Enzymes booklet student
advertisement

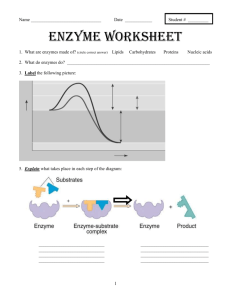
Biology and Disease FRI ENZYMES A huge number of chemical reactions take place inside every living cell. Some release energy, some synthesise new substances, some break down waste products. Enzymes play a vital role in these reactions Enzymes are biological catalysts They are made by… They can be… They regulate the chemical reactions which take place in many biological processes. They are required in very… They are used over and over again. All enzymes are proteins Their activity depends on the tertiary structure of the protein and this influences their requirements for optimal activity. The enzyme will be sensitive to environmental conditions for example changes in. Each enzyme is coded for by one gene. Biology and Disease FRI Why Are enzymes Important? The substances that react together in an enzyme controlled reaction are called ______________. E.g. What are the substrates for the chemical reaction of respiration? To actually start this reaction would need a lot of energy to break the bonds already in existence between the molecules of the substrates. The energy needed is usually in the form of heat, e.g. sugar will only react with oxygen when it is heated. Animals need to release the energy in sugar and break it down inside their bodies. Such high temperatures are likely to cause damage to or kill the animal! The chemical reactions necessary to support life need to occur quickly and within a suitable temperature range. Body temperature is _______. Temperatures greatly above this would cause damage to chemicals such as proteins, so the high activation energy needs to be lowered. This is where enzymes are important: *___________________________ The minimum amount of energy needed to bring molecules together so that they will react with each other is called the ACTIVATION ENERGY Enzymes, in the same way as all catalysts, work by lowering the amount of energy needed to start a reaction. Mechanisms could be: binding the reactants next to each other increases the chance of a reaction or reactants are held in such a way that bonds are exposed to attack Enzymes cannot alter a reaction – they cannot cause it to proceed in a different way, or influence the final concentrations of reactants and products. All the enzyme does is _____________________ _______________. Biology and Disease FRI Activation Energy Graphs In any reaction, the substrates will only bond together and release products if they have enough energy. The following graph shows some of the energy changes involved in a chemical reaction which does not involve enzymes. The amount of energy needed is very high and is not suitable in living organisms. Enzymes LOWER the activation energy required by…………. The following graph compares the activation energy required for a reaction with and without an enzyme Biology and Disease FRI How do enzymes function? 1, Lock and key hypothesis 2, Induced Fit hypothesis Show using diagrams how this enzyme would function to catalyse a breakdown reaction. Biology and Disease FRI Factors affecting enzyme activity Enzyme and Substrate Concentration Enzymes work by forming enzyme-substrate complexes. The rate of reaction depends on the number of substrate molecules that bind with enzyme molecules in any given time. The more enzyme molecules in the solution, the greater the chance of a substrate molecule finding an active site, and the faster the rate of reaction. Similarly, the more substrate molecules in a solution, the greater the chance that an enzyme-substrate complex will form and the greater the rate of reaction. 1) 2) 1. a) Referring to the diagram and the graph, describe how changes in substrate concentration affect rate of reaction. b) Explain using your knowledge of enzyme activity why this happens. c) Mark on the graph with a letter X the point of saturation (when all active sites are occupied) 2. a) Referring to the diagram and the graph, describe how changes in enzyme concentration affect rate of reaction b) Draw out the shape of the graph for the change in rate of reaction as enzyme concentration increases if substrate concentration was not a limiting factor. 3. Describe the differences between the lock and key hypothesis and the induced fit hypothesis. Biology and Disease FRI Temperature and enzyme activity As the temperature rises, the rate of a chemical reaction normally increases. This is because the molecules gain_________ ___________ so they move faster, collide more often and the __________ are more likely to lead to a reaction. This also holds true for reactions controlled by enzymes. However, as temperature rises the atoms within the enzyme molecules also gain _________ _____________ and ___________ so rapidly that the weak bonds that maintain the __________ structure of the protein molecule break and the protein can _________. This means a change in shape of the ______ _______which will inactivate the __________. Once broken, the __________ bonds do not reform their original positions and even if ________, the damage is ______________. The enzymes is said to be ___________________. Most enzymes in the body are denatured by temperatures above approximately 45ºC (however denaturation is not instantaneous). They work fastest just below this, at about 40ºC. This is their __________ ____________. However other organisms living in extreme temperatures have enzymes which function best at other temperatures. 1. Why is the rate of reaction so low below 10ºC? 2. Divide the y axis into an even scale from 0-10 (use a ruler!) to represent the rate of reaction in arbitrary units. 3. What is the rate of reaction at 10ºC, 20ºC and 30ºC. 4. What is the effect of raising the temperature by 10ºC? 5. what would the rate of reaction be if some of the enzyme and its substrates were frozen and then warmed to 40ºC? 6. A protease enzyme in washing powder works best at 55ºC. a) What is the advantage of using a protease with this optimum temperature in a washing powder? b) Explain how proteases in washing powder help to remove protein stains such as blood or egg from clothes. Biology and Disease FRI pH and enzyme activity As well as having an optimum temperature, enzymes also have an optimum pH. Most enzymes are denatured in solutions that are strongly ____________ or strongly ____________. This is because the Hydrogen ions in an acid or the hydroxyl ions in an alkali are attracted to the charges on the amino acids in the polypeptide chains that make up the enzyme. They interact with the amino acids and disrupt the bonds that are maintaining the molecules 3-D shape, destroying the active site of the enzyme. Once the original structure is lost, it cannot reform and the enzyme no longer ______ to its substrate. 7. The optimum pH for this enzyme is pH 8. If this were a digestive enzyme suggest where it may be produced within the human digestive system. 8. Describe how changes in pH affect this enzyme and explain why. 9. Draw onto the graph the curve that would show how the enzyme activity of a protease enzyme found in the stomach would change with pH. 10. The enzyme catalase speeds up the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Describe how you would carry out an experiment to investigate the effect of pH on the activity of the enzyme catalase in yeast cells. HINT 1: you would need hydrogen peroxide, a suspension of yeast cells, a range of buffer solutions at different pH’s, test tubes, a water bath at 30ºC, measuring cylinders HINT 2: enzyme activity can be determined by measuring the rate of production of product Biology and Disease Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity Competitive and Non-competitive Inhibition 1) Competitive Inhibition 2) Non-Competitive Inhibition FRI