Web Content
advertisement

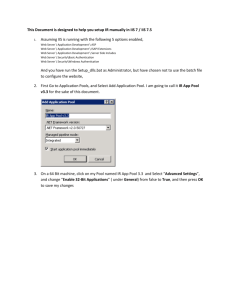
Web Content A static web page is made up of HTML code and sometimes javascript. The web page, or program is interpreted by the clients browser. The browser parses the code and displays the output on the Clients computer. (page 10-12) A web server is a program that handles requests for information on the internet. A common protocol for a web server to handle is http, hypertext transport protocol on port 80. Some common web servers are Apache, IIS and IPlanet. ASP.NET works on IIS 5.0 in Windows XP professional and Windows 2000. Dynamic content on the client is written mainly in javascript or employ specific plugins that tap into programming environments that are not HTML. Dynamic content on the server, server-side programming allows the web server to look at the page for instructions on handling the web page (web program) before sending it to the client. There are various languages and technologies for creating dynamic content on the server. These include CGI, ASP, JSP, ColdFusion, PHP and ASP.NET. Languages for creating ASP.NET include VB.NET, C#, JScript.NET. You can also write .NET applications in PErl, Python and even Cobol. We can see how content is handled in the framework by viewing the online multimedia file: http://munro.humber.ca/~dymond/cpan450/2310A_01A001.htm. The speed and efficiency of ASP.NET rivals PHP and Perl (pearl with fast cgi is still the top performer) and outperforms jsp ( jave server pages) and cold fusion applications. For administrative puprposes IIS 4+ and ASP.NET offer a very secure development environment. Team Suite also offers am excellent set of tools for collaboration and team development. Installing .NET and IIS 6.0 – 7.0 IIS is available on XP Pro, Vista Busimess, Server 2003 and 2008. Visual Studio ships with a built in testing server that should work on consumer versions of the windows OS ( Vista Home, XP standard ). It is best practice to use IIS server rather than the test server. You will find that the required NET assemblies will be installed with VStudio .NET. Test your current configuration out. Try accessing your web site by pointing your web browser to this URL -> http://localhost/ (as well you can use http://127.0.0.1 and your machine name http://j-129.humber.ca etc) If the page isn't found go to the administrative tools flyout, choose Internet Information Services: Below is a screen shot of business vista’s admin tool location. Click on the IIS Manager (not the 6.0 version) . The next console should pop up: Make sure the Start option in the upper right panel is grayed out. We will look at IIS services in depth later in the course, for now that should get us up and running. Below is a screen shot with all the available options in view. The following screen shot applies to XP pro and Server 2003 Building a test application. The following program tests your service to see if IIS is running ASP.NET. Open a new project in VStudio and select web application (on Vista start VStudio with the run as administrator option) Click on browse and select the Local IIS and highlight the Default Website item from the list. Make sure to add a name for the project: <script language="vb" runat="server"> Sub Page_Load() time.text=Hour(Now) & ":" & Minute(Now) & ":" & Second(Now) End Sub </script><html> <head><title>The Punctual Web Server</title></head> <body> <h1>Welcome</h1> In WebServerLand the time is currently: <asp:label id="time" runat="server" /> </body> </html> The test web page should appear as below when accessed through the web browser. What exactly is DOT NET? We use .NET without thinking about it often. When it was introduced it had a major impact on web development and project design. Java had been at work on EJB, yet the kind of large scale distributed development was first successful in .NET. Now project management, project design and large scale distributed computing owe a great deal to the ASP.NET model introduced years ago (2001!). Today Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) Cloud computing and Virtualization are direct descendents of the .NET web development model. .NET integrates the following technologies: COM+ component services ASP web development framework XML and object-oriented design Web Services Protocols such as SOAP, WSDL, and UDDI. Languages C# Jscript.NET VB.NET J# Development tools Visual Studio.NET provides a powerful devlopment environment. Common Language Runtime to execute objects built within this framework A comprehensive class library for building web services and web and Windows applications Specialized servers .NET Enterprise Servers SQL Server 2000, relational data storage Exchange 2000, email BizTalk 2000, B2B commerce Web services .NET My Services initiative (formerly called HailStorm). Developers can build fee for service applications based upon customer identities. Delivered via the network. Protocols SOAP- Simple Object Access Protocol, WSDL Web Services Definition Language UDDI Devices Cell Phones, PDA's, Game Boxes can all be .NET enabled While the main focus of .NET is to allow developers to create software as a service it is also a response to changes in the software development environment. Distributed computing, Componentization , Enterprise services ,Web paradigm shifts and Maturity factors all play significant roles in .NET programming. Distributed computing Simplifies the development of robust client/server applications. Current distributed technologies require high vendor-affinity and lack interoperation with the Web. Microsoft .NET provides a remoting architecture that exploits open Internet standards, including the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Extensible Markup Language (XML), and Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). Componentization Simplifies the integration of software components developed by different vendors. The Component Object Model (COM) has brought reality to software plug-and-play, but COM component development and deployment are too complex. Microsoft .NET provides a simpler way to build and deploy components. Enterprise services Allow the development of scalable enterprise applications without writing code to manage transactions, security, or pooling. Microsoft .NET continues to support enterprise services, since these services greatly reduce the development time and effort involved in building large-scale applications. Web paradigm shifts Represents changes in web technologies to simplify the development of web applications. Over the last few years, web application development has shifted from connectivity (TCP/IP), to presentation (HTML), to programmability (XML and SOAP). A key goal of Microsoft .NET is to enable software to be sold and distributed as a service. Maturity factors Represents lessons that the software industry has learned from developing large-scale enterprise and web applications. A commercial web application must support interoperability, scalability, availability, and manageability. Microsoft .NET facilitates all these goals. Although these are the main concepts that Microsoft .NET incorporates, what's more notable is that Microsoft .NET uses open Internet standards (HTTP, XML, and SOAP) at its core to transmit an object from one machine to another across the Internet. In fact, there is bidirectional mapping between XML and objects in .NET. For example, a class can be expressed as an XML Schema Definition (XSD); an object can be converted to and from an XML buffer; a method can be specified using an XML format called Web Services Description Language (WSDL); and an invocation (method call) can be expressed using an XML format called SOAP. The platform contains five main components. They are: 1. Visual Studio .NET 2 .NET enterprise servers including Application Center BizTalk Server Commerce Server Exchange Server Host Integration Server Internet Security and Acceleration Server SQL Server 2000 Sharepoint Etc. 3. .NET Framework The .NET Framework includes the Common Language Runtime (CLR) and a common framework of classes that can be used by all .NET languages for the development of business applications on the Windows platform 4 .NET Building Block services Microsoft Passport is a building-block service. It allows you to use a single username and password at all web sites that support Passport authentication.As developers, you will be creating your own building block services or adding and expanding upon existing ones. 5. Desktop operating systems.