lab final study guide
advertisement

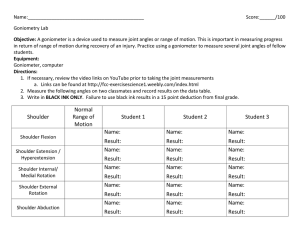
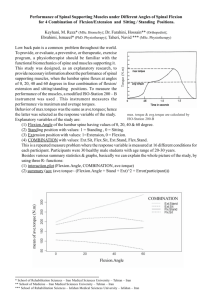
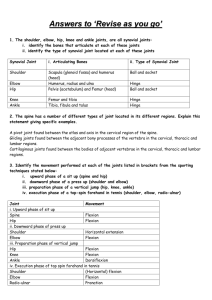
BIO 234 LAB FINAL Study Guide You must be able to identify all muscles listed on the CAT DISSECTION checklist as well as all structures on the SHEEP BRAIN handout. You should know the function for all muscle groups covered in lab: Suprahyoid muscles – raise hyoid; depress mandible (open mouth) Infrahyoid muscles – lower hyoid; fixate hyoid Pectoral muscles – shoulder flexion; shoulder adduction Lattisimus dorsi – shoulder extension; shoulder adduction Deltoids – shoulder abduction Trapezius – head extension/abduction (unilateral) as well as many actions on scapulae Rhomboids – retract scapulae Rhomboideus capitis – elevate scapulae Serratus anterior – scapular protraction (pushing) Triceps – elbow extension Biceps/brachialis/brachioradialis – elbow flexion Abdominals Rectus abdominus – trunk flexion Ext/Int obliques/transverse abdominus – increase intra-abdominal pressure (defectaion, urination, childbirth, forced expiration…) Gluteals – hip extension/external rotation Hamstrings – knee flexion/ hip extension Quadriceps – knee extension/ hip flexion Gastrocmemius/Soleus/Flexor digitorum – plantar flexion of ankle Tibialis anterior/Extensor digitorum – dorsiflexion (extension) of ankle Fibularis (peroneus) – eversion of foot You should review Labs 16B and 18B Review sheet questions and lecture slides from these labs Skeletal muscle physiology (Lab 16B) 3 phases of muscle twitch – latent, contraction, relaxation Multiple motor unit summation vs. Temporal (wave) summation Treppe Threshold voltage Be able to explain muscle control in terms of strength and smoothness of contractions. Isometric vs. Isotonic contractions Length-Tension relationship (curve) o Optimum resting length Neurophysiology (nerve impulses) (Lab 18B) Speed – myelinated vs. non-myelinated Large vs. small fibers Action potentials o Phases (know spike graph) o Resting membrane potential o Depolarization o Repolarization o Hyperpolarization o Refractory period o What is happening to Na+/K+ channels at all parts of the spike? Difference between local and action potentials Nerve conduction Unmyelinated Myelinated – saltatory conduction (nodes of Ranvier)