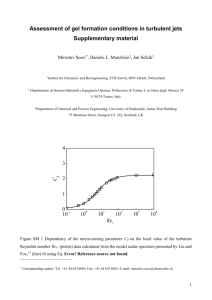
Lecture slides (MS word).
advertisement

308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Intel 8086 (1979?)
Used in IBM PC.
Early CPU of the family: 8086 (8088), 80186, 80286, 80386,
80486, Pentium, Pentium II.
Original clock rate: 4.1 Mhz.
Variable length machine codes.
Use of 6 byte prefetch queue.
1
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Registers.
Instruction pointer:
IP
Four 16 bit, general-purpose registers:
AX,BX,DX,CX
Four 16 bit, index registers:
BP,SP,SI,DI
Four 16 bit, segment registers:
CS,DS,SS,ES
SP
BP
SI
DI
- Stack pointer.
- Base pointer (frame pointer).
- Source index.
- Destination index.
CS
DS
SS
ES
- Code segment.
- Date segment.
- Stack segment.
- Extra segment.
Four general purpose registers can be accessed as eight 8 bit
registers:
AL - AX low
AH - AX low
etc.
Starting from 80386, 32 bit registers: EAX, EBX, ECX, etc.
2
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
3
Assembly language for 8086 (MS-DOS).
ADD destination,source
source,destination).
(as
opposed
to
68K’s
ADD
Many registers are used implicitly by instructions: DIV BL
computes: AX/BL and places the result into AL and AH
(reminder).
Special instructions for increment and decrement: INC, DEC.
No instruction length suffix: (movl, movw etc). Specified by the
argument instead:
MOV AL,AH
MOV AX,CX
MOV byte ptr CS:[SI],78h
Predefined set of indirect addressing modes:
[BX+offset]
[BP+offset]
[SI+offset]
[DI+offset]
[BX+SI+offset]
[BX+DI+offset]
[BP+SI+offset]
[BP+DI+offset]
(Offset is either 0, 8 bit value or 16-bit value)
(byte length)
(word length)
(byte length)
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
main()
{
int a=3;
int b=0;
if(a>1) b+=1;
}
_TEXT segment byte public ‘CODE’
assume cs:_TEXT,ds:DGROUP
_main proc near
enter
mov
xor
cmp
jle
inc
@1@86:
leave
ret
_main endp
2,0
word ptr [bp-2],3
ax,ax
word ptr [bp-2],1
short @1@86
ax
4
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
main()
{
int i=0;
int a=0;
while(i<5)
{
a+=5;
i++;
}
}
_TEXT segment byte public ‘CODE’
assume cs:_TEXT,ds:DGROUP
_main proc near
push bp
mov bp,sp
xor ax,ax
xor dx,dx
jmp short @1@86
@1@58:
inc ax
@1@86:
cmp ax,5
jl
short @1@58
pop bp
ret
_main endp
5
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
6
No CLR instruction (may use: XOR AX,AX instead).
Special PUSH, POP instructions.
Indirect address calculation uses the value of segment register.
MOV word ptr DS:[SI],5
The effective address is: (DS<<4)+SI
RET N returns also removing N bytes from the stack.
Repeat prefix: REPNZ, repeat following instruction while CX
not zero. Decrements CX at every iteration.
REPNZ STOS byte ptr [DI],al
Different indirect addressing modes use particular segment
registers by default. This may be changed by stating other
segment register:
REPNZ STOS byte ptr SS:[DI],al
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Instruction set.
---------------------------------------------------------------|Mnemonic
|ODITSZAPC|Description
|
|------------------+---------+---------------------------------|
|AAA
|?---??*?*|ASCII Adjust for Add in AX
|
|AAD
|?---**?*?|ASCII Adjust for Divide in AX
|
|AAM
|?---**?*?|ASCII Adjust for Multiply in AX |
|AAS
|?---??*?*|ASCII Adjust for Subtract in AX |
|ADC d,s
|*---*****|Add with Carry
|
|ADD d,s
|*---*****|Add
|
|AND d,s
|*---**?**|Logical AND
|
|CALL a
|---------|Call
|
|CBW
|---------|Convert Byte to Word in AX
|
|CLC
|--------0|Clear Carry
|
|CLD
|-0-------|Clear Direction
|
|CLI
|--0------|Clear Interrupt
|
|CMC
|--------*|Complement Carry
|
|CMP d,s
|*---*****|Compare
|
|CMPS
|*---*****|Compare memory at SI and DI
|
|CWD
|---------|Convert Word to Double in AX,DX |
|DAA
|?---*****|Decimal Adjust for Add in AX
|
|DAS
|?---*****|Decimal Adjust for Subtract in AX|
|DEC d
|*---****-|Decrement
|
|DIV s
|?---?????|Divide (unsigned) in AX(,DX)
|
|ESC s
|---------|Escape (to external device)
|
|HLT
|---------|Halt
|
|IDIV s
|?---?????|Divide (signed) in AX(,DX)
|
|IMUL s
|*---????*|Multiply (signed) in AX(,DX)
|
|IN d,p
|---------|Input
|
|INC d
|*---****-|Increment
|
|INT
|--00-----|Interrupt
|
|INTO
|--**-----|Interrupt on Overflow
|
|IRET
|*********|Interrupt Return
|
|JB/JNAE a
|---------|Jump on Below/Not Above or Equal |
|JBE/JNA a
|---------|Jump on Below or Equal/Not Above |
|JCXZ a
|---------|Jump on CX Zero
|
|JE/JZ a
|---------|Jump on Equal/Zero
|
|JL/JNGE a
|---------|Jump on Less/Not Greater or Equal|
|JLE/JNG a
|---------|Jump on Less or Equal/Not Greater|
|JMP a
|---------|Unconditional Jump
|
|JNB/JAE a
|---------|Jump on Not Below/Above or Equal |
|JNBE/JA a
|---------|Jump on Not Below or Equal/Above |
|JNE/JNZ a
|---------|Jump on Not Equal/Not Zero
|
|JNL/JGE a
|---------|Jump on Not Less/Greater or Equal|
|JNLE/JG a
|---------|Jump on Not Less or Equal/Greater|
|JNO a
|---------|Jump on Not Overflow
|
|JNP/JPO a
|---------|Jump on Not Parity/Parity Odd
|
|JNS a
|---------|Jump on Not Sign
|
|JO a
|---------|Jump on Overflow
|
|JP/JPE a
|---------|Jump on Parity/Parity Even
|
|JS a
|---------|Jump on Sign
|
7
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
|LAHF
|---------|Load AH with 8080 Flags
|
|LDS r,s
|---------|Load pointer to DS
|
|LEA r,s
|---------|Load EA to register
|
|LES r,s
|---------|Load pointer to ES
|
|LOCK
|---------|Bus Lock prefix
|
|LODS
|---------|Load memory at SI into AX
|
|LOOP a
|---------|Loop CX times
|
|LOOPNZ/LOOPNE a
|---------|Loop while Not Zero/Not Equal
|
|LOOPZ/LOOPE a
|---------|Loop while Zero/Equal
|
|MOV d,s
|---------|Move
|
|MOVS
|---------|Move memory at SI to DI
|
|MUL s
|*---????*|Multiply (unsigned) in AX(,DX)
|
|NEG d
|*---*****|Negate
|
|NOP
|---------|No Operation (= XCHG AX,AX)
|
|NOT d
|---------|Logical NOT
|
|OR d,s
|*---**?**|Logical inclusive OR
|
|OUT p,s
|---------|Output
|
|POP d
|---------|Pop
|
|POPF
|*********|Pop Flags
|
|PUSH s
|---------|Push
|
|PUSHF
|---------|Push Flags
|
|RCL d,c
|*-------*|Rotate through Carry Left
|
|RCR d,c
|*-------*|Rotate through Carry Right
|
|REP/REPNE/REPNZ
|---------|Repeat/Repeat Not Equal/Not Zero |
|REPE/REPZ
|---------|Repeat Equal/Zero
|
|RET (s)
|---------|Return from call
|
|ROL d,c
|-------- |Rotate Left
|
|ROR d,c
|*-------*|Rotate Right
|
|SAHF
|----*****|Store AH into 8080 Flags
|
|SAR d,c
|*---**?**|Shift Arithmetic Right
|
|SBB d,s
|*---*****|Subtract with Borrow
|
|SCAS
|*---*****|Scan memory at DI compared to AX |
|SEG r
|---------|Segment register
|
|SHL/SAL d,c
|*---**?**|Shift logical/Arithmetic Left
|
|SHR d,c
|*---**?**|Shift logical Right
|
|STC
|--------1|Set Carry
|
|STD
|-0-------|Set Direction
|
|STI
|--0------|Set Interrupt
|
|STOS
|---------|Store AX into memory at DI
|
|SUB d,s
|*---*****|Subtract
|
|TEST d,s
|*---**?**|AND function to flags
|
|WAIT
|---------|Wait
|
|XCHG r(,d)
|---------|Exchange
|
|XLAT
|---------|Translate byte to AL
|
|XOR d,s
|*---**?**|Logical Exclusive OR
|
----------------------------------------------------------------
8
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Flags.
---------------------------------------------------------------|
|-*01?
|Unaff/affected/reset/set/unknown |
| OF
|O
|Overflow Flag (Bit 11)
|
| DF
| D
|Direction Flag (Bit 10)
|
| IF
| I
|Interrupt enable Flag (Bit 9)
|
| TF
|
T
|Trap Flag (Bit 8)
|
| SF
|
S
|Sign Flag (Bit 7)
|
| ZF
|
Z
|Zero Flag (Bit 6)
|
| AF
|
A |Auxilary carry Flag (Bit 4)
|
| PF
|
P |Parity Flag (Bit 2)
|
| CF
|
C|Carry Flag (Bit 0)
|
----------------------------------------------------------------
9
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Instruction set encoding.
Firt byte:
Second byte:
opcode (6), direction(1), length(1).
mod(2), reg(3), reg/mem(3).
Consecutive bytes:
immediate operands and memory offsets.
mod:
00
01
10
11
(memory, no offset)
(memory, 8 bit offset)
(memory, 16 bit offset)
(register)
reg/mem: 000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
[BX+SI]
[BX+DI]
[BP+SI]
[BP+DI]
[SI]
[DI]
[BP] (16 bit offset when mod=00)
[BX]
reg:
AX
CX
DX
BX
SP
BP
SI
DI
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
(AL when W=0)
(CL when W=0)
(DL when W=0)
(BL when W=0)
(AH when W=0)
(CH when W=0)
(DH when W=0)
(BH when W=0)
10
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
Assembly language for 80386 (UNIX).
main()
{
int a=3;
int b=0;
if(a>1) b+=1;
}
.text
.align 4
.globl main
main:
pushl
movl
subl
movl
movl
cmpl
jle
incl
L2:
L1:
leave
ret
%ebp
%esp,%ebp
$8,%esp
$3,-4(%ebp)
$0,-8(%ebp)
$1,-4(%ebp)
L2
-8(%ebp)
11
308-273 Principles of Assembly Languages.
Overview of various CPUs.
main()
{
int i=0;
int a=0;
while(i<5)
{
a+=5;
i++;
}
}
main:
L2:
L4:
L3:
L1:
.text
.align
.globl
pushl
movl
subl
movl
movl
4
main
%ebp
%esp,%ebp
$8,%esp
$0,-4(%ebp)
$0,-8(%ebp)
cmpl
jle
jmp
.align
addl
incl
jmp
.align
$4,-4(%ebp)
L4
L3
4
$5,-8(%ebp)
-4(%ebp)
L2
4
leave
ret
12