Light_bulb_lesson - The SOLIDWORKS Blog

SolidWorks Lesson Template for Teachers to Contribute
Faculty Member Name: Mr. Don Drozynski Date: 8/15/2006 School District: Shenango High School, New Castle, Pennsylvania Teacher’s School Email Address: d_drozynski@shenango.k12.pa.us
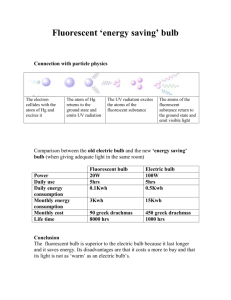
Title of Lesson/Unit: Energy Systems – Light Bulb (Science, Technology, Engineering and Math) STEM Concepts Addressed: Energy conversion. Three requirements for fire; fuel, oxygen, and heat. The atomic model and release of a photon. Using ohms law to calculate watts. Parts of an incandescent light bulb. Thomas Edison’s contribution to development of the incandescent bulb. Types of light producing technologies. Computer modeling, rendering, and assembling of a light bulb. Construction of a light bulb including cutting, bending, and assembling a working light bulb. Length of Instruction: 6 Periods of 42 Minutes Grade Level: 9 – 10 D:\106751663.doc Page 1 of 24
Objectives: The student will be able to describe the interrelationships among inputs, processes, outputs, feedback and control in specific systems. The student will be able to explain the conversion of one form of energy to another by applying knowledge of each form of energy. The student will be able to describe safe procedures for using tools and materials. The student will be able to describe and use appropriate instruments to gather and analyze data. The student will be able to apply accurate measurement knowledge to solve everyday problems. The student will be able to apply software designed to meet specific needs. The student will be able to analyze the human need that prompted its invention and the social impacts of the specific invention. The student will be able to apply ohms law to calculate the wattage of their light bulb. The student will be able to use a multi-meter to measure the current and voltage of their light bulb The student will be able to demonstrate the ability to produce measures with specified levels of precision. Materials:
The Design of the Light Bulb:
SolidWorks Workstation The Construction of the Light Bulb: (cost less than $1) Clear Glass Vial with Cork (SpecialtyBottle.Com Part No. VC5C) 6 ” of 18 Gage (.0403) Copper Wire (or equivalent) 3 ” of Braided Picture Hanging Wire (or equivalent) Plastic Drinking Straw (or coffee stirring stick) Masking Tape
The Testing of the Light Bulb:
2 Alligator Clips 6 Volt DC Power Source Single Pole Single Throw Pushbutton Switch Multi-meter
The Poster:
Word Processor or Page Layout Software Internet and Printing Capability D:\106751663.doc Page 2 of 24
.02R. Procedures: Period 1 – Model the Light Bulb Body and Cork in SolidWorks Step 1. Open SolidWorks. Start a New 3D Part for the glass vial. Step 2. Choose English Units. Step 3. Sketch the glass vial profile and centerline axis on the front plane. To be revolved. Step 4. Revolve Base complete at 360 degrees. Step 5. Fillet the top inside and outside, bottom inside and outside at Step 6. Assign the Glass material. Step 7. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 3 of 24
Step 1. Start a New 3D Part for the cork. Step 2. Choose English Units. Step 3. Sketch a .75 diameter circle on the top plane. To be extruded. Step 4. Extrude from Sketch Plane. Blind in Direction 1, 0.50 inch with a taper of 5deg, check in Draft outward. Blind in Direction 2, .5 inch with a taper of 5deg, no check in Draft outward.
Step 5. Assign the Wood Beech material. Step 6. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 4 of 24
Step 1. Start a New Assembly for the light bulb. Step 2. Insert the vial component. Step 3. Insert the cork component. Step 4. Use Mate to add a concentric constraint using the cork outside face and the vial inside face. D:\106751663.doc Page 5 of 24
Step 5. Use Move Component to move the cork up the Y axis to the component collision position. Step 6. Use PhotoWorks and render. Step 7. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 6 of 24
Procedures: Period 2 – Model the Filament, Leads and Straw in SolidWorks Step 1. Open SolidWorks. Start a New 3D Part for the filament. Step 2. Choose English Units. Step 3. Sketch the profile on the front plane, any spline about .5 long. Step 4. Sketch the path on the top plane, a .01 diameter circle. Step 5. Sweep Base using the circle as the profile and the spline as the path. Step 6. Assign the Alloy Steel material. Step 7. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 7 of 24
Step 1. Start a New 3D Part for the leads. Step 2. Choose English Units. Step 3. Sketch the path on the front plane, a 180 degree .06 radius arc, and a tangent vertical line about 2.25 inches long. Step 4. Sketch the profile on the top plane, a .05 diameter circle. Step 5. Sweep using the circle as the profile and the line-arc sketch as the path. Step 6. Assign the Copper material. Step 7. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 8 of 24
Step 1. Start a New 3D Part for the straw. Step 2. Choose English Units. Step 3. Sketch a circle on the top plane. To be extruded. Step 4. Extrude from Sketch Plane. Blind in Direction 1, 8 inches. Check Thin Feature on with a thickness of .005 inches. D:\106751663.doc Step 6. Assign the Plastic - PBT General Purpose material. Step 7. Save the file. Page 9 of 24
Step 1. Open the cork part for drilling holes. Step 2. View the top. Step 3. Use the Hole Wizard to drill a .25 diameter hole for the straw. Locate it anywhere off center. Step 4. Use the Hole Wizard to drill two .0469 diameter holes for the leads. Locate them left and right of center about a .5 inch apart. Step 5. Save the file. D:\106751663.doc Page 10 of 24
Procedures: Period 3 – Assemble the Light Bulb in SolidWorks Step 1. Open the light bulb assembly to add the straw, leads, and filament. Step 2. Insert Component the straw part. Step 3. Add a concentric Mate. Step 4. Move Component as necessary. Step 5. Insert Component the lead. Step 6. Add a concentric Mate. Step 7. Move Component as necessary. D:\106751663.doc Page 11 of 24
Step 8. Select a Feature Driven component pattern. The component to Pattern is the lead, the Driving Feature is the second 3/64 hole. D:\106751663.doc Page 12 of 24
Step 9. Insert Component the filament. Step 10. Move Component as necessary. Step 11. Exit and Save the light bulb assembly. D:\106751663.doc Page 13 of 24
Step 1. Open the leads. Step 2. Edit the sketch of the profile and add a bend at the top. Add any three tangent arcs. Step 3. Exit and Save the filament. Step 4. Open the light bulb assembly. Update it. Step 5. Render the image.
Step 6. Print.
Step 7. Exit and Save. D:\106751663.doc Page 14 of 24
Procedures: Period 4 – Create a Light Bulb Poster Step 1. Include the graphic design elements of unity, variety and balance. (See SAMPLE POSTER) Step 2. Choose a topic: How is a photon produced? List the advantages of a light bulb over a candle. What was Thomas Edison’s contribution to the light bulb? Label the parts of an incandescent light bulb. Describe an incandescent light. Describe a halogen light. Describe a florescent light. Describe a Laser. Describe a LED. Describe a neon light. Why doesn’t a light bulb filament burn? Where are incandescent light bulbs used? How are incandescent light bulbs rated? What kind of light technologies might be developed in the future? What is a black light? What are the three requirements for fire? Describe Volts, Amps, and Watts. What materials are used for the filament and other parts of a light bulb? Step 3. Save the file. Step 4. Be sure to add your name and print. D:\106751663.doc Page 15 of 24
Procedures: Period 5 – Construct the Light Bulb Step 1. Construction Safety precautions should be implemented here and should include but are not limited to: Wear eye protection. Use tools and materials the way they were designed. Do not crowd or distract the operator of a tool. Keep hands from in front of sharp cutting edges. Step 2. Drill two .0469 diameter holes top of the cork for wire leads. Step 3. Drill one .25 diameter hole through top of the cork for straw. Step 4. Cut two pieces of 3 inch 18 gage copper wire leads. Step 5. Insert wire leads through cork. Step 6. Bend wire lead tops into U-shape for connection to alligator clips. Step 7. Cut one 3 inch piece of 1 strand of hanging wire. Step 8. Fashion the wire into a coil shape for filament. Step 9. Attach filament to wire leads by twisted connection. Step 10. Place cork on bottle with a force fit. Step 11. Insert straw through cork with a force fit. Step 12. Create a vacuum in the bottle: suck the air out of the bottle through the straw, quickly crimp the straw, and seal in closed with masking tape. Step 13. Apply a piece of masking tape on the bottom of the light bulb and label it with your name. Step 14. Store the light bulb in a secure dry place until it is tested. D:\106751663.doc Page 16 of 24
Procedures: Period 6 - Test the Light Bulb and Calculate the Wattage Step 1. Electrical Safety precautions should be implemented here. They include but are limited to: Always disconnect the power when changing the circuit. Make electrical connections with one hand. Have the instructor check the circuit before connecting the power. Step 2. Set up a testing station which includes a DC power source and a single pole single throw pushbutton switch. Connect alligator clips from the circuit to the light bulb leads. Step 3. Have a multi-meter ready to measure voltage. Switch on DC Dial on 20V Leads in COM and V Leads are placed across the circuit, do not break the circuit. Close the switch, read and record the voltage, open the switch. Volts = ____________ Step 4. Have a multi-meter ready to measure amperage. Switch on DC Dial on 10A Leads in COM and A Leads are placed in the circuit, break the circuit. Close the switch, read and record the amperage, open the switch. Amps = __________ Step 5. Use Ohms law to calculate the watts. W = EI Watts = _________________ D:\106751663.doc Page 17 of 24
Assessment: SolidWorks Light Bulb Model ______5 pts. Revolved Clear Glass Vial Part is Complete and Sized Properly Has appropriate Material ______5 pts. Extrude of the Cork Part is Complete and Sized Properly Has Three Hole Operations Has appropriate Material ______5 pts. Sweep of a Lead Wire Part is Complete and Sized Properly Has appropriate Material ______5 pts. Sweep of a Filament Part is Complete and Sized Properly Has appropriate Material ______5 pts. Extrude of the Straw Part is Complete and Sized Properly Has appropriate Material ______5 pts. Assembly All Parts are Present in Assembly, Glass Vial, Cork, 2 Wire Leads, Filament, and Straw Parts are Mated Properly Assembled File is Saved Exploded Rendered File is Saved ______5 pts. Rendered Image Makes Proper use of Materials Makes Proper use of Viewpoint Makes Proper use of Scenery Assessment: Light Bulb Poster ______5 pts. Page Layout Title is Main Focus ______5 pts. Informative Answers the Prompt Includes Text Includes Graphics Includes Borders, Ruling Lines, or Bullets Uses a Color Scheme Uses Font Treatment Appropriately All Content is Relative ______5 pts. Technical Spelling is Correct Grammar is Correct Gives Credit to Source of Information Printed Properly Includes Your Name D:\106751663.doc Page 18 of 24
Assessment: Light Bulb Project ______5 pts. Condition of Jar Name on Bottom Is Clean and Transparent ______5 pts. Lighting Element Cut and Twisted Properly ______5 pts. 2 Lead Wires Cleaned Completely Shaped for Connecting Wires Attached to Element Properly ______5 pts. Cork Placed Securely to Seal Holes Drilled Properly for Leads Holes Drilled Properly for Straw ______5 pts. Straw Placed Properly for Vacuum Taped to Hold the Vacuum ______10 pts. Performance Lights for Several Seconds or More Without Burning Provides Good Light ______10 pts. Calculation of Watts Show the Formula for Calculating the Watts of Your Light Bulb Assessment: Light Bulb Lesson Test ______29 pts. Completion and Correctness of Test D:\106751663.doc Page 19 of 24
Name: _______________________________ Title: Light Bulb Lesson Test Instructions: Fill in the blank. Score: _____ of 29 List three tools used for the construction of the light bulb. 1. _________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________ List three materials used for the light bulb project. 4. _________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________ 6. _________________________________________ List three manufacturing operations for building light bulb project. 7. _________________________________________ 8. _________________________________________ 9. _________________________________________ List three safety rules for the construction and testing of the light bulb. 10. _________________________________________ 11. _________________________________________ 12. _________________________________________ A light bulb converts what type of energy to what type of energy. 13. _________________________________________ 14. _________________________________________ List three uses of a light bulb. 15. _________________________________________ 16. _________________________________________ 17. _________________________________________ In the light bulb project, what is the function of the glass vial? 18. ____________________________________________________ D:\106751663.doc Page 20 of 24
In the light bulb project, what is the function of the filament? 19. ____________________________________________________ In the light bulb project, what is the function of the two wire leads? 20. ____________________________________________________ In the light bulb project, what is the function of the straw? 21. ____________________________________________________ Write Ohms Law for calculating watts. 22. ____________________________________________________ Calculate watts when volts = 12 and amps = .2. 23. ____________________________________________________ What does incandescent mean? 24. ____________________________________________________ Name the United States inventor that created the long lasting carbon filament in an incandescent light bulb. 25. ____________________________________________________ Name the wave or particle that is emitted from an atom when an electron moves from higher energy shell to a lower energy shell. 26. ____________________________________________________ Name one advantage of an incandescent light bulb over using a candle for light? 27. ____________________________________________________ Name one disadvantage of an incandescent light bulb. 28. ____________________________________________________ D:\106751663.doc Page 21 of 24
Name: _______________________________ Title: Light Bulb Lesson Test - Answers Score: 29 of 29 Instructions: Fill in the blank. List three tools used for the construction of the light bulb. 1. Drill 2. Scale 3. Wire Cutters List three materials used for the light bulb project. 4.
Glass 5. 6. Cork Plastic List three manufacturing operations for building light bulb project. 7. 8. Laying Out Bending 9. Drilling List three safety rules for the construction and testing of the light bulb. 10. Wear eye protection 11. Don’t crowd around other students 12. Be sure glass vial is clean before sucking the air out A light bulb converts what type of energy to what type of energy. 13. Electricity 14. Light List three uses of a light bulb. 15. Lamp 16. 17. Flashlight Decoration In the light bulb project, what is the function of the glass vial? 18. To contain the filament and the vacuum, allows light to pass D:\106751663.doc Page 22 of 24
In the light bulb project, what is the function of the filament? 19. To glow and produce light In the light bulb project, what is the function of the two wire leads? 20. To create a path for electricity to flow through he light bulb In the light bulb project, what is the function of the straw? 21. To help create a vacuum in the vial Write Ohms Law for calculating watts. 22. Watts Equals Volts Times Amps or W = V*A Calculate watts when volts = 12 and amps = .2. 23. 12 Volts * .2 Amps = 2.4 Watts What does incandescent mean? 24. to give off light and heat Name the United States inventor that created the long lasting carbon filament in an incandescent light bulb. 25. In 1879 Thomas Alva Edison invents the first incandescent light bulb that can burn for a significant length of time. Name the wave or particle that is emitted from an atom when an electron moves from higher energy shell to a lower energy shell. 26. photon Name one advantage of an incandescent light bulb over using a candle for light? 27. widely available, many sizes and shapes, relatively low cost, easy incorporation into electrical systems, low voltage operation Name one disadvantage of an incandescent light bulb. 28. inefficient, gives off heat D:\106751663.doc Page 23 of 24
Resources Used:
www.discoveryschool.com
www.dictionary.com
www.howthingswork.com
www.pde.state.pa.us
http://blogs.solidworks.com/teacher/ D:\106751663.doc Page 24 of 24