A) Web site name
advertisement

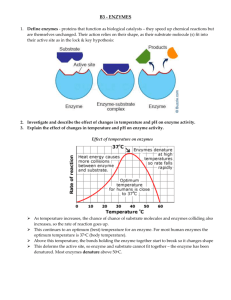
Name: _________________________ Biology 135 Enzymes Webquest Enzymes Enzymes are vital chemicals in all living things. They are proteins that speed up, and control, the chemical reactions inside the cells. If enzymes do not function properly, the cell or even the whole organism can die. This chapter will look at enzymes, and also some deficiency diseases, where people are born with a lack of a particular enzyme. A) Web site name: FCCJ Web URL: http://web.fccj.org/~dbyres/enzyme1.html Read “Mechanisms of Enzyme Action” 1). What are the two main roles of enzymes? ___________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2). What is a “substrate”? ___________________________________________ 3). In the first diagram (with sucrose), is the substrate broken apart into two products, or are two substrates joined to make a single product? _____________________________________________________________ 4). What are two ways that the barrier of activation energy can be overcome? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 5). If the temperature of an enzyme controlled reaction increased from 10oC to 30oC, the reaction rate will typically : a) double b) triple c) quadruple d) increase 9-fold 6). What happens to most enzymes above 50oC ? ________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 7). Which organisms have enzymes that can work efficiently at –2oC ? _____________________________________________________________ Name: _________________________ Biology 135 Enzymes Webquest 8). What is the optimum pH for pepsin? _______________________________ 9). What is inhibition? _____________________________________________ 10). Chemicals that are very similar to the true substrate are ________________ inhibitors. 11). Why are non-competitive inhibitors unaffected by substrate concentration? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 12). What is a “prosthetic group”? _____________________________________ 13). Why does the stomach lining not get digested by pepsin? _______________ _____________________________________________________________ 14). What type of reaction is done by Lyases? ___________________________ 15). How are the following enzymes used commercially? a) Substilin : __________________________________________________ b) Glucose oxidase : ____________________________________________ B) Web site name: Maricopa Community College Web URL: http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookEnzym.html#Enzymes Read “Enzymes: Organic Catalysts” 16). What is a “catalyst”? ____________________________________________ 17). How do catalysts lower the activation energy? ________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 18). Carbonic anhydrase causes chemicals to react ________ times faster than without the enzyme. Name: _________________________ Biology 135 Enzymes Webquest 19). What is the “induced fit hypothesis”? _______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 20). What are “thermolabile enzymes” ? ________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 21). What is the optimum pH for the enzyme Arginase? ____________________ 22). How does sulfanilamide kill bacteria? ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 23). Which of the four competitive inhibitors shown in the diagram is the most similar in structure to succinate? __________________________________ 24). What effect do the following inhibitors have ? a) nerve gas : _________________________________________________ c) Penicillin : _________________________________________________