Abdominal lecture notes
advertisement

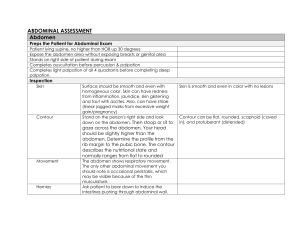
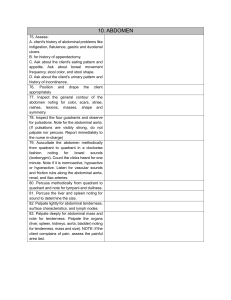
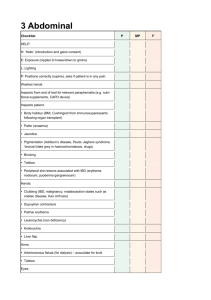
Page 1 of 5 Abdominal Assessment Infants and Children Newborns In newborn, umbilical cord shows prominently on abdomen Contains two arteries and one vein Liver takes up proportionately more space in abdomen at birth than in later life Urinary bladder located higher in abdomen than in adult During early childhood abdominal wall less muscular, so organs may be easier to palpate Pregnancy Nausea and vomiting/“morning sickness” first and second missed periods Cause unknown; may be due to hormone changes Acid indigestion/heartburn (pyrosis) /reflux Gastrointestinal motility decreases, which prolongs gastric emptying time Constipation increased venous pressure in lower pelvis may lead to ___________________ Skin changes on abdomen include striae and linea nigra Aging Adult More adipose tissue in abdomen and hips suprapubic area in females as a result of decreased estrogen levels Males prone to “spare tire” Salivation decreases, causing a dry mouth and a decreased sense of taste Gastric acid secretion decreases with aging; may cause pernicious __________ (because it interferes with vitamin B12 absorption), iron deficiency anemia, and malabsorption of calcium Incidence of gallstones increases with age, 10% to 20% of middle-aged and older adults; more common in females Drug metabolism decreases (age 60 to 80) years blood flow through liver is decreased Constipation frequently reported Abdominal Signs and Symptoms Nausea and vomiting Anorexia Dysphagia Diarrhea or constipation Abdominal Distension Abdominal pain Increased flatulence Dysuria Nocturia 1 Page 2 of 5 Dysguesia Lactose Intolerance Lactase is digestive enzyme necessary for absorption of carbohydrate lactose (milk sugar) abdominal pain, bloating, and flatulence when milk products are consumed Incidence of lactose intolerance is 70% to 90% in African Americans, American Indians, Asians, and Mediterranean groups 15% in Europeans and Americans Referred Pain Upper GI Patient may complain of “ heart pain” or “chest pain” May point to or describe substernal area Lower GI Intestinal blockage – constipation Appendicitis – radiating pain from RLQ to umbilicus Liver Upper right quadrant and right shoulder Subjective Questioning and ROS GI nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatitis, peptic ulcers, gallstones, gastroesphageal reflux, or loss of appetite GU changes in color, dysuria, hesitancy, urgency, frequency, nocturia, incontinence, polyuria, dribbling, loose of force of stream, kidney stones, flank pain, testicular and penile pain, penile discharge, enlarged prostate, emissions, and hernias. GYN pain during intercourse, vaginal drainage, odor Medical History Abdomen specific acute or chronic disease processes of the stomach, intestines, kidneys, liver, spleen, uterus, prostate, etc. Nonabdomen specific CHF (ascites), cancer (possible metastases), fibromyalgia (possible IBS), pituitary disorders (adrenal, polycystic ovaries), alcoholism (hepatitis), spinal cord damage (constipation, dysphagia), diabetes (kidney dysfunction). Surgical GI, reproductive, urinary procedures N/V,D/C due to medication sensitivities GI procedures Injuries/accidents Trauma, PID, peritonitis, ruptured appendix Family health history Cancers (stomach, pancreas, liver, kidney, colon), PUD, DM, polyps, IBS, colitis, malabsorption (celiac) Social history alcohol (malabsorption), cirrhosis, upper/lower GI bleeding 2 Page 3 of 5 Allergies Health maintenance activities Medications: Histamine: two antagonists Antibiotics Lactulose Antacids Antiemetics, Antidiarrheals Laxatives or stool softeners Pancreatic enzymes Steroids Chemotherapeutics Antiflatulents Alcohol use Drug use Travel history Work environment Stress Physical Assessment Sequence of Steps Inspection __________________ Percussion ___________________ Empty Bladder Supine Arms at side Characteristics Determined by Inspection Contour Flat Round Scaphoid Protuberant Symmetry Rectus abdominis muscles Pigmentation and color Scars _____________________ Respiratory movement Masses or nodules Visible peristalsis Pulsation Umbilicus Inspection: 7 F’s of Abdominal Distension 1. Fat 2. Fluid (______________) 3 Page 4 of 5 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Flatus Feces Fetus Fatal growth (malignancy) Fibroid tumor Auscultation Assess all four quadrants Listen for at least ____________ before concluding bowel sounds are absent Hypoactive Hyperactive Normal findings Bowel sounds are heard in all quadrants Usually sounds are high pitched Occur 5 to 30 times per minute Bell Low pitch Vascular Sounds Diaphragm Hi pitch Gastric Sounds Palpation- Normal Findings Light vs. Deep Light: ½ inch Deep: 1-3 inches Palpate all quadrants One-handed method Bimanual method Do not palpate a rigid abdomen Normal findings No tenderness Abdomen feels soft No muscle guarding No masses or organomegaly No bladder distension Aorta <3 cm, if palpated Palpation – Abnormal Findings Rigidity Tenderness on palpation Muscle guarding on expiration Presence of masses, bulges, or swelling __________________________ At a site away from tenderness, press down perpendicular to abdomen. Push down slow, lift up fast. Causes structures to rebound. Negative = no pain Peritoneal inflammation, appendicitis 4 Page 5 of 5 Documentation Example Abdomen symmetrical and rounded. Color pink with even distribution of pigmentation. No, masses, pulsations, peristalsis, retractions, or rectus abdominis muscles visible. Positive bowel sounds heard in all quadrants. No masses, muscle guarding, tenderness upon light palpation. No complaints of pain. --------------------------------------------------------------Sam Smith ADNS Chippewa Valley Technical College 5