Study Guide 1
advertisement

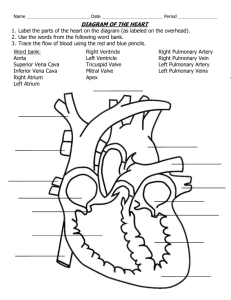
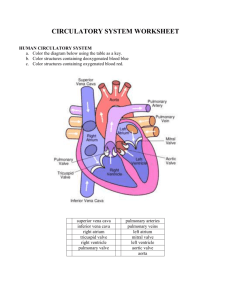
BIO 142 Study Guide for Practical l, Fall 2011 Disclaimer: This study has been edited by Dr. S. Harris and thus may differ with other professor. In addition, this is not the “end all, be all” – please refer back to lab material data sheets, powerpoints and model keys when studying for this practical. Slides: You will not be allowed to adjust the coarse focus, move the eyepieces or stage during the practical Thyroid gland o identify organ as thyroid gland (any power) o identify structure: colloid filled follicle o identify substance: colloid or thyroglobulin within follicle o identify cell:follicle cells surroundingfollicle (can be cuboidal orsquamous epithelial cells) o know that follicle cells secrete thyroglobulin o know that parafollicular cells secrete calcitonin Pituitary Gland o identify organ as pituitary gland at 4X or LOX o identify regions of organ: posterior pituitary vs. anterior pituitary o know which hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary o know which hormones are released by the posterior pituitary Pancreas o identify organ as pancreas (any power) o identify structure: pancreatic islets (endocrine tissue) o know that cells present in islets are responsible for secreting insulin (beta cells) and o glucagon (alpha cells) (you will not identify alpha from beta cells on slide) o identify exocrine tissue of organ composed of acinar cells (simple cuboidal epithelium) Blood o o o o o o smear identify platelets identify red blood cells identify white blood cells (lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils) identify which cells are categorized as granular, which are agranular know the major function of each cell (platelet, RBC, lymphocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils) Cardiac muscle cells o identify cell type as cardiac muscle cell o identify structure: intercalated discs o know the characteristics of cardiac muscle cells (striations, intercalated discs, branched structure, involuntary control) o Artery, vein or capillary o distinguish between an artery and a vein on a slide o identify the tunics (tunica intima, tunica media and tunica externa)of the vessel (from either an artery or vein) o know the major differences in structure of an artery vs. vein o identify a capillary at 40X o know that a capillary does not have the 3 layers seen in arteries & veins, it has only endothelium with a basement membrane Aorta o o o o & vena cava identify aorta and vena cava at 4X or LOX distinguish the difference between the thick walled elastic artery of the aorta compared to the thinner walled vena cava (tunica media of vena cava is smaller than aorta) certain slides are stained for elastin, be able to identify the elastin when present Thymus o identify organ as thymus at 4X or 10X o identify region: cortex (darker) vs, medulla (lighter) o identify structure: capsule o know which white blood cell population constitutes the majority of cells in this organ o know the function of the thymus Lymph node o identify organ as lymph node at 4X or 10X o identify structure: capsule o identify regions: cortex and medulla o identify structure: lymphoid follicle of lymph node (1OX or 40X) o know that follicles will be found in cortex of lymph node Spleen o identify organ as spleen at 4X or 10X o identify structure: capsule o identify structure: lymphoid follicle Tonsils o identify tissue as tonsil at 4X or 10X o identify structure: lymphoid follicle Trachea o identify o identify o identify o identify o identify layers of wall of trachea: mucosa, submucosa, adventitia cells: pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium of mucosa structures: cilia tissues: hyaline cartilage in adventitia structure: seromucous glands in submucosa Bronchiole and alveoli o identify: alveoli (individual “grapes”) o identify cell: simple squamous epithelium of alveoli Heart o o o o function identify deflection waves of a ECG know what is happening electrically during these waves (depolarization & repolarization) know the mechanical status of the atria and ventricles (systole & diastole) during these waves know what is responsible for making the 1st & 2nd heart sounds Blood o o o o o o Typing be able to interpret the results of a blood typing assay from a picture determine the blood type from the results make recommendations on potential blood donors know the difference between an antigen and an antibody know which antibodies are present in a person's serum with either type A, B, AB, O or Rh blood know which antigens are present on a person's RBCs with either type A, B, AB, O or Rh blood Wet Tissue: you will not be able to pick up or move the wet tissue during the practical Heart o identify position of heart as anterior or posterior o identify external structures: R & L atria, R & Lventricre, apex, trunk/artery, aorta, brachiocepharic L common carotid artery, L subcravian artery, auricres, purmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries' pulmonary veins, superior vena cava, anterior interventricurar artery identify internalstructures: chordae tendinae, papillary muscle, R & L atria, R & L ventricle, myocardium, interventricular septum, trabeculae carneae Aorta with kidney o identify: arch of aorta, brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, left subclavian artery descending thoracic aorta, abdominal aorta Trachea o bifurcation of trachea (carina) o main (primary) bronchi o tracheal cartilage o arytenoid cartilage Lungs o o o with trachea and heart trachea right and left lung tracheal cartilage Larynx – Review lab material data sheets Models: unless otherwise noted, you may touch or pick up models during the practical Refer to model keys for each svstem o Endocrine system o Blood o Heart o Blood Vessels o Lymphatic and lmmune systems o Respiratory system organs and structure