Are You suprised ?
advertisement
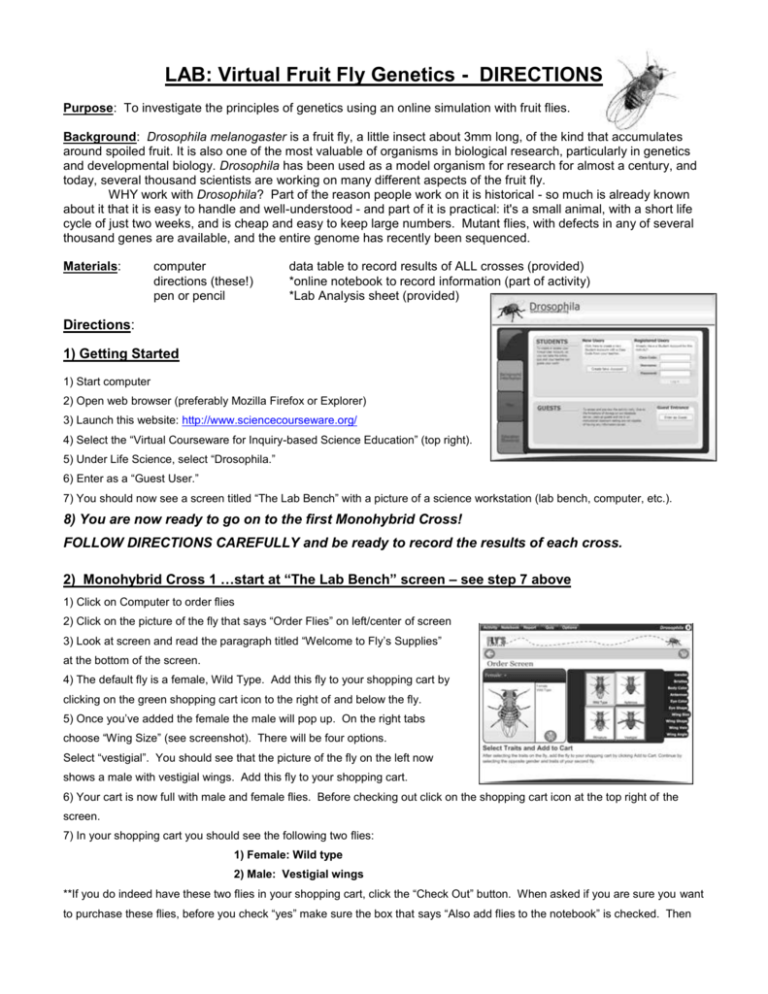
LAB: Virtual Fruit Fly Genetics - DIRECTIONS Purpose: To investigate the principles of genetics using an online simulation with fruit flies. Background: Drosophila melanogaster is a fruit fly, a little insect about 3mm long, of the kind that accumulates around spoiled fruit. It is also one of the most valuable of organisms in biological research, particularly in genetics and developmental biology. Drosophila has been used as a model organism for research for almost a century, and today, several thousand scientists are working on many different aspects of the fruit fly. WHY work with Drosophila? Part of the reason people work on it is historical - so much is already known about it that it is easy to handle and well-understood - and part of it is practical: it's a small animal, with a short life cycle of just two weeks, and is cheap and easy to keep large numbers. Mutant flies, with defects in any of several thousand genes are available, and the entire genome has recently been sequenced. Materials: computer directions (these!) pen or pencil data table to record results of ALL crosses (provided) *online notebook to record information (part of activity) *Lab Analysis sheet (provided) Directions: 1) Getting Started 1) Start computer 2) Open web browser (preferably Mozilla Firefox or Explorer) 3) Launch this website: http://www.sciencecourseware.org/ 4) Select the “Virtual Courseware for Inquiry-based Science Education” (top right). 5) Under Life Science, select “Drosophila.” 6) Enter as a “Guest User.” 7) You should now see a screen titled “The Lab Bench” with a picture of a science workstation (lab bench, computer, etc.). 8) You are now ready to go on to the first Monohybrid Cross! FOLLOW DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY and be ready to record the results of each cross. 2) Monohybrid Cross 1 …start at “The Lab Bench” screen – see step 7 above 1) Click on Computer to order flies 2) Click on the picture of the fly that says “Order Flies” on left/center of screen 3) Look at screen and read the paragraph titled “Welcome to Fly’s Supplies” at the bottom of the screen. 4) The default fly is a female, Wild Type. Add this fly to your shopping cart by clicking on the green shopping cart icon to the right of and below the fly. 5) Once you’ve added the female the male will pop up. On the right tabs choose “Wing Size” (see screenshot). There will be four options. Select “vestigial”. You should see that the picture of the fly on the left now shows a male with vestigial wings. Add this fly to your shopping cart. 6) Your cart is now full with male and female flies. Before checking out click on the shopping cart icon at the top right of the screen. 7) In your shopping cart you should see the following two flies: 1) Female: Wild type 2) Male: Vestigial wings **If you do indeed have these two flies in your shopping cart, click the “Check Out” button. When asked if you are sure you want to purchase these flies, before you check “yes” make sure the box that says “Also add flies to the notebook” is checked. Then complete the purchase by checking “yes.” 8) Back at your lab station, click on the box to unpack the flies you ordered. This will open your box and add both male and female flies to your mating jar. Extra male and female flies will be placed into flasks and stored in the incubator in case you need them for future crosses. 9) Follow the prompt to click on the mating jar to place it in the incubator. Your flies will mate and lay eggs. The eggs will hatch and eventually become adults, the F1 generation. 10) Follow the prompts to remove your mating jar from the incubator, anesthetize the flies and place them under the microscope for viewing. Once they are under the ‘scope, click on “Sort Flies” to separate the flies by both sex and phenotype. 11) Move the cursor over each of the piles to see the sex and phenotype. Click on a pile to view it close up. 12) While viewing under close up you will be able to select two additional options: 1) Add to notebook. 2) Use in new mating. For each pile do both of these things. On the top right of the page next to the male and female symbols and the count for each you should see a small jar icon (added to new mating jar) and a red square icon (added to notebook). (see the icons in the diagram below, to the left of the ‘male’ symbol).1 (“Zoom out” in order to switch piles) 13) Record all F1 offspring data in your paper data table & fill in the correct genotypes. 14) Before you perform a cross of the F1 generation please go to your “notebook” to make sure that everything has been added. (To see your lab notebook click on the “Notebook” tab on the top left of the screen). REMEMBER TO SAVE THE NOTEBOOK when you are done!!! To return to the activity click on the “Activity” tab in the upper left section. 15) Do the “Checkpoint” and “Check for Understanding” questions for Monohybrid Cross 1. (on lab analysis sheet provided) 16) Now that you have added both male and female flies from this F1 generation to the new mating jar return to the lab to perform the next cross. (click the “Return to Lab” button) 17) Click on the new mating jar on the lab bench and follow the prompt to put in the incubator. Again, your flies will mate and lay eggs. The eggs will hatch and eventually become adults of the F2 generation. 18) Follow the prompts to remove your mating jar from the incubator, anesthetize the flies and place them under the microscope for viewing. Make sure that you have chosen the correct mating jar, the SECOND cross, not the first. Once they are under the ‘scope, again click on ‘“Sort Flies” to separate the flies by both sex and phenotype. 19) Click on each pile to investigate the sex and phenotype. As you view each group make sure to “Add to Notebook” so you can save your data. Also record these F2 results on your paper data sheet in the appropriate section. 20) Once you have added all of the data to your paper data table as well as your computer lab notebook (and SAVED your notebook data!), return to the lab. (go back to “Activity” and click the “Return to Lab” button) 21) Answer the last question on your student handout. 22) Before proceeding to your next cross, clean up your “lab station” by clicking on the TRASH CAN and follow prompts to perform the clean up – this will clean out the flies from the previous cross and reset your computer. Continue on to the next cross! 2) Dihybrid Cross 1 (2 Gene Cross) 1) Back at the lab station, click on Computer to order flies. 2) Click “Order Flies” on left/center of screen. 3) The default fly is a female, Wild Type. Add this fly to your shopping cart 4) Once you’ve added the female the male will pop up. This cross is a DIHYBRID CROSS, meaning we are looking at two traits at once. To do this you will need to select two separate traits to compare with the wild type found on the female you’ve already added to your shopping cart. 5) On the right tabs choose “Wing Size”. There will be four options. Select “vestigial”. You should see that the picture of the fly on the left now shows a male with vestigial wings. 6) To select the second trait click on the tab labeled “Eye Color”. There will be five options shown, one of which is “sepia”. Select sepia eyes. You should now see that the fly on the left is a male with vestigial wings and sepia eyes. Add this fly to your shopping cart. 7) Your cart is now full with male and female flies. Before checking out click on the shopping cart icon at the top right of the screen. 8) In your shopping cart you should see the following two flies: 1) Female: Wild type 2) Male: Vestigial wings & Sepia eyes **If you do indeed have these two flies in your shopping cart, click the “Check Out” button. 9) Back at your lab station, click on the box to unpack the flies you ordered. This will open your box and add both male and female flies to your mating jar. 10) Follow the prompt to click on the mating jar to place it in the incubator. Your flies will mate and lay eggs. The eggs will hatch and eventually become adults, the F1 generation. 11) Follow the prompts to remove your mating jar from the incubator, anesthetize the flies and place them under the microscope for viewing. Once they are under the ‘scope, click on “Sort Flies” to separate the flies by both sex and phenotype. 12) Move the cursor over each of the piles to see the sex and phenotype. Click on a pile to view it close up. 13) While viewing under close up you will be able to select two additional options: 1) Add to notebook. 2) Use in new mating. 3) For each pile, write down your data on your student handout sheet & be sure to click on “Use in new mating.” On the top right of the page next to the male and female symbols and the count for each you should see a small jar icon (added to new mating jar) and a red square icon (added to notebook). 14) RECORD F1 results in your paper data sheet as well and answer the one follow up question. 15) Now that you have added both male and female flies from this F1 generation to the new mating jar return to the lab to perform the next cross. 16) Click on the new mating jar on the lab bench and follow the prompt to put in the incubator. Again, your flies will mate and lay eggs. The eggs will hatch and eventually become adults of the F2 generation. 17) Follow the prompts to remove your mating jar from the incubator, anesthetize the flies and place them under the microscope for viewing. Make sure that you have chosen the correct mating jar! Once they are under the ‘scope, again click on “Sort Flies” to separate the flies by both sex and phenotype. 18) You will have many more piles this time. The computer separates out male and female for you, even if they have the same phenotype. Click on each pile to investigate the sex and phenotype. Record all data in your paper data sheet. 19) Be sure to fill in the genotype & then calculate the ratio of phenotypes. The number of offspring with vestigial wing shape & sepia colored eyes should be “1” in the ratio. 20) What ratio did Mendel determine results from a cross between 2 heterozygote parents? This is the “rounded ratio” at the bottom of the table. LAB: Virtual Fruit Fly Genetics – ANALYSIS SHEET Name ______________________________ MONOHYBRID CROSS #1: Record the appropriate information in the data table provided. Monohybrid Parent Sex/ Parent Sex of Phenotype of # with Cross #1 Phenotype Genotype Offspring Offspring Phenotype Parent Genotype CHECKPOINT / “Check for Understanding”: 1) What does the notation “+” mean? 2) What does the notation “VG” mean? 3) For this first cross, what was the “wild-type” phenotype? 4) For this first cross, what was the “vestigial” phenotype? 5) Identify the dominant trait and the recessive trait. Explain how you figured this out. DOMINANT TRAIT: RECESSIVE TRAIT: > How do you know? > What percent of offspring have the wild type phenotype? _______ vestigial phenotype? ___________ The offspring from the Parent cross (P) above will be the new parents for the F 1 cross. Fill in the parent information for the F1 cross in the table below. Monohybrid Parent Sex/ Parent Phenotype of # with Genotype (if more than 1 possibility, Cross #1 Phenotype Genotype Offspring Phenotype separate by a “/” F1 6) What is the ratio of wild type : vestigial flies? Raw Data numbers (take from table above): ______________________ Reduced ratio: _______________ 2-Gene Cross #1 Parent Sex/ Phenotype Parent Genotype (both genes) Sex & Phenotype of Offspring # with Phenotype Offspring Genotype Gene#1: Gene#2: WING EYE COLOR Parent Allele option for all gametes produced through Meiosis from these parents that led to the F 1 offspring: FEMALE: ____________________ MALE: ____________________ Results of F1 cross (F2 offspring): Sex of # offspring with all offspring wild phenotype # offspring with wild wing shape & sepia eyes # offspring with vestigial wing shape & wild eyes Females Males TOTAL with PHENOTYPE GENOTYPE Calculated Ratio Rounded Ratio : : : : : : # offspring with vestigial wing shape & sepia colored eyes