File
advertisement

Line
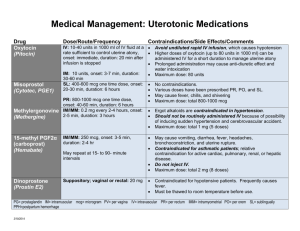
Medication
Dose/diluent underlined is the
standard concentration
CISATRACURIUM (Nimbex)
100 mg qs to 100 ml NS
(1 mg/ml)
DEXMEDETOMIDINE (Precedex)
200 mcg/50 ml NS
400 mcg/100 ml NS
(4 mcg/ml) ~$130-900/day
MIDAZOLAM (Versed)
100 mg in 100 ml NS (1 mg/ml)
Use 5 mg/ml concentrations for high
doses
$4-19/day
P
PROPOFOL (Diprivan)
1 gm in 100 ml premixed
(10 mg/ml) $8-52/day
NEURO-ICU COMMON MEDICATIONS , NYP/CU (revised 11/7/12)
SEDATIVES/ANALGESICS/NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKER
Summary
Bolus Dose
Maintenance Dose
Use lower dose in
extubated patients
MOA: Nondepolarizing
neuromuscular blocking
agent , Duration 46 – 60 min
MOA: -2 agonist, Sedative,
analgesic
t1/2 ~ 2 h
0.1 mg/kg over 15-30
sec
P
MOA: GABAergic
Sedative, anxiolytic,
anterograde amnesia
t1/2 ~ 3-11h
Sedation: 0.5-5 mg over
2 min
P
MOA: GABAergic
NMDA receptor blocker,
Sedative hypnotic agent
t1/2 ~ 1-12 h
Status Epilepticus:
Load: 1-2 mg/kg IV over
3-5 min; repeat boluses
every 3-5 minutes until
seizures stop, up to
maximum total loading
dose of 10 mg/kg.
P
Change drug/tubing every 12 hrs
FENTANYL(Sublimaze)
1 mg/100 ml NS – premix (10 mcg/ml)
2 mg/100 ml NS – premix (20 mcg/ml)
$13-64
P
MOA: Opioid analgesic
t1/2 ~ 2-6 h
Load (Optional):
0.5 mcg/kg IV over 20
min
20-100 mcg IV push
over 1-2 min
Comments
Start 1-3 mcg/kg/min - titrate by 0.5 mcg/kg/min
q 5-15 min to Train of Four goal
Soft max 5 mcg/kg/min
Start at 0.2 mcg/kg/hr - titrate 0.1 mcg/kg/hr q
15-30 min to Pain / RASS Scale or BSAS
Soft max: 1.5 mcg/kg/hr
May aggravate preexisting
neuromuscular disorders
Hoffmann-elimination
Hypertension may be seen on load
Hypotension, bradycardia
Sedation (No analgesia): Start 1 mg/hr - titrate
by 1 mg/hr q 15-10 min to goal RASS, Max: 10
mg/hr
Status Epilepticus: Load: 0.2 mg/kg IV over 2-5
min; repeat 0.2-0.4 mg/kg boluses every 5
minutes until seizures stop, up to a maximum
loading dose of 2 mg/kg.
Initial rate: 0.1 mg/kg/h. Bolus and increase rate
until seizure control
Maintenance: 0.05-2.9 mg/kg/hour
Sedation (No analgesia): 5-60 mcg/kg/min titrate by 5 mcg/kg/min q 5-10 min to goal
RASS, limit to <72 hrs of use
Accumulates in fat tissue
Active metabolite excreted renally
Rebolus every time drip rate is
increased
Hypotension
Initial rate: 33 microgram/kg/min (2 mg/kg/hr).
Bolus and increase rate until seizure control
Maintenance: 17 – 250 microgram/kg/min (1-15
mg/kg/hour). See comment column.
Start 25 mcg/hr - titrate by 25 mcg/hr q 15-30
min to goal Pain Scale
Soft max: 400 mcg/hr
SE: Hypotension, hypertriglyceridemia,
pancreatitis, Propofol Infusion
Syndrome (metabolic acidosis,
bradycardia, cardiac arrest,
rhabdomyolysis)
Monitor pH, bicarbonate, cpk and
cardiac function
Accumulates in fat tissue
Contraindications: allergy to soy, egg
Avoid doses > 80 microgram/kg/min
(5 mg/kg/hour) for > 24-48 hours
Best in renal impairment
No histamine induced hypotension
Accumulates in fat tissue
RASS
+4:
+3:
+2:
+1:
0:
Overtly combative, violent, immediate danger to staff prior to stimulation
Pulls or removes tube(s) or catheter(s); aggressive prior to stimulation
Frequent non-purposeful movement, fights ventilator prior to stimulation
Anxious but movements not aggressive, prior to stimulation
Alert and calm
AMINOCAPROIC ACID (Amicar)
5 grams/250 ml NS
ARGATROBAN
250 mg/250 ml NS (1mg/ml)
prepared by pharmacy
P
P
MOA: Inhibits activation of
plasminogen to plasmin
MOA: Direct thrombin
inhibitor
Requires Heme Approval
CONIVAPTAN (Vaprisol)
20 mg/100 ml D5W
~$473/20 mg
P
MOA: Vasopressin V1 & V2
receptor antagonist
FUROSEMIDE (Lasix)
100 mg/100 ml NS (1mg/ml)
Protect from light
P
DESMOPRESSIN (DDAVP)
P
MOA: Inhibits reabsorption
of sodium and chloride in the
ascending loop of henle,
increases excretion of water,
Na, Cl, Mg, Ca
MOA: von Willebrand factor
and factor VIII, enhances
reabsorption of water in
kidneys
MOA: Osmotic diuretic
Inhibits tubular reabsorption
of water and electrolytes and
increases urine output
Reduction of ICP
4 mcg/ml ( 1ml inj)
MANNITOL (Osmitrol)
20% IVPB (100 gm/ 500 ml, premix bag)
0.2 micron filter required during
administration
AMIODARONE (Cordorone)
450 mg/250 ml D5W in glass bottle
(1.8 mg/ml)
0.2 micron filter required during
preparation and administration
P
MOA: Atrial and ventricular
refractoriness and prolong
QTc interval, & blocker
DILTIAZEM (Cardizem)
125 mg qs to 125 ml D5W (premix), NS
(1 mg/ml)
$39-117/day
P
MOA: Calcium channel
blocker
DOBUTAMINE (Dobutrex)
500 mg/250 ml D5W (2 mg/ml) premix
250 mg/250 ml D5W (1 mg/ml) premix
C
DOPAMINE (Intropin)
400 mg/250 ml D5W (1.6 mg/ml) premix
200 mg/250 ml D5W (0.8 mg/ml) premix
May use peripheral line for
200 mg/250 ml
$5-30
EPINEPHRINE (Adrenalin)
2, 4, 8, 16 mg/250 ml NS
(8, 16, 32, 64 micrograms/ml)
C
Ino-dilator
1 1 2
2-10 + ++++ ++
>10 ++ ++++ +++
Dose 1 2 1 2
1-3
0 0 + 0
3-10 0/+ 0 ++++ 0
>10-20+++ 0 ++++ 0
C
-1: Not fully alert, but has sustained awakening (eye opening/eye contact) to voice (> 10 seconds)
-2: Briefly awakens with eye contact to voice (<10 seconds)
-3: Movement or eye opening to voice (but no eye contact)
-4: No response to voice, but movement or eye opening to physical stimulation
-5: No response to physical stimulation
MISCELLANEOUS
4 grams x 1 hr
1 gram/hr 8 hours or until until bleeding stops
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, thrombosis
Max: 30 grams/24 hours
1-2 mcg/kg/min, 0.15-0.5 mcg/kg/min for liver failure
Check PTT in 2 hrs, then q 6 hr. Dose
adjust to 1.5 x baseline PTT
titrate per MD/PA order to desired PTT by 0.25-0.5 mcg/kg/min
In clinical trials, INR ~ 3. Hold for INR
>4
No dose adjustment for renal failure
20 mg/100 ml over 30
20 mg over 24 hours (4.2 ml/hr)
Serum Na+ q 6-8 hours
min
Infuse through large vein
Hold for Na+ elevation > 12 mEq/24
hours
Observe for infusion related reactions
20-80 mg IVP over 2min
Start 1 mg/hr – titrate to UOP
Monitor electrolytes (consider standing
po potassium replacement while on
higher boluses should
Max: 1000 mg/day
be in 50 ml NS/D5W
Max rate = 4 mg/min
drip)
over 15 –20 min
40 mg furosemide = 1 mg bumetanide
= 10 mg torsemide
Uremic bleeding: 0.3 mcg/kg, dilute in 50 ml NS
Mild facial flushing and headache,
and infuse over 15-30 min
water retention and hyponatremia
Diabetes insipidus:
2-4 mcg/day in 2 divided dose SC
Cerebral edema:
Only dose if osmol gap normal (~<12)
1-1.5 g/kg/dose
Osmol gap = Measured osmolality
through 0.22
(mOsm/kg) – Calculated osmolarity
micron filter
(mOsm/L){ 1.86Na+BUN/2.8 + Glu/18}
Max rate 5 g/min
Avoid serim osmolality > 330 mOsm
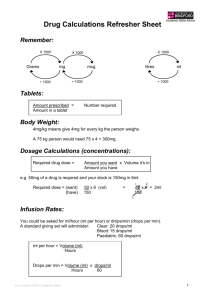
VASOACTIVE MEDICATION
Stable arrhythmia:
1 mg/min over 6 hours, then 0.5 mg/min over 18
Oral dose conversion may be lower for
150 mg/50 ml D5W over
hours Then consider conversion to PO:
afib
10 min (may repeat)
< 1 week: 800-1600 mg/day
1-3 week: 600-800 mg/day
Heart block, QT prolongation, abd pain,
Pulseless VT/VF:
> 3 weeks: 400 mg/day
hypo/hyperthyroidism, pulmonary
300 mg IVP
fibrosis
Potent inhibitor of CYP3A4
digoxin dose by half
Afib: 0.25 mg/kg over 2
5 mg/h, titrate by 5 mg/h q 5-10 min to goal BP,
Hypotension, AV block
min, repeat bolus of
soft max 20 mg/h
Infusion > 24 hours not recommended
0.35 mg/kg in 15 min if
PO conversion:
Intermediate release tablets: 30, 60, 90,
inadequate
mg/day: (rate(mg/hr) x 3 + 3) x 10
120 mg
round to nearest tablet size
NOT RECOMMENDED
Start 2.5 mcg/kg/min
Hypotension
Soft max 20 mcg/kg/min
DA
++++
++++
++++
Dose 1 2
1
2
0.8-4 ++ ++ ++++ +++
>4
++++ ++++ +++ +
NOT RECOMMENDED
Start 1 mcg/kg/min, titrate by 2.5 – 5
mcg/kg/min q 2-10 min to goal BP
Contraindications: volume deficit
AEs: Tachyarrythmias, tachycardia
Soft max 20 mcg/kg/min
25 mcg IVP
PER ATTENDING
APPROVAL
Start 1 mcg/min, titrate by 1-5 mcg/min q 2-5
min to goal BP
Soft max 32 mcg/min
Contraindications: volume deficit
The standard concentration most frequently used is underlined.
C: central line, P: peripheral line, AEs: adverse effects, px=prophylaxis, tx= treatment, Diluents underlined are the hospital standard concentrations
ESMOLOL (Brevibloc)
2.5 g/250 ml (0.01 g/ml)
2 g /100 ml (0.02 g/ml)
$294-1484
All in 0.59% NaCl premixed bag
LABETALOL (Normodyne)
400 mg/ 200 ml NS (2 mg/ml)
1000 mg/200 ml FS (5 mg/ml) $23-127
MILRINONE (Primacor)
20 mg/100 ml D5W (200 mcg/ml) premix
NICARDIPINE (Cardene)
25 mg/250 ml NS (0.1 mg/ml)
50 mg/250 ml NS (0.2 mg/ml)
100 mg/100 ml NS (1 mg/ml)
$40-286
NOREPINEPHRINE (Levophed)
4, 8, 16, 32 mg /250 ml NS
(16, 32, 64, 128 mcg/ml) $11-64
PHENYLEPHRINE (Neosynephrine)
20 mg/250 ml NS (80 mcg/ml) $5-17
40 mg/250 ml NS (160 mcg/ml)
100 mg /250 ml NS (400 mcg/ml)
VASOPRESSIN (Pitressin)
50 units in 50 ml NS (1 unit/ml)
$2.88
Summary
Line
Medication
Dose/diluent underlined is the
standard concentration
NEURO-ICU COMMON MEDICATIONS , NYP/CU
VASOACTIVE MEDICATION
Bolus Dose
Maintenance Dose
P
MOA: Cardioselective blocker (ultra short acting)
P
MOA: Non-selective blocker and selective 1blocker
MOA: phosphodiesterase
inhibitor, Ino-dilator,
P
P
P
C
C
C
MOA: calcium channel
blocker
1
+++
2
+++
1
+ ++
2
+
1
+++
500 mcg/kg IV push
over 30 seconds
may repeat prior to each
in maintenance rate
10-20 mg IV push over
2 min
50 mcg/kg/min, titrate rate by 25 mcg/kg/min
increments q 5 min, rebolus prior to each
increase, titrate to blood pressure
Soft max 300 mcg/kg/min
Start 1-2 mg/min – titate by 1 mg/min q 5 min,
Soft max 6 mg/min
50 mcg/kg over 10 min
0.125 –0.75 mcg/kg/min
Soft max 0.75 mcg/kg/min
NOT RECOMMENDED
Start at 3-5 mg/hr, titrate by 2.5 mg q 5-10 min,
Soft max 15 mg/hr
Contraindications: volume deficit
2
0
No bolus
Initiate at 10 mcg/min, titrate by 10-20 mcg/min
q 2-15 min to goal BP
Soft max 400 mcg/min
Reflex bradycardia may acompany the
pressor response
ACLS: 40 units IV push
Start at 1-2.4 unit/hr
Hard max: 6 units/hr
Contraindications: blood volume deficit
splanchnic blood flow,
hyperbilirubinemia, platelet
1
+
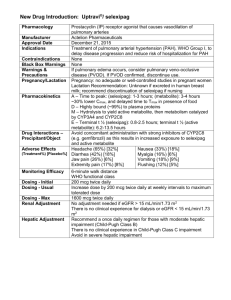
FOSPHENYTOIN (Cerebyx)
Dilute in NS 2-25 mg/mL
1 gm IV: $9
P
Conversion half-life to
phenytoin ~ 15 minutes
KETAMINE (Ketalar)
P
MOA: Block NMDA receptor
Beta t ½: 2.5 hours
Major substrate: CYP2B6,
2C9, 3A4
LORAZEPAM (Ativan)
P
MOA: GABAergic
t1/2 ~ 8-15 hrs
Status Epilepticus:
4 mg IV over 2 mins; if still seizing, repeat X 1 in 5 mins
LACOSAMIDE (Vimpat)
Dilute in 50 mL NS*
200 mg/20 mL Inj
P
MOA: Enhances slow
inactivation of sodium
channels
t1/2 13 h
Protein Binding < 15%
LEVETIRACETAM (Keppra)
500 mg inj ($16) may dilute in 100 ml NS
500, 750, 1000 mg tablet ($2, 3, 5)
100 mg/ml solution
P
MOA unknown
Protein Binding < 10%
t1/2 6-8 h
Not metabolized by CYP450
Elimination 66% unchanged,
27% hydrolysis
Dose adjustments in
dialysis: HD: 50%
removed, dose q 12 h,
add 50% of am dose to
pm dose post dialysis.
CRRT: consider ↑ in
total daily dose by 50%
Load: 2.5 g IV over 5
min (1-4 g over 15 min)
PentoBARBITAL (Nembutal)
1000 mg/250 ml NS (4 mg/ml)
2000 mg/250 ml NS (8 mg/ml)
5000 mg/100 ml NS (50 mg/ml)
1000 mg/20 mL vial: $743
Dilute up to 50 mg/mL NS
P
MOA: GABAergic
t1/2 15-50 hrs
Protein Binding 35-55%
Induces CYP 2A6, 3A4
PhenoBARBITAL (Luminal)
15, 30, 60,100 mg tab
Dilute in NS Max conc 130 mg/mL
P
PHENYTOIN (Dilantin)
Dilute in NS ONLY 1-10 mg/mL
P
300 mg IV: $2-6
1 gm IV: $4-8
ANTI-EPILEPTICS
Load: 20 mg PE/kg IV
Max IV rate 150 mg/min
Maintenance: See
phenytoin
Load: 1.5 mg/kg q 3-5
min until seizure stop,
up to max of 4.5 mg/kg
SE: Caution in patients with cardiac
disease, hypertension,elevated ICP,
Consider combining with BZ to lower
dose requirements
Targeted trough level: 25-60 mg/L.
Unclear relationship between serum
levels and efficacy. Dose guided by
clinical response.
Load: 5 mg/kg IV up to
50 mg/min; repeat 5
mg/kg boluses until
seizures stop.
Initial: 3-6 g/day divided in 3-4 divided doses
Maintenance: 2-12 g/day IV/PO in 3-4 divided
doses
Dose adjustments in dialysis: HD: 50%
removed, dose q 12 hours, add 50% of am dose
to pm dose post dialysis.
CRRT: consider ↑ in total daily dose by 50%
upon initiation in 4 divided doses
Initial rate: 1 mg/kg/hour
Maintenance: 0.5-10 mg/kg/hour traditionally
titrated to suppression-burst on EEG but titrating
to seizure suppression is reasonable as well
MOA: GABAergic
Induces CYP: 3A4, 2B6, 2C9,
2A6, 1A2
t1/2 53-140 h
Protein Binding 20-45%
Load: 20 mg/kg IV up to
60 mg/min
Maintenance:
1-3 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses
SE : Hypotension, hypoventilation,
metabolic acidosis (diluted in 40%
propylene glycol)
Targeted trough levels: 20-50 mg/dl
MOA: Block sodium channels
Protein binding 90%
t1/2 10-15 hrs (IV)
Load: 20 mg/kg IV up to
50 mg/min, 25 mg/min
in elderly, patients with
pre-existing
cardiovascular
conditions
Doses < 300 mg IV over 3-5 min (up to 60
mg/min)
Low alb, high bili, uremia
DPH levels; Fever may
DPH levels
MOA: GABAergic
t1/2 9-16 h
Protein Binding 90%
Weak Induce: CYP 2A6
Weak inhibitor: 2C9, 2C19,
2D6, 3A4
Maintenance: 5- 7 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided
doses ( with suspension)
Lower doses required in elderly
Infuse through dedicated line with 0.22 -5 µm
filter
Flush with NS following administration
Tube feeding inhibits absorption; hold feeds
for administration, flush with NS pre and post
administration, may require higher doses
Consider using injectable solution instead of
suspension results in more rapid absorption
(Pharmacotherapy 1998;18(3):6a7-45)
CYP: 2C19, 2CP substrate,
1A2, 2B6, 2C, 3A3/4, 3A5-7
inducer
Drip:
2 grams/250 mL NS
4 grams/250 mL NS
500 mg/5 mL inj
SE: Hypotension, arrhythmias
SE: may prolong PR interval
Highly variable hepatic
clearance, evidence of it’s
own enzyme induction
P
Requires continuous cardiac monitoring
See phenytoin regarding monitoring
NOTE: fosphenytoin is dosed in phenytoin
equivalents (PE)
Refractory Status Epilepticus
Initial: Sedation: start 2-7 mcg/kg/min, status
epilepticus: 20 microgram/kg/min (1.2
mg/kg/hour), Bolus and increase rate by 10-20
microgram/kg/min until seizure control
Maintenance:
5- 125 microgram/kg/min (0.3-7.5 mg/kg/hour)
Initial: 300 mg IV over 15-30 min
Maintenance: 200 – 300 mg mg IV/PO over 3060 min q 12 hours
Avoid small vein administration
VALPROATE
Dilute:
< 2500 mg in 50 mL NS
> 2500 mg in 100 mL NS
max 50 mg/mL
Contraindications: Sinus bradycardia,
heart block, cardiogenic shock, cardiac
failure
Reduce dose in renal impairment
SE: Arrhythmias, hypotension,
thrombocytopenia
Potent antihypertensive, peak effects
seem in 15-20 min. Avoid in MI (ADP)
Start 2-4 mcg/min - titrate by 1-4 mcg/min q 3-10 min to goal BP
Soft max: 32 mcg/min
MOA: Stimulate V1:vascular
smooth muscle of peripheral
vessels, gut, heart, skin; V2,
kidney
30 mg/mL (1 mL), 60 mg/mL (1 mL), 65
mg/mL (1 mL), 130 mg/mL (1 mL)
Contraindications: Sinus bradycardia,
heart block, cardiogenic shock, cardiac
failure
2
+/++
C
500 mg/250 ml NS (2 mg/ml)
500 mg/500 ml NS (1 mg/ml)
2500 mg/25 ml NS (100 mg/ml)
Comments
SE: Side Effects
Load: 40 mg/kg ~IV over
10 min; if still seizing,
additional 20 mg/kg over
~5 min (max rate 6
mg/kg/min)
Initial: 1 g IV q 6 hours
Infusion dose range: 2-12 mg/kg/hour
Meropenem significantly levels
VPA strongly inhibits lamotrigine metabolism
SE: Hypotension, gastric stasis,
myocardial suppression,
thrombocytopenia, metabolic acidosis
(diluted in 68-75% propylene glycol)
Targeted trough levels: hypnotic 1-5
mg/L, Coma 10-50 mg/mL
Requires continuous cardiac
monitoring
SE: Hypotension, arrhythmias,
metabolic acidosis (diluted in 40%
propylene glycol
Precipitation with many drugs/dilurents:
D5W, potassium, insulin, heparin,
norepinephrine, cephalosporin,
dobutamine
Targeted trough levels:
Total: 15-25 mg/L, Free: 2-3 mg/L
Obtain trough levels daily in seizing
patient, otherwise only 3-5 days
Adjusted levels:
With low alb = Total DPH level
(Alb x 0.2 ) + 0.1
Renal Failure: = Total DPH level
(Alb x 0.1 ) + 0.1
SE: tremor, thrombocytopenia,
encephalopathy, hepatic toxicity,
pancreatitis, low fibrinogen levels,
platelet dysfunction, hyperammonemic
encephalopathy
Targeted trough levels:
Total: 80-140 mg/L
Free: 4-11 mg/L (only consider if
toxicity suspected)
The standard concentration most frequently used is underlined.
C: central line, P: peripheral line, AEs: adverse effects, px=prophylaxis, tx= treatment, Diluents underlined are the hospital standard concentrations