variables and dependent variables Know the meaning of an intercept of a curve Identify increasing curves and decreasing curves Putting it all together to sketch a qualitative graph Qualitative Graphs & Independent and Dependent Variables Let t represent time in minutes and T represent temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. Consider each of the graphs below. a) b) T T t c) T t t 1. How are these graphs different from the graphs you may have seen or created in Beginning Algebra? In your own words define “Qualitative Graph.” 2. Which of the above graphs could describe the temperature of potato baking in the oven? Explain. 3. Does time, t, depend on the temperature, T, of the potato, or does the temperature of the potato depend on the time the potato spends in the oven? 4. In your words define each of the following: Quantity: Dependent Variable: Variable: Independent Variable: 5. On a graph which variable (dependent/independent) is matched with the horizontal axis? The vertical axis? Examples: In each of the following situations, identify the two quantities and determine which quantity is the independent variable and which quantity is the dependent variable. a. The population, P, of a small town increases over the years, t, between 2000 and the present. b. The distance, s, a woman runs measured in minutes, t, since she left her house. c. The percentage of smokers, P, each year, t, since 1965. Interpreting Qualitative Graphs: Interpreting Intercepts: Increasing and Decreasing Curves Ex. 1: The following graph represents the percentage of the U.S. population, P that is foreign born t years after 1970. 1. What year is represented by t 0 ? How is this related to the vertical intercept? P t 2. Label the part of the graph which represents a decrease over time in the percentage of the U.S. population that is foreign born. Label the part of the graph which represents an increase over time of the percentage of the U.S. population that is foreign born. 3. Label the part of the graph which represents the lowest percentage of the U.S. population that is foreign born. 4. Fill in the blanks: The shape of this curve is quadratic because it has the shape of a . Ex. 2: The following graph represents a steadily decreasing population, P, over time – where t represents the number of years since 1990 through 2002. P t 1. Do you think this curve accurately represents a decreasing population? Explain. 2. Identify and label both the vertical and horizontal intercepts. What do they mean in the context of this situation? 3. The shape of the curve is linear because it is a . In your own words interpret each of the following: Increasing Curve: Decreasing Curve: Putting it All Together Ex. 1: Work with your neighbor to complete # 2 from section 1.1 in your textbook. Ex. 2: Work with your neighbor to sketch a graph that shows the relationship between the variables defined in the following exercise. Justify your graph. a. An airplane flew from New York to Chicago. Let h represent the height of the airplane at t seconds after takeoff. b. Let F represent the temperature at a specific outdoor location at t hours after 6 A.M. on a specific day. (What does t = 0 represent?). Section 1.1 Homework: # 1, 4, 6, 17, 23, 25.