Arabia section one
advertisement

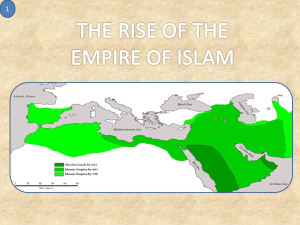
Name _______________________ Social Studies—Period _________ Date ___________________ Teacher ________________ Reader’s Guide Chapter Eleven: Islamic Civilization The Rise of Islam (Pages 372-378) Geographical Information Arabia is a huge peninsula in southwestern Asia. It lies south of the Fertile Crescent and east of Egypt. Today the region of Arabia contains several nations, including Yemen, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia. While some of Arabia is desert, the coastal areas receive enough rain to support agriculture. Towns and trade developed in fertile regions, at desert edges, and oases. Trade linked ancient Arabia with Egypt and Fertile Crescent. Overview Islam developed in the Arabian region. Islam means, “submit to the will of God/Allah” in Arabic, the Arab language. Followers of Islam are called Muslims. The story and teachings of Islam have been written down in the Quran, the most important book of Islam. Its words are sacred to more than 1 billion Muslims in the world today. Directions: Define the following vocabulary terms, people, and places in your vocabulary notebook. Vocabulary/People/Places Definitions 1. oases Green areas in a desert fed by underground water 2. sheikh Leader of an Arab tribe 3. caravan A group of traveling merchants and animals 4. Quran Holy book of Islam 5. Bedouins Desert herders who traveled from oasis to oasis for water and to graze their camels, goats, and sheep 6. Muhammad Founder of Islam whose words are recorded in the Quran. 7. Makkah Also known as Mecca, became the largest and richest trading area. It was a crossroads for merchants and it was an important religious site. The holiest place in Arabia was in this city. 8. Kaaba Mecca’s temple-A low square building surrounded by statues of gods and goddesses. Arabs believe the great stone inside the Kaaba was from heaven. 9. Madinah/Medina “The city of the prophet”- Yathrib welcomed Muhammad and his followers and renamed the city Madinah 10.The Five Pillars Five basic duties of all Muslims- purpose was to strengthen Muslims’ ties to Allah and to other people. 11. Allah Arabic word for God 12. Islam Means “submit to the will of God” in Arabic. 13. Muslim Followers of Islam 14. Pilgrimage A journey for religious purposes 15. hijra Arabic for “migration”- Muhammad’s hijra marked the turning point in Islamic history. The year of the hijra, 622, marks the starting point of the Islamic calendar. What Did You Learn? 1. What are oases, and why were they important to Arabs? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. Why is the Quran important and name some of the activities that it prohibits. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. Why do you think Muhammad’s teachings were popular with poorer people? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. How did Muhammad link religion and government? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. Complete the Venn diagram to compare and contrast Islam, Judaism, and Christianity. Islam Judaism All Three Christianity 6. Use the chart below to answer the questions that follow. The Five Pillars of Islam Belief Muslims must declare that there is no god but Allah and that Muhammad is his prophet. Prayer Muslims must pray five times per day facing toward the holy city of Makkah/Mecca. Charity Muslims must give to the poor. Fasting Muslims must not eat from dawn to dusk during the holy month of Ramadan. Pilgrimage Muslims must visit Makkah/Mecca once in their life. a) How many times should Muslims pray per day?_________________________________ b) What city must Muslims face while praying?___________________________________ c) How are The Five Pillars similar to the Ten Commandments?______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ d) When do Muslims fast?____________________________________________________ e) Are Muslims polytheistic or monotheistic? Explain.______________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Main Ideas: The deserts, coastline, and oases of Arabia helped shape the Arab way of life. The prophet Muhammad brought the message of Islam to the people of Arabia. The Quran provided guidelines for Muslims’ lives and the governments of Muslim states.