Effect of fluid dynamics on particle size distribution in
advertisement
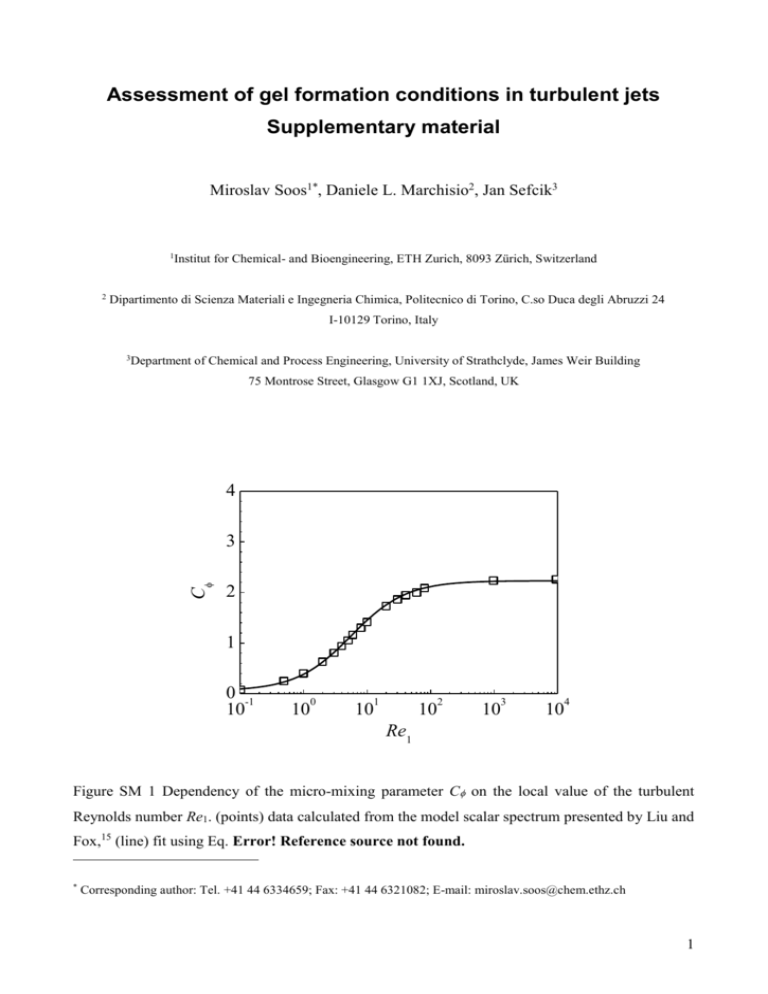
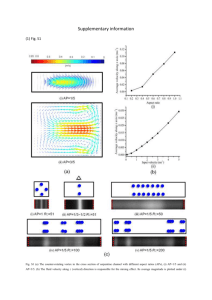
Assessment of gel formation conditions in turbulent jets Supplementary material Miroslav Soos1*, Daniele L. Marchisio2, Jan Sefcik3 1 Institut for Chemical- and Bioengineering, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zürich, Switzerland 2 Dipartimento di Scienza Materiali e Ingegneria Chimica, Politecnico di Torino, C.so Duca degli Abruzzi 24 I-10129 Torino, Italy 3 Department of Chemical and Process Engineering, University of Strathclyde, James Weir Building 75 Montrose Street, Glasgow G1 1XJ, Scotland, UK 4 C 3 2 1 0 -1 10 0 10 1 2 10 10 3 10 4 10 Re1 Figure SM 1 Dependency of the micro-mixing parameter C on the local value of the turbulent Reynolds number Re1. (points) data calculated from the model scalar spectrum presented by Liu and Fox,15 (line) fit using Eq. Error! Reference source not found. * Corresponding author: Tel. +41 44 6334659; Fax: +41 44 6321082; E-mail: miroslav.soos@chem.ethz.ch 1 4 10 3 /0 10 2 q = 2.0 10 1 10 q = 1.3 0 10 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 /m Figure SM 2 Dynamic viscosity of the fluid as a function of the reduced volume fraction 2 a b c d e Figure SM 3 Profile of probability in environment 1,2 and 3 – p1 , p2 , p3 (a - c) together with the mean mixture fraction (d) and mixture fraction variance 2 (e) inside the computational domain calculated for size of primary particles equal to 100 nm and solid volume fraction in the feed equal to 0.008 using combined Brownian and shear aggregation mechanism including micromixing model. Velocity of the colloidal dispersion in the capillary equal to 2 m/s and velocity of the coagulant solution equal to 4 m/s. 3 a b 1 1.005 1.01 c Figure SM 4 Profile of normalized mean radius of gyration g , occupied volume fraction occ and dynamic viscosity of the mixture (in mPa.s) inside the computational domain calculated for size of primary particles equal to 100 nm and solid volume fraction in the feed equal to 0.008 using combined Brownian and shear aggregation mechanism with micro-mixing model. Velocity of the colloidal dispersion in the capillary equal to 2 m/s and velocity of the coagulant solution equal to 4 m/s. 4 Tube radius / (mm) 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 0 5 10 15 1 2 3 4 5 10-5 10-3 10-1 g occ Uax (m/s) Figure SM 5 Radial profile of mean axial velocity, g and occ evaluated at various axial distances from the colloidal dispersion inlet, (short dash lined) 0 mm, (dash-double dot line) 6 mm, (dash-dot line) 15 mm, (dot line) 30 mm, (dash line) 60 mm and (solid line) 150 mm calculated for colloidal dispersion stream velocity of 2 m/s and velocity of coagulant solution stream equal to 4 m/s. Size of primary particles equal to 100 nm and solid volume fraction in the feed equal to 0.008 using combined Brownian and shear aggregation mechanism including micro-mixing model. 5