File
advertisement

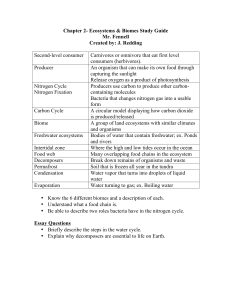
Lesson Plans DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Teacher Nina Cook (Ann Schultz) Week# 12 of semester 2 Week of: April 30 – May 4, 2012 Subject: Biology Hours: 3rd, 5th, 6th Revised 5/3/2012 Accommodations: Student Name: XXXXXXXXXX Identification Number: XXXXXXXXXX Hour: 6 Resource Teacher: Marsha Burrell Lesson Modification: Close proximity, multi-sensory activities, small group instruction, extended time Area(s) for Modification __ LD __AI __HI __CI __POHI Student Name: XXXXXXXXXX Identification Number: XXXXXXXXXX Hour: 5 Resource Teacher: Marsha Burrell Lesson Modification: Close proximity, multi-sensory activities, small group instruction, extended time Area(s) for Modification __ LD __AI __HI __CI __POHI Student Name: XXXXXXXXXX Identification Number: XXXXXXXXXX Subject: Biology Hour: 6 Resource Teacher: Marsha Burrell Lesson Modification: Close proximity, multi-sensory activities, small group instruction, extended time Area(s) for Modification _X_ LD __AI __HI __CI __POHI 1 Lesson Plans DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Accommodations (continued): Student Name: XXXXXXXXXX Identification Number: XXXXXXXXXX Subject: Biology Hour: 6 Resource Teacher: Marsha Burrell Lesson Modification: Close proximity, multi-sensory activities, small group instruction, extended time Area(s) for Modification _X_ LD __AI __HI __CI __POHI Overarching Question: How are organisms affected by, and how do they interact with, their living and nonliving environment? Focus Question: What types of energy transformations occur in an ecosystem, and what energy transformation cause and effect relationships can be predicted? Key Concepts/Vocabulary: Abiotic factor p. 37 Autotroph p. 46 Biological community p. 39 Biomass p. 52 Biosphere p. 36 Biotic factor p. 38 Carbon cycle p. 55 Carnivore p. 47 Commensalism p. 44 Consumer p. 47 Decomposer (bacteria and fungi) p. 47 Detritivore (animal consumer of dead matter) pp. 42-43 Ecology p. 36 Ecosystem p. 41 Food chain p. 49 Food web p. 50 2 Lesson Plans Habitat p. 42 Herbivore p. 47 Heterotroph p. 47 Mutualism p. 44 Niche p. 43 Nitrogen cycle p. 56 Omnivore p. 47 Organism p. 40 Parasitism p. 44 Phosphorus cycle pp. 56-57 Population p. 38 Producer p. 46 Species p. 7 Symbiosis p. 44 Trophic level p. 50 Trophic Level Pyramid pp. 51-52 Water cycle pp. 53-54 Condensation Evaporation Precipitation Transpiration Combustion Consumption Fossil Fuel Photosynthesis Respiration Leguminous Plant Nitrogen Fixation Absorption Erosion Leaching CDV and CCV DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY 3 Lesson Plans DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Teaching Resources/Materials: Black History Month 5/3 NB#40 Andrew Jackson Beard 1849-1921 Copies of biography and information about Andrew Jackson Beard Copies of NB#37 Water Cycle reading and coloring pages Water cycle diagram http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/watercycle.gif Copies of NB#38 Carbon Cycle reading and coloring pages Copies of Worksheet 1 The Carbon Cycle Carbon cycle diagram http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Water/co2_cycle.html Carbon cycle diagram http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/carboncycle.gif Carbon cycle online game http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/climate/carbon_cycle.html Copies of NB#39 Nitrogen Cycle reading and coloring pages Copies of Worksheet 2 The Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen cycle diagram http://www.welchclass.com/Biology/ecology/nitrogencycle.JPG Nitrogen cycle diagram http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Life/nitrogen_cycle.html Nitrogen cycle diagram http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/nitrogencycle.gif Traveling Nitrogen classroom game http://www.windows2universe.org/teacher_resources/teach_nitrogen.html Traveling Nitrogen Passport http://www.windows2universe.org/teacher_resources/nitrogen_worksheet.html Dice codes and reservoir station signs http://www.windows2universe.org/teacher_resources/n_dicecode.html Teacher key to stamps http://www.windows2universe.org/teacher_resources/nitrogen_teacherkey.html Copies of NB#41 Phosphorus Cycle reading and coloring pages Phosphorus cycle diagram http://www.flatheadwatershed.org/natural_history/images/fig2_27_phosphorus_cycle_flat.jpg Phosphorus cycle diagram http://faculty.southwest.tn.edu/rburkett/ES%20%20we33.jpg Phosphorus cycle diagram http://arnica.csustan.edu/carosella/biol4050w03/figures/phosph1.jpg Phosphorus cycle diagram http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/pix/phosphoruscycle.gif Phosphorus cycle diagram http://1.bp.blogspot.com/_sAGgbMmkqPM/TTbiy0AxRvI/AAAAAAAAAA8/BZaLoRfiiNI/s1600/phosphorus-cycle.jpg Copies of History of a Carbon Atom Copies of NB#42 Terrestrial Biomes Copies of NB#43 Aquatic Biomes 4 DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Lesson Plans 5 Index cards Internet access Smart board Making a Bag Garden in Uganda video http://vimeo.com/7264277 Seeds, waxed paper bags, paper towels, gravel, cardboard tubes, potting soil Globe Fearon Success in Science: Basic Biology Glencoe Science Biology: the Dynamics of Life Assessment/Criteria for Success (How will you know students have gained an understanding of the concepts?) Cook E-Question: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Cook E-Question: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Research Based Instructional Strategies (check strategy that applies to the lesson) X Identifying similarities and differences X Questions, cues and advance organizers X Homework and practice Monday Do Now’s: X Reinforcing effort and providing recognition X Summarizing and note taking X Technology Tuesday Do Now’s: Impromptu: What are biogeochemical cycles? Pages 52-57 X Nonlinguistic representation X Cooperative learning Generating and testing hypotheses Wednesday Thursday X Setting objectives and providing feedback Friday Do Now’s: Do Now’s: Do Now’s: Impromptu: History of a Carbon Atom essay Impromptu: Black History: NB# 40 Copy info about Andrew Jackson Beard Impromptu: Which element is considered the building block of the molecules of life? Pages 54-55 Objective: Objective: Objective: Objective: Objective: B1.2C Develop an understanding of a scientific concept by accessing information from multiple sources. Evaluate the B1.2D Evaluate scientific explanations in a peer review process or discussion format. B1.2C Develop an understanding of a scientific concept by accessing information from multiple sources. Evaluate the B1.2C Develop an understanding of a scientific concept by accessing information from multiple sources. Evaluate the B1.2D Evaluate scientific explanations in a peer review process or discussion format. DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Lesson Plans scientific accuracy and significance of the information. B3.3b Describe environmental processes (e.g., the carbon and nitrogen cycles) and their role in processing matter crucial for sustaining life. CCSS 7 Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g., a table or chart) and translate information expressed visually or mathematically (e.g., in an equation) into words. B3.3b Describe environmental processes (e.g., the carbon and nitrogen cycles) and their role in processing matter crucial for sustaining life. CCSS 2 Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary that makes clear the relationships among the key details and ideas. scientific accuracy and significance of the information. scientific accuracy and significance of the information. B3.3b Describe environmental processes (e.g., the carbon and nitrogen cycles) and their role in processing matter crucial for sustaining life. B3.3b Describe environmental processes (e.g., the carbon and nitrogen cycles) and their role in processing matter crucial for sustaining life. CCSS 2 Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary that makes clear the relationships among the key details and ideas. CCSS 4 Determine the meaning of symbols, key terms, and other domainspecific words and phrases as they are used in a specific scientific or technical context relevant to grades 9–10 texts and topics. 6 B3.5e Recognize that and describe how the physical or chemical environment may influence the rate, extent, and nature of population dynamics within ecosystems. CCSS 7 Translate quantitative or technical information expressed in words in a text into visual form (e.g., a table or chart) and translate information expressed visually or mathematically (e.g., in an equation) into words. Materials: Materials: Materials: Materials: Materials: NB#37 Water Cycle reading and coloring pages NB#38 Carbon Cycle reading and coloring pages NB#39 Nitrogen Cycle reading and coloring pages NB#40 information about and biography of Andrew Jackson Beard NB#42 Terrestrial Biomes reading and coloring pages Index cards Copies of Worksheet#1 The Carbon Cycle Copies of Worksheet#2 The Nitrogen Cycle Index cards Index cards Internet access Smart board Making a Bag Garden in Uganda video http://vimeo.com/7264277 NB#41 Phosphorous reading and coloring pages Index cards Materials for bag gardens seed germination: Waxed paper bags Paper towels Materials for bag gardens seed germination: Waxed paper bags Paper towels Materials for bag gardens seed germination: Waxed paper bags NB#43 Aquatic Biomes reading and coloring pages DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Lesson Plans Seeds Seeds Paper towels Seeds 7 Copies of History of a Carbon Atom Procedure: Procedure: Procedure: Procedure: Procedure: Differential Learning Strategies Differential Learning Strategies Differential Learning Strategies Differential Learning Strategies Differential Learning Strategies Students will respond to Impromptu: What are biogeochemical cycles? Pages 52-57 Teacher will introduce students to the Carbon Cycle and associated vocabulary: Combustion Consumption Fossil Fuel Photosynthesis Respiration Students will respond to Impromptu: How do plants obtain nitrogen? Page 56 Black History Impromptu: NB#40 Students will copy information about Andrew Jackson Beard Students will respond to Impromptu: Which element is considered the building block of the molecules of life? Pages 54-55 Teacher will lead class discussion about biogeochemical cycles Teacher will introduce students to the Water Cycle and associated vocabulary: Students will read handout on the Water Cycle and color NB#37 The Water Cycle Teacher will introduce Ugandan bag garden project Students will watch video “Making a Bag Garden in Uganda” Students will read handout on the Carbon Cycle and color NB#38 The Carbon Cycle Teacher will distribute Worksheet#1 The Carbon Cycle Students will complete Worksheet#1 The Carbon Cycle Teacher will distribute materials to germinate seeds for Ugandan bag gardens Teacher will lead class discussion about nitrogen fixation Page 56 Teacher will introduce students to the Nitrogen Cycle and associated vocabulary: Leguminous Plant Nitrogen Fixation Students will read handout on the Nitrogen Cycle and color NB#39 The Nitrogen Cycle Teacher will distribute Worksheet#2 The Nitrogen Cycle Students will complete Worksheet#2 The Nitrogen Cycle Students will read biography of Andrew Jackson Beard Teacher will introduce students to the Phosphorus Cycle and associated vocabulary: Absorption Erosion Leaching Students will read handout on the Nitrogen Cycle and color NB#41 The Phosphorus Cycle Students will re-soak seeds in preparation for making Ugandan bag gardens Teacher will lead class discussion about the importance of carbon in forming the molecules essential to life Teacher will introduce NB#43 Terrestrial Biomes and NB#44 Aquatic Biomes Students will read handouts and include NB#42 Terrestrial Biomes and NB#43 Aquatic Biomes in their biology notebooks – Extra Credit for coloring Teacher will introduce student group Biome Project Student groups will begin DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Lesson Plans Students will soak seeds in preparation for making Ugandan bag gardens Students will re-soak seeds in preparation for making Ugandan bag gardens Teacher will distribute History of a Carbon Atom worksheet If time allows: Teacher will direct Traveling Nitrogen game (see Teaching Resources) 8 researching their assigned biomes Students will re-soak seeds in preparation for making Ugandan bag gardens Students will write fictional, creative story about the history of an atom of carbon in the palm of their hands Closure: Closure: Closure: Closure: Closure: Teacher will direct students to read pages 53-54 and make Water Cycle Flashcards: Condensation Evaporation Precipitation Transpiration Teacher will direct students to read pages 54-55 and make Carbon Cycle Flashcards: Combustion Consumption Fossil Fuel Photosynthesis Respiration Teacher will direct students to read page 56 and make Nitrogen Cycle Flashcards: Leguminous Plant Nitrogen Fixation Teacher will direct students to read pages 56-57 and make Phosphorus Cycle Flashcards: Absorption Erosion Leaching Teacher will direct students to read pages 70-83 and make Biome Flashcards Teacher will remind students to respond to Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Teacher will remind students to respond to Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Teacher will remind students to respond to new Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Teacher will remind students to respond to Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Teacher will remind students to respond to Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Assessment: Impromptu: What are Cook E-Question on Impromptu: How do plants Cook E-Question on Impromptu: Which element DETROIT INTERNATIONAL ACADEMY Lesson Plans biogeochemical cycles? Pages 52-57 www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 obtain nitrogen? Page 56 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 9 is considered the building block of the molecules of life? Pages 54-55 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Homework: Read pages 53-54 and make Water Cycle Flashcards: Condensation Evaporation Precipitation Transpiration Read pages 54-55 and make Carbon Cycle Flashcards: Combustion Consumption Fossil Fuel Photosynthesis Respiration Read page 56 and make Nitrogen Cycle Flashcards: Leguminous Plant Nitrogen Fixation Read pages 56-57 and make Phosphorus Cycle Flashcards: Absorption Erosion Leaching Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Nitrogen Cycle reading and coloring pages Carbon Cycle reading and coloring pages Worksheet#2 The Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet#1 The Carbon Cycle Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Compare biotic and abiotic factors. Page 38 Cook E-Question on www.edmodo.com: Explain why scientists study an organism’s environment. Page 5 Lesson Plans are subject to Change.