Dr. Mukhtar Salah
advertisement

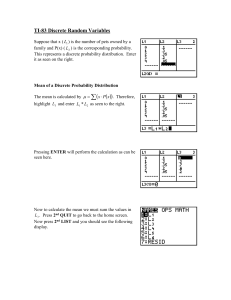
Course Syllabus Instructor Name Course Title: Prerequisite: Academic Year: Lecture Times: Office Hours Dr. Mukhtar Salah - Statistics and Probability Co-requisite: 2014/2015 Semester: Su.:10-11, Tu.:10-12, Su. 11-12, Mo.10-12,Tu. 9-10 --- STAT 201 Cr.Hrs: Course code: We.:11-12 Exercise Time: Fall semester Office number 3 003-2-41-5 Course Description Descriptive statistics: statistical classification of data, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode for raw and grouped data), measures of dispersion (range, mean deviation, quartile deviation, standard deviation and variance). Simple and multiple linear regressions, significance tests, estimation, sampling. Statistical software (Excel, StatGraph, MiniTab) and their applications. Probability: introduction, properties, Conditional probability, Bayes law, applications. Random variables: discrete and continuous random, the expected value and variance, sums of discrete random variables. Selected distributions: Uniform, Poisson, Exponential, and Normal 1 2 3 4 5 Course Goals and Objectives Use statistical methodology and tools in the engineering problem-solving process Understand the basic concepts of probability, random variables, probability distribution Understand some basic concepts of confidence intervals and its application in engineering problem Construct and use the testing hypothesis Use the simple regression and it applications in solving engineering problems 1 2 Course Outcomes Apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering. An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems. 9 Course Contents Short Description Introduction to engineering experiments, statistics and data classifications Graphical presentations of observations Measures of Central Tendency , Dispersion and Positions for ungrouped data Probability: sample space, event, axioms of probability, conditional probability and independence Random variable: discrete and continuous Common Distributions: Bernoulli, Binomial, Poisson, Normal and Exponential distribution Confidence Intervals CI: Large and small sample CI for population mean, CI for proportion, CI for the difference between two means Testing Hypothesis: Large and small sample test for population mean, test for a population proportion, large and small sample test for difference between two means Correlation and simple linear regression 1 2 3 4 First Midterm Exam Second Midterm Exam Quiz and homework assignments Final Exam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Week 1/3 2/3 2,3 4,5 6 7,8 9,10 11,12,13 14,15 Mode of Assessment Textbook: References: Books William Navida , Statistics for Engineers and Scientists, 3rd edition. McGraw-Hill, 2011. ISBN 978-0-07-337633-2 Prem S. Mann and Christopher J. Lacke, Introductory Statistics, 7th edition, Willey, 2010. 20 points 20 points 20 points 40 points