lab bench organization - PetyaPisanScienceAQ
advertisement

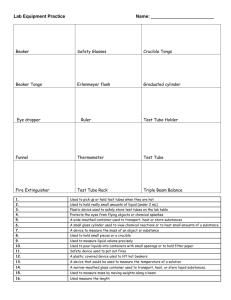
LAB BENCH ORGANIZATION TOP DRAWER Bunsen burner lighter Bunsen burner + rubber tubing crucible tongs beaker tongs 1 tweezers test tube tongs 1 clay triangle 1 ring clamp 1 test tube clamp 1 wire heating pad plastic funnel 2nd DRAWER 400 mL beakers (2) 250 mL beakers (4) 100 mL beakers (2) 50 mL beakers (2) 1 dropper + bulb glass stirring rod 3rd DRAWER 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask (1) 125 mL Erlenmeyer flask (1) 100 mL graduated cylinder (2 50 or 25 mL graduated cylinder 10 mL graduated cylinder (2) gas collection bottle SIDE CUPBOARD (right) retort stand large heating pad hotplate (only in some cupboards) TOP SIDE DRAWER (right) fume hood TOP SIDE DRAWER (left) reaction tray/water trough burette clamp meniscus reader MIDDLE SIDE DRAWER (left) 10 test tubes test tube holder (2) test tube cleaning brush BOTTOM SIDE DRAWER (left) deflagrating spoon well plates delivery tube CHEMISTRY SCAVENGER HUNT PURPOSE: to review the names and proper use of lab equipment INTRODUCTION: During this activity you will be finding a series of pieces of lab equipment and placing in on your lab bench and then showing the equipment to your instructor. You will also be answering a series of questions to demonstrate your understanding of proper use of equipment. 1) Find a test-tube tong, a beaker tong and a crucible tong. Place them on your lab bench a) Give two reasons why you wouldn’t use beaker tongs to pick up a crucible that was being heated at high temperatures. (2 marks) Ans: Beaker tongs can not withstand the heat that crucible tongs can. 2) Find a 100 mL beaker and a 100 mL graduated cylinder. a) Give one reason why you would use a 100 mL beaker instead of a graduated cylinder and one reason why you would use a 100 mL graduated cylinder instead of a beaker (2 marks) 3) Find a 250 mL beaker and a 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask. a) Give two reasons why you might choose to use an Erlenmeyer flask instead of a beaker (2 marks) i) ii) An Erlenmeyer flask is used when we perform titrations An Erlenmeyer flask is used when we want to mix chemicals together 4) What is a retort stand used for? (1 mark) To hold equipment is place such as a titration apparatus. 5) You should ALWAYS wear safety goggles when conducting and experiment, why? Where are the safety goggles located? (2 marks) 6) Where should you conduct a reaction that you know is going to produce a foul smelling gas? Why?(1 mark) In the fume hood so you could keep the smell as contained as possible. 7) Where is the dustpan and broom to sweep up broken glassware? Where do you put broken glassware? Why? (2 marks) 8) Where is the eyewash station? (1 mark) 9) Why should you always pour a chemical you will be using into a beaker before pouring it into a graduated cylinder? (1 mark) 10) Should you ever allow a chemical reaction to occur in a graduated cylinder? Why or why not? (2 marks) 11) Where should you put any waste products from an experiment? (2 marks) 12) What should you do if you spill a hazardous chemical on your hand? (2 marks)