hominid review sp10
advertisement

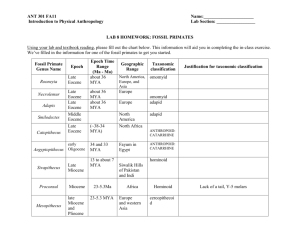
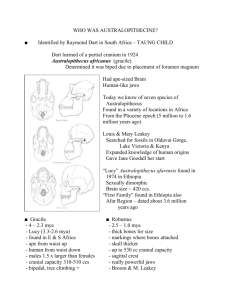
EARLY HOMINIDS Genus/Species MYA/KYA Skull shape, bones, foramen magnum Teeth Habitat / Other Middle Awash Basin – Ethiopia 5.8-4.4 mya Pneumatized1 basil cranium (P) Foramen located under skull (H) Small incisor-like canines (H2), Small molars (P), thin tooth enamel (P) Forested environments, ~90 fossil specimens-teeth & post crania Ororrin tugenensis Tugen Hills – Kenya ~6.0 mya Climbing & bipedal adaptations Ape-like teeth, thick tooth enamel (H) Woodland & savannah, 13 fossil specimens Australopithecus anamensis Kanapoi – Kenya 4.2-3.8 mya Small, ellipse-shaped ear holes (P), receding chin (P) Mixture of dry woodlands, gallery forest (along rivers), >50 fossil specimens afarensis(Lucy) Hadar – Ethiopia 4-3 mya africanus South Africa 3.0-2.2 mya Large molars Fast maturation garhi Awash Valley – Ethiopia 2.5 mya Malapa, South Africa 1.95-1.78 mya Pneumatized basil cranium (P), small endocranial volume (P) bipedal adaptation, sub-nasal prognathism3 Fewer airpockets in skull (than afarensis), short face, reduced subnasal prognathism Small brain, sub-nasal prognathism, sagittal crest, elongated femur (relative to afarensis) Small brain, ape-like arms, derived pelvis Large molars w/thick enamel (H), u-shaped dental arcade(P) V-shaped dental arcade, intermediate 3rd premolar morphology, “modest” diastema4 Ardipithecus ramidus sediba 1 Location Broad base at back of skull H=hominid (derived) trait P=pongid (ancestral) trait 3 Prognathic face 4 Gap between teeth 2 Broader canines & larger molars than afarensis & africanus Small teeth Full biped; likely descended from africanus; relationship to Homo unclear!? Genus/Species Location MYA/KYA Skull shape, bones, foramen magnum Teeth Habitat/Other Human-like skulls and teeth but retain small brains Larger brains but retain robust skulls and teeth Mixture of derived & ancestral traits Anthros divided on whether the same or not Post-crania & development similar to Australopithecines Associated with tools Originally classified as Homo Sagittal crest, flatter face, forehead & shorter snout than africanus Small brain, bipedal “hyper-robust”, larger body than robust, skull specialized for chewing “massive” chewing apparatus “massive” chewing apparatus Meat important in diet? Thick enamel, small molars “a dizzying mosaic of features” habilis East Turkana – Kenya 2.0-1.6 mya rudolfensis East Turkana – Kenya 2.0-1.6 mya West Turkana – Kenya 2.5 mya Swartkrans – S. Africa Olduvai GorgeTanzania 1.8-1.0 mya 2.2-1.3 mya West Turkana – Kenya 3.5-3.2 mya Small ear hole, small braincase, broad flat face Sahelanthopus tchadensis Toros-Menalla – Chad 7.0-6.0 mya Relatively flat face, massive brow ridge, foramen magnum under skull, small braincase 320350 cc Homo5 floresiensis Flores, Indonesia 95.0-13.0 kya Paranthropus aethiopicus robustus boisei Kenyanthropus platyops 5 Hominid Evolution - No simple progression (ie. Not goal oriented) - Many different (?) species with a variety of adaptations - The importance of (intra-specific) variation Genus/Species MYA/KYA Skull shape, bones, foramen magnum East & South Africa 1.8-1.1 mya erectus Java & China 1.8 mya-30 kya Larger braincase-800cc, supraorbital torus or browridges -“eye bar”, zygomatic arch, long skeletons, rounded skull, short face, Thicker skull, more pronounced browridges, sides of skull more sloped, more pronounced occipital torus, sagittal keel, heidelbergensis neandertalensis Africa & W. Eurasia W. Eurasia 90-130 kya 127-30 kya sapiens Global distribution 200-150 kya Eastern Eurasia Late Pleistocene – 300-50 kya Late Pleistocene – < 150 kya Homo ergaster Location Teeth Habitat/Other Associated w/ Oldowan (Mode 1) tools, first “migrant” out of Africa ~1.7 mya, combination of ancestral and derived traits Only associated with Oldowan tools, Mode 1 “archaic” Large browridge, short, muscular bodies, low foreheads, large brains1600cc, more rounded crania, big faces, Small face w/ protruding chin, rounded skull, high forehead, less robust postcranial skeleton Small back teeth & large, heavily worn front teeth High population densities, longer life spans, less evidence of disease Premodern/ ”archaic” humans Western Eurasia African hominids Late Pleistocene – Large brains case~1300cc Rounded skulls, BUT massive browridges Mix of derived & primitive features, “bulging” features, double-arched browridges, rounded basilcrania Robust features like H. heidelbergensis, large H. erectus & H. heidelbergensis H. heidelbergensis & neandertal Distinct from neandertals Tools Oldowan Tools Acheulean Tools Mode I Mode II Levallois Tools Mode III Upper Paleolithic Mode IV 300-200 kya cranial volumns (13701510cc) 2.5-1.5 mya 1.6/1.5 mya300 kya Beginning 300 kya Earliest ~45 kya in Near East Simple cores and flakes Bi-face choppers, hammers, scrapers Hand axes, cleavers, picks First appearance of stone tools Standardization of design Prepare a core with one convex surface Highly variable in time and space Make a striking platform at one end Blade tools, many distinct, standardized tool types Knock off flake by hitting the platform Earliest evidence of modern culture