Anatomy & Biomechanics Lesson Plan: Agonist & Antagonist Muscles
advertisement

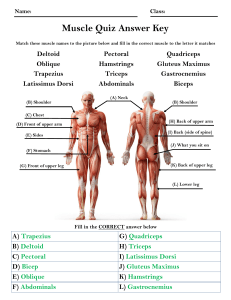
LESSON PLAN Subject – Perf PE Ashlee Ross Class – 12 Perf PE Unit – Anatomy/ Biomechanics Topic – 3. Anatomy Achievement Objective(s) 7B1 – Appraise specialised motor skills and adapt them to extend physical competence in recreational opportunities? Learning Outcome(s) and/or Learning Intentions Assessment and/or Success Criteria What should the students learn? How do we know what we have learnt? 1. Describe the difference between an agonist and an 1. Will be able to write down a definition on their summary antagonist worksheet and identify the difference in the examples. 2. Identify the agonist and the antagonist for each joint 2. Will participate and contribute to class discussions and movement in sporting examples. answers from the worksheets. Key Competency Focus - How is this key competency developed in this lesson? Participating and contributing – this will be developed via questioning, demonstrations and quizzes which will require both participation from everybody in the class and contribution of answers to enhance understanding. Time Student Learning Activities Teacher Activities Introduction - Get students to sit towards the front of the class. 5mins - sitting quietly listening to instructions - Alright, sit down thanks - Bags under your desk, books out, pens down eyes this way – DON’T START UNTIL SILENCE ‘Before we start today I am going to discuss my expectations of you - I am studying to be a teacher I expect you to all listen and not talk while I am talking. I also expect that you pay attention during the lesson and to complete the homework that I set to help revise for the anatomy test coming up. ‘From now on there will be consequences for those misbehaving or distracting others or talking while I am talking and for those who do not complete the homework I set.’ - Write up names of those talking/ off task if need be - write up objectives/ plan on the board (refer to these) 15mins Quiz 20 questions– both upper and lower limb 10mins Complete Fencing example Will give answers if asked. 10mins Agonists and Antagonists - Fill in gaps on worksheet from Power Point - Complete example of a Biceps Curl 10mins - Volleyball example 10 mins Go through the powerpoint of movements and agonist and antagonist muscles. - Homework worksheet of badminton player Complete crossword. Equipment – white board markers, We are going to start with a quiz which is on your hand out - I expect this to be done in silence and I will collect this in. Are there any questions. Make sure your books are off your desks. START NOW. - Name your test. You have about 5 mins to complete the test. - Switch with a partner and mark by asking students for answers. Collect them in to assess level of understanding, what areas need more revision and who is struggling. Ask who has completed the fencing example to put their hands up – give them the badminton example Give the others 5 mins to try and complete fencing worksheet and then go over the answers - Remember when looking at a picture we always use their body part. (left/ right etc) - Hand out worksheet of volleyball while they attempt bicep curl in their workbooks - Go over answers - Continue on to the volleyball example – Go over answers - Choose a person from each group that will report back for each of the frames. Read out the answers once I have checked students booked to ensure they have attempted the crossword. - Hand out homework worksheet of badminton player – BE STERN and explain that if not completed there will be consequences If extra time - Anatomy Crossword – overview Resources – badminton worksheet, fill in the blanks movements and muscles, quiz printed D:\533576136.doc Teacher Evaluation Student achievement – where to next? Teacher practice – what have I learnt? what will I change? D:\533576136.doc TEST ANSWERS 1. What movement does ilio psoas produce? a. Hip flexion 2. Label the 4 parts of quadriceps a. Rectus femoris, vastus intermedius, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis. 3. What movement does the quadriceps produce at the knee? a. Extension 4. Label the 3 parts of the hamstrings a. Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, semimembranosus. 5. Which muscles produce plantarflexion – pointing toes? a. gastrocnemius and soleus 6. What is the muscle responsible when preparing to punch something? a. Flexor Digitorum 7. Which muscle produces inversion? a. Tibialis anterior. 8. What are the movements of the Trapezius? a. Raise the head, pull shoulders back, raise the scapula, drop the scapula 9. When you turn your head to look at someone next to you – what is this called? a. Rotation 10. Which are the only two joints that can perform circumduction? Why? a. Shoulder/ Hip – Ball and socket. 11. What muscle is being used as you straighten out from a pike dive? a. Erector Spinae 12. What two movements does the Triceps Brachii produce? a. Elbow and shoulder extension 13. In knee flexion which muscle is working? a. Hamstrings 14. In hip extension which muscle is working? a. Hamstrings 15. Describe the six key parts of the spine? How many vertebrae are at each section 1. Cervical (7), Thoracic (12), Lumbar (5), Intervetebral Discs, Sacrum, Coccyx D:\533576136.doc NAME ________________________________________________________________________ 1. What movement does ilio psoas produce? 2. Label the 4 parts of quadriceps 3. What movement does the quadriceps produce at the knee? 4. Label the 3 parts of the hamstrings 5. Which muscles produce plantarflexion – pointing toes? 6. What is the muscle responsible when preparing to punch something? 7. Which muscle produces inversion? 8. What are the movements of the Trapezius? 9. When you turn your head to look at someone next to you – what is this called? 10. Which are the only two joints that can perform circumduction? Why? 11. What muscle is being used as you straighten out from a pike dive? 12. What two movements does the Triceps Brachii produce? 13. What is the main muscle which causes knee flexion? 14. What is the main muscle which causes hip extension? 15. Describe the six key parts of the spine? How many vertebrae are at each section D:\533576136.doc Agonist and Antagonist Muscles Summary – Answer Copy Agonist / prime mover – muscle directly responsible for the movement at a joint. Antagonist – muscle that is relaxing and has the opposite action to the agonist. MOVEMENTS Wrist flexion – AGONIST (prime mover) Flexor Digitorum ANTAGONIST (relaxed) Extensor Digitorum Wrist extension – Extensor Digitorum Flexor Digitorum Elbow flexion – Biceps Brachii Triceps Brachii Elbow extension – Triceps Brachii Biceps Brachii Shoulder flexion – Anterior Deltoid Pectoralis Major Posterior Deltoid Latissimus Dorsi Shoulder extension - Posterior deltoid Latissimus Dorsi Anterior deltoid Pectoralis Major Shoulder adduction – Latissimus Dorsi Pectoralis major Deltoid (middle) Shoulder abduction – Deltoid (middle) Latissimus Dorsi Pectoralis major Spine/ Trunk flexion – Rectus Abdominis Erector Spinae Spine/ Trunk extension Erector Spinae Rectus Abdominis Hip flexion – Iliopsoas Quadriceps Gluteus Maximus Hamstrings Hip extension – Gluteus Maximus Hamstrings Iliopsoas Quadriceps Knee flexion – Hamstrings Gastrocnemius Quadriceps Knee extension – Quadriceps Hamstrings Gastrocnemius Dorsiflexion – Tibialis Anterior Plantarflexion – Gastrocnemius + soleus Gastrocnemius + soleus Tibialis Anterior D:\533576136.doc Agonist & Antagonist Muscles: Summary Revision Agonist –____________________________________________________________________ Antagonist – _________________________________________________________________ 1) MOVEMENTS Wrist flexion AGONIST (prime mover) Flexor Digitorum ANTAGONIST (relaxed) Extensor Digitorum Anterior Deltoid Pectoralis Major Posterior Deltoid Latissimus Dorsi Latissimus Dorsi Pectoralis major Deltoid (middle) Deltoid (middle) Wrist extension 2) Elbow flexion Elbow extension 3) Shoulder flexion Shoulder extension Shoulder adduction Shoulder abduction 4) 5) Spine/ Trunk flexion Rectus Abdominis Erector Spinae Spine extension – Rectus Abdominis Hip flexion – Hip extension – 6) Knee flexion – Gluteus Maximus Hamstrings Hamstrings Gastrocnemius Iliopsoas Quadriceps Quadriceps Gastrocnemius Soleus Tibialis Anterior Knee extension – 7) Dorsiflexion – Plantarflexion – D:\533576136.doc