Learning Objectives for Minitest #1
advertisement

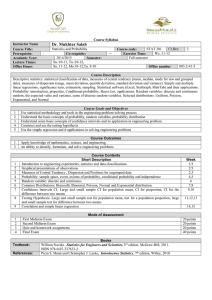
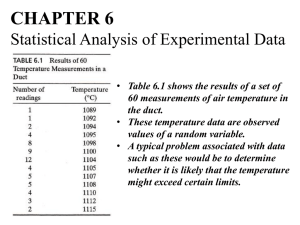
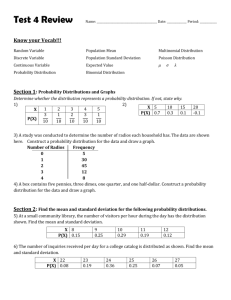
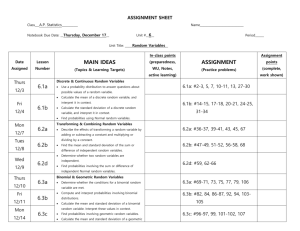
Learning Objectives for Minitest #1 Lecture 6 The student will be able to: 1. Correctly identify discrete versus continuous random variables and distributions. 2. Use the 4 characteristics( 0 P(xi) 1, mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive, and P(xi) = 1) of a discrete probability distribution to determine if a distribution is a probability distribution. 3. Calculate the mean of a given discrete probability distribution. 4. Calculate the variance and standard deviation of a given discrete probability distribution. 5. Translate verbal probability questions to symbolic probability statements for a given discrete probability distribution. 6. Find the corresponding probabilities for the probability statements. 7. Given a story problem or short description of a problem: a. Identify the story problem or description as a binomial probability problem. b. Express the problem in symbolic probability statements by hand and word-processed. c. Find the probability for a binomial problem using the binomial tables and Minitab. 8. Calculate the mean of the binomial distribution by hand. 9. Calculate the variance and standard deviation of the binomial distribution by hand. 10. Explain in his or her own words whether or not an event is likely to happen based on the calculated probability. Lecture 7 The student will be able to: 1. Given a story problem or short description of a problem: a. Identify the story problem or description as a Poisson probability problem. b. Express the problem in symbolic probability statements by hand and word-processed. c. Find the probability for a Poisson problem using the Poisson tables and Minitab. 2. Calculate the mean of the Poisson distribution by hand. 3. Calculate the variance and standard deviation of the Poisson distribution by hand. 4. Calculate the covariance for a given X and Y probability distribution. 5. Explain in your own words what a negative covariance means in terms of risk. 6. Calculate the portfolio expected return for a given X and Y probability distribution. 7. Calculate the portfolio risk for a given X and Y probability distribution. 8. Compare risk among portfolio options and choose the best from a set of options based on risk tolerance. Lecture 8 The student will be able to: 1. Find probabilities using the standard normal table in the text and using Minitab. 2. Transform a value from a normal distribution with a given mean and standard deviation into a standard normal (z) value. 3. Extract the pertinent information from a story problem to answer a probability question about a normally distributed variable with a known mean and standard deviation. 4. Write a symbolic probability statement for a probability question involving the normal distribution. 5. Calculate the value for a variable that meets a specified probability criterion given the variable follows a normal distribution with a given mean and standard deviation. Explain in your own words what changing the mean and/or the standard deviation does to the shape of the normal curve