Aspirin-Lab-Word
advertisement

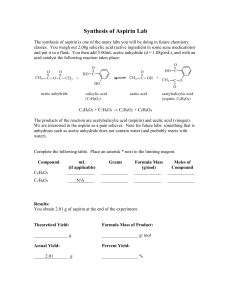
Chemistry 2015 Aspirin Lab Name _________________ Purpose: To compare the chemical and physical properties of various brands of aspirin. Materials: Test tubes, Graduated cylinder, Dropper Bottles, Iron Chloride FeCl3 , Iodine, NaHCO3, Aspirin (various brands) Acetic Acid, Procedure: Part 1 – 1. Obtain one of each pain reliever. Record the physical properties of each substance on your data sheet. 2. Record the active ingredients, mass and mg of acetylsalicylic acid as listed on the label. 3. Calculate the % acetylsalicylic acid and price per tablet. Part 2In part 2, you will test for additives added to aspirin tablets. These will be white powders or crystals. Some will be water soluble and some will not be soluble in water. All were substances that were readily available in the early 1900’s. Additives are often binding agents, substances that help bind it together in pill form. These fillers are used in counterfeit and illegal drugs as well. 1.Test each additive by putting a pinch of each additive in 5 test tubes or in 5 wells of a reaction surface. 2. Test each of the 5 substances one at a time with H2O, FeCl3, Lugols Iodine, sodium bicarbonate, acetic acid . Record your observations. Part 3 – In part 3, you will test for additives and other substances / breakdown products in aspirin tablets. Test one tablet at a time. You will be given only 1 tablet per lab group so proceed carefully. 1. Break each of the aspirin tablets into 5 pieces. Place a small piece in one test tube. 2. Add water and record your results. Compare the solubility of the tablets. 3. Repeat with the remaining pieces testing with Iron Chloride FeCl3; Iodine; sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), and acetic acid. Part 4 – In part 4, you will test the acidity of the various brands. Too much acid can upset your stomach. 1. Using a mortar and pestle, crush one tablet and add it to a test tube. 2. Add 5 mL of water and 5 drops of universal indicator to each tube. 3. Record the starting pH using pH paper. 4. Perform a titration on each aspirin tablet and record the number of drops of NaOH used to neutralize the solution. A green solution is neutral. DataTable 1: Aspirin Composition Tablet Bufferin Ecotrin Bayer Generic Excedrin O’Ryan Physical Properties Active Ingredients [labels] Acetylsalicylic acid mg Mass of tablet mg % Acetylsalicylic acid in tablet Price per tablet (price/#) Chemistry 2015 Data Table 2: Physical and Chemical Properties aspirin Aspirin Physical properties Water H2O [soluble?] Iron (III) Chloride FeCl3 Lugol’s Iodine KI + I2 Baking Soda NaHCO3 Acetic Acid CH3COOH Bufferin Ecotrin Bayer Generic Excedrin Conclusion: Which brand of aspirin would you choose. Refer to ALL relevant data to support your answer. Price, presence of salicylic acid and acetic acid, active ingredients and mg of acetylsalicylic acid should all be considered. (5 – 8 sentences.) Water FeCl3 Lugol’s Iodine Sodium Bicarbonate Compare solubility Red/ Purple = salicylic acid. Vinegar smell = acetic acid Black/Purple = starch present as filler Bubbles if acetic acid is present 1. How did the different aspirin brands differ in terms of active ingredients and fillers? 2. Which aspirin brand/s were lowest in acetylsalicylic acid? 3. Describe two ways (chemical tests or observations) to tell that the acetic acid and salicylic acid are NOT chemically combined. What can cause this? 4. Which fillers were present in the aspirin tablets? 5. Here is the reaction for the synthesis of aspirin. Balance the equation and tell the molar mass for acetylsalicylic acid. 6. Most of the aspirin brands tested had 325 mg of acetylsalicylic acid. How many grams is this? ______. How many moles? ___________ O’Ryan Chemistry 2015 7. Calculate the mass of salicylic acid needed to make 1 aspirin tablet. Extra Credit: Today aspirin is made from crude oil, not willow bark. But if we did use willow bark, 1 kilogram of willow bark could produce about 27 grams of aspirin. 1. Since one can only strip about 91 kg of bark from a willow tree without killing it, how many 325 milligram tablets of aspirin could be made from one willow tree? 2. How many willow trees would it take to make the 80 million aspirin tablets consumed each day in the United States alone? 3. Given that one acre of wet ground can support about 15 willow trees, how much land would be needed to produce one day's supply of aspirin for the United States? O’Ryan