Learning About the Skeletal System
advertisement
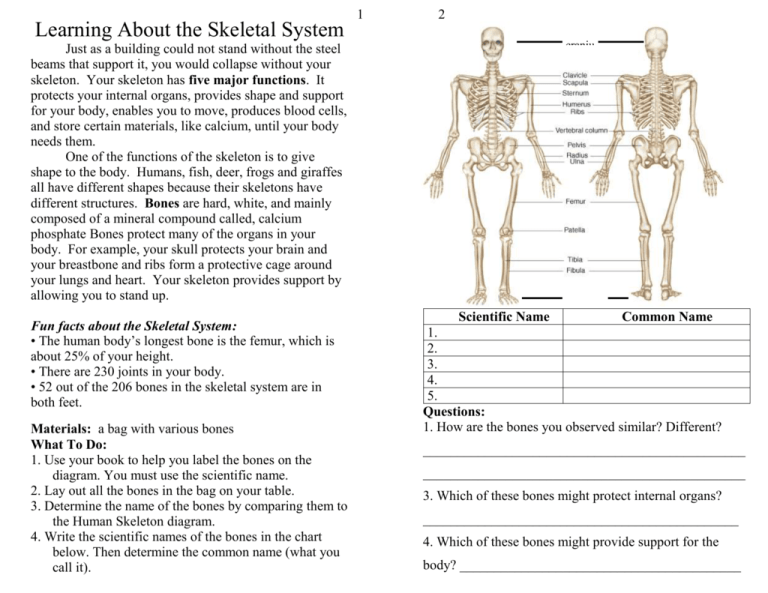
1 2 Learning About the Skeletal System craniu m Just as a building could not stand without the steel beams that support it, you would collapse without your skeleton. Your skeleton has five major functions. It protects your internal organs, provides shape and support for your body, enables you to move, produces blood cells, and store certain materials, like calcium, until your body needs them. One of the functions of the skeleton is to give shape to the body. Humans, fish, deer, frogs and giraffes all have different shapes because their skeletons have different structures. Bones are hard, white, and mainly composed of a mineral compound called, calcium phosphate Bones protect many of the organs in your body. For example, your skull protects your brain and your breastbone and ribs form a protective cage around your lungs and heart. Your skeleton provides support by allowing you to stand up. Fun facts about the Skeletal System: • The human body’s longest bone is the femur, which is about 25% of your height. • There are 230 joints in your body. • 52 out of the 206 bones in the skeletal system are in both feet. Materials: a bag with various bones What To Do: 1. Use your book to help you label the bones on the diagram. You must use the scientific name. 2. Lay out all the bones in the bag on your table. 3. Determine the name of the bones by comparing them to the Human Skeleton diagram. 4. Write the scientific names of the bones in the chart below. Then determine the common name (what you call it). Scientific Name Common Name 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Questions: 1. How are the bones you observed similar? Different? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ 3. Which of these bones might protect internal organs? ______________________________________________ 4. Which of these bones might provide support for the body? _________________________________________ 3 How Your Body Bends Bones move and allow you to bend only at joints. The soft connective tissue between joints is called cartilage. Ligaments attach bones to each other so that they can move and tendons connect muscles to bones. There are three main kinds of joints in the body. They are fixed joints, partly moveable joints and moveable joints. Fixed joints do not allow any movement. The joints of your skull are not moveable after you are born. Partly moveable joints, like the ones in your ribs allow a little movement. Most of the joints of your body are moveable joints. There are four kinds of moveable joints. Look at the pictures below. 4 The Integumentary System The integument is another name for skin. It is the body’s largest organ. The system includes the skin, hair, nails and some glands. There are several functions of the integumentary system. The first, and most important, is to act as a physical barrier to invaders such as bacteria and viruses. It also helps to regulate our temperature and keeps us cool by using the sweat glands and uses UV sunlight to make vitamin D. It also contains the nerves – called receptors - that allow us to gather information from the environment like feeling pain, touch, hot and cold. In addition, it eliminates waste through our sweat glands. Fun facts about the Integumentary System: • You lose about 30,000 to 40,000 dead skin cells every minute. • The skin is the largest organ in the human body. Watch the video segment and circle where each kind of joint can be found. Ball and socket Hip Finger Shoulder Hinge Hip Knee Finger Color the section of skin above the following colors: Pivot Arm Neck Hip Gliding Spine Wrist Toe Pores – purple Epidermis –pink Dermis – yellow Sweat gland – blue Hair shaft – brown Hair follicle –green Receptors (nerves) – red Fat cells, Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) - orange Those Crazy Bones Lab 5 Complete the procedure listed in your student guide and answer the questions below. 2. Describe the function of the skin: _________________ ______________________________________________ 3. Describe the muscle of the chicken leg: ____________ ______________________________________________ 5. What do the tendons look like and what is their function? ______________________________________ ______________________________________________ Human Leg 4. What is the function of the muscle in the chicken’s leg? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 10. Draw and label two diagrams comparing the legs of a chicken and a human. Chicken Leg 1. Describe the texture of the skin: __________________ ______________________________________________ 6 Those Crazy Bones Lab, continued 6. Describe the chicken’s bones. What do bones do? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 7. Describe the hinge joint. What is this joint’s function? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 8. Describe the bone marrow. What does the bone marrow do? __________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 9. In what ways is the chicken’s leg similar to a human’s leg? __________________________________________ ______________________________________________ 11. What are the 5 main functions of the skeletal system? _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________ Love the Skin You’re in Lab 7 Use the paperclip and instructions in your Student Guide to complete the following. Body Part Index finger Bottom of wrist Upper arm Upper lip Cheek Nose Back Calf Top of foot Bottom of foot Paper clip gap (mm) 8 Name ___________________ period _____ date______ EXIT TICKET- Skeletal/Integumentary Systems 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of the skeletal system? A. Support your body B. Give shape to your body C. Bring oxygen to your body D. Protect your body 2. Where are you able to bend your skeleton? A. In the middle of the bones B. At the joints C. Anywhere you want Most sensitive areas tested 3. Where in your body would you find a ball and socket joint? Least sensitive areas tested A. Skull B. Hip C. Ribs D. Fingers 4. Which of the following in NOT a part of the integumentary system: What are the main functions of the skin? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________ A. heart B. hair C. nails D. glands 5. What is the most important function of the integumentary system? __________________________________________