EASIER STUDY GUIDE B for Chapter 6 RETEST 2/19
advertisement

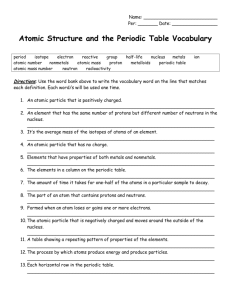
EASIER STUDY GUIDE B for Chapter 6 RETEST 2/19 The atom (from a-tomos, which means not able to be cut or divided) is the smallest particle that an element can be reduced to. ATOMIC DISCOVERIES Dalton rediscovered the idea of the atom. Dalton believed that: o Everything is made from atoms, which was proven correct. o Atoms are small particles that cannot be created, divided or destroyed, which was proven false. Dalton’s theory was changed in 1897 when Thompson discovered the negatively charged electron (like plums in the Plum Pudding model) Rutherford discovered at the center of the atom the positively charged nucleus which is very small and dense, and that most of an atom is empty space. Bohr discovered the energy levels where he thought the electrons moved in definite paths like the orbits of planets in the solar system. Schrödinger discovered electron clouds, a more accurate idea of energy level areas around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found. ATOMS A dime has more atoms than Earth has people. Every atom of a given element has the same number of protons. The number of protons in an atom, called the atomic number, is found at the top of each small square of the periodic table. The mass number (the bottom number in a square of the periodic table) is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom of that element. Electrons are not counted in the mass number because they have the least mass (very tiny) compared to protons and neutrons ISOTOPES Isotopes, like brothers and sisters of the same element have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons, and therefore, different mass numbers. For example, there are three isotopes of hydrogen, all of which have one proton. In addition to the one proton, o Hydrogen-1, the most common form of hydrogen has no neutrons. o The hydrogen-2 isotope, called deuterium has one neutron. o The hydrogen-3 isotope has two neutrons. Radioactive isotopes are unstable and produce energy as they change. EASIER STUDY GUIDE B for Chapter 7 RETEST 2/19 Chapter 7 ReTest 2-19 EASIER STUDY GUIDE Periodic is a word used to describe something that happens over and over at regular intervals. The Periodic Law says that properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements. All of the recently discovered elements follow the periodic law The Periodic Table of the Elements is arranged Horizontally from left to right in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons). o o Each horizontal row is a “period”. Originally, Mendeleev grouped the elements in order of increasing atomic mass instead of atomic number Vertically in Groups or Families of elements with: o Similar chemical and physical properties o Same number of valence electrons. Similar types of elements are in particular places on the periodic table: Elements left of the zigzag line are metals. o Metals are shiny (luster) o Electrically and thermally(heat) conductive o Malleable (can be bent) and Ductile (can be made into wire) o Most of the elements on the periodic table are metals. The Elements to the right of the zigzag line are nonmetals o o o o They are easily shattered. many are gases at room temperature, including the noble gases. They are dull. They are not conductors of electric current or heat. Elements next to the zigzag line are semimetals or metalloids o They are semi-conductors, like silicon, important for making computer chips. LOOK UP THE PROPERTIES IN THE BOOK FOR THE OTHER GROUPS AND KNOW THEM. For example: The alkali metals are o so soft that they can be cut with a knife o react violently with water. o very reactive. When halogens (group 17) non metals react with a metal, a salt is the new compound that is formed through ionic bonds. CHEMICAL SYMBOL The chemical symbol is the abbreviation in larger letters in each square of the periodic table. usually a single capital letter, sometimes with another lower case letter Oftentimes on periodic tables, the color of the chemical symbol will tell you what the physical state of an element is at room temperature --Know how to find out which element has a given number of protons (look for the atomic number, and that is the element) --Know where to find the metalloids. --Nothing can burn unless it has oxygen, which makes up about 20% of the air we breathe. --Carbon comes in many forms, such as diamonds, buckyballs, soot, graphite (pencil “lead”) and others. --Sulfur is widely used in the chemical industry…can you tell why? Family Name Group Number Alkali Metals 1 Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals 2 3-12 Boron Group 13 Carbon Group 14 Nitrogen Group 15 Oxygen Group 16 Halogens 17 Noble (inert) Gases Hydrogen 18 Not in a group Calculate Valence Electrons Same as group number Same as group number varies Group number minus 10 Group number minus 10 Group number minus 10 Group number minus 10 Group number minus 10 Group number minus 10 # Valence Electrons 1 2 varies 3 4 5 6 7 8 1