Unit 2 Test Retake Review Sheet – Cell Biology Answer questions
advertisement

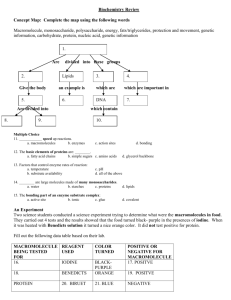
Unit 2 Test Retake Review Sheet – Cell Biology Answer questions on separate sheet of paper & define vocab before coming to retake the test Content Standard:2.0 Cell Biology—Knowledge of the structure and function of macromolecules is necessary for an understanding of the biochemistry of cells. Objective: 2.1 Compare and contrast the 4 major classes of organic macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids—in terms of their structure, function, importance, and synthesis (CS 1h) Objective: 2.2 Explain how proteins which differ in their amino acid number and sequence differ in shape, function, and chemical properties. Objective: 2.3 Identify and describe the structure and function of enzymes, and how their environment—including pH, temperature, and ionic conditions—alter their efficacy (CS 1b) Knowledge and Skills Covered: (Answer in space below and on back or on separate sheet of paper) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. Why are macromolecules important components of living things? Macromolecules are polymers composed of repeating sub-units called ___________. Identify the basic monomer for each type of macromolecule. Describe the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Distinguish the functions and importance of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Look up and draw the monomer structure for each type of macromolecule (nucleotide, etc). What do enzymes do to the activation energy required for a chemical reaction? Explain how enzymes are specific to a substrate. Explain that the key to enzyme function is in its shape. How do we have many different enzymes? Infer how an enzyme’s effectiveness would change in an altered environment (temperature, pH, ionic conditions). What conditions do enzymes like best? Identify the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Give an example. Chemical reactions neither create nor destroy atoms. What happens to the atoms? As polymers are broken down into their monomer subunits, _______ molecules are released. Chemical reactions either absorb or ___________ energy. What are the three different types of energy that a chemical reaction can release? Be able to analyze a graph by first looking at title, x axis, and y axis. Redraw the “analyzing data” graph and discuss what happened when a base or acid was added. Which two elements must be found in organic molecules? All enzymes are catalysts but not all catalysts are _________________. Explain the lock and key model and relate it to enzymes and substrates. Explain why specific enzymes only catalyze (speed up) specific reactions. Which macromolecule has peptide bonds? (Look on concept map) How are proteins different from one another? Can enzymes be used up? True or False: All proteins are made of amino acids even if their shape is different. Draw an enzyme’s role in a chemical reaction. Label the enzyme, substrate, active site, and products. Which macromolecule do we associate with ENERGY? Cellulose is an example of which macromolecule? Key Vocabulary: (write a short definition on this paper, next to the term) Activation Energy Active Site – Amino Acid Carbohydrate Catalyst Chemical Reaction Enzyme Lipid Monomer Monosaccharide Nucleic Acid Nucleotide Organic Chemistry Polymer Product Protein Reactant Substrate Spontaneous vs. non spontaneous reactions pH