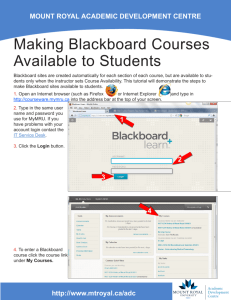
VII - Content Editor
advertisement

Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
VII - Content Editor
Overview
The content editor module integrated in the system allows different users to create
textual content in a collaborative manner. Diverse and disperse users can, together,
create content simply by editing a shared document available to all group users in the
system database. In a wide perspective of the concept, different types of data can be
shared and remotely edited, from text to video, as well as giving a mixture of extra
functionalities to custom content.
Due to time constrains, this module provides only text editing. This specific type of online
collaboration is usually known as a blackboard system.
In a traditional approach, a blackboard system, in computer science, is composed of
an area of shared memory, referred to as the blackboard that contains a problem to
be solved and a collection of software agents or processes, often referred to as
knowledge sources, which can access and modify the blackboard. Each agent scans
the changes to the blackboard, and posts an updated partial solution based on the
state of the blackboard whenever its own internal conditions for doing so are met.
These partial solutions cause other agents to update their portions of the solution on the
blackboard until eventually an answer is found. In this fashion, the agents work together
to solve the problem.
Being just a module inside a complex collaborative system, it needs to have
interactions with other modules that provide and/or receive information. Since, this was
a cooperative lab work, some work done in this module was supported by other groups
functions and interfaces.
In an initial phase, the module runs outside eGroupWare using a simple PHP interface
just for testing, but already with an eGroupWare database connection. In a second
phase, with Synchronous User Interface group help, a standard module will provide all
the previous functionalities, but now in accordance to the global system and allowing
a straightforward integration.
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 1 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
Interaction
In the following figure, it’s possible to situate the Content Editor Module area between
two other modules to understand how it is integrated and what services are used in
these interactions.
User Interface Manager
Content Editor
6/14/2006
Whiteboard feature
Content Filename
This feature provides collaborative
text content creation
Get CE
Content
Get CE
Files
Update
Content
Lock
Create
New
Content
Add
User
Database Interface
egw_ev_ce_object
id_object: int(11)
fk_id_group_owner: int(11)
fk_id_group_owner: int(11)
Name: varchar(100)
Locked: tinyint(4)
stream_path: text
fk_id_group_that_locked: int(11)
last_update: datetime
fk_id_group_last_update: int(11)
Ilustração 1: Content Editor Module interactions
The User Interface Manager must provide the file to edit name or the new one to be
created, as well as the respective Session ID when wants to execute a Content Editor
session, in order to specify which file should be collaboratively editable.
After that information is conceded, the Content Editor interface allows the user to edit
the chosen file, if it is not currently being edited. The file text content is displayed to the
user and, if he wants to edit the actual content, he locks the file for edition, edits it and
saves it again with the new changes. After that, all the other allowed users can see the
changes made to the file content.
In order to access each file, we need to communicate with the global system
database. All the database interactions were passed into simple function by the
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 2 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
Database Interface group and available for simple database request inside internal
module code.
The functions provided the Database Interface group were:
get_ce_content($content_name)
This function returns one egw_ev_ce_object with all information about the file with
name equals to content_name.
get_ce_files()
This function returns all the filenames of editable files.
update_content_lock($new_locked_status,$object_name)
This function sets a new_locked_status in the egw_ev_ce_object which file with name
equals to object_name. It sets “1” to block the file for editing and “0” for unlock it.
create_new_content($group_host_name,$content_name,
content_extension)
This one creates new content editor object in eGroupWare database, according to
filename and actual user.
add_user($group_name,$content_name)
This last function, gives editing content privileges to specific user.
The final step to complete eGroupWare system integration is the junction between
developed Content Editor source code and the user interface provided by the
Synchronous User Interface group. The final result is an eGroupWare module, easily
integrated in the final system with all Content Editor services available there to the final
user.
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 3 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
Implementation
At the beginning, the approach was to develop a stand-alone module that provides all
content editor functionalities, using a custom SQL database. Here, the main objectives
were to select, open, write new content and upload it.
After that, it was changed to communicate with a common eGroupWare database,
using the functions provided by the database interface group. Now, the user needs to
lock the file before he can edit it so that the other “editors” cannot change its content
while he is editing. After he finishes his content edition, he unlocks the file so that others
can edit afterwards, seeing in the moment the most actual content.
Finally, the initial user interface was substituted by an integrated one for the entire
eGroupWare collaborative system, provided by the Synchronous User Interface group.
Start
Select
Available
Files?
No
Choose
Filename to
create it
No
Open file
(Editing mode
available)
Yes
File is
locked?
Yes
Return
Open file
(Editing mode
not available)
Start editing
file?
Yes
Editing File
(Lock file)
Upload file
No
End editing file
(Unlock file)
Ilustração 2: Content Editor module flowchart
This flowchart can be clarified by the according interfaces (still outside eGroupWare
platform):
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 4 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
…
<?php
echo "<BR><TEXTAREA
NAME=NewName COLS=25 ROWS=1>";
echo "</TEXTAREA><BR>";
?>
…
…
create_new_content($username,$NewName,
"txt");
add_user("evr",$NewName);
$objectoX = get_ce_content($NewName);
…
…
$Names = get_ce_files();
…
echo"<select NAME=\"Name\">";
foreach ($Names as $name){
echo "<option VALUE=$name>$name</option>";
echo"</select>";
…
…
$FILE_PATHX = $objectoX[2];
sscanf($FILE_PATHX, "http:////localhost%s",$X);
$FILE_PATH = str_replace("//","/",$X);
$FILE_PATH =
$_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'].$FILE_PATH;
…
$all_data = "";
$fp=fopen($FILE_PATH, "a+");
while (!feof($fp))
{
$all_data .= fread($fp, 1024);
}
fclose($fp);
…
…
update_content_lock(1,$Name);
…
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 5 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
…
$LOCAL_PATH = $FILE_PATH;
$fp=fopen($LOCAL_PATH, "w");
fwrite($fp,$NewText);
fclose($fp);
…
…
update_content_lock(0,$Name);
…
…
echo "<br><br><a href=EscolherFicheiro.php>Return</a>";
…
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 6 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
After the first prototype completed and fully operational, the interface needed to be
changed in order to be integrated inside the developed eGroupWare collaboration
system. For that, it was used the user interface developed by the Synchronous User
Interface group in a similar way. The final version module interface is present in that
group report area.
Critical Analysis
The initial Content Editor module goals were too extensive, regarding implementation
time available, since it was used PHP (a programming language not experienced
before by the group members).
Another problem was the long time wasted on lab work phase 1 tasks. The lab work
objectives were constantly changing, leaving sometimes the developers unaware
about what to do next. For example, the collaboration platform to be used first
(PhProjekt) was substituted by eGroupWare system, leaving some groups with their
phase 1 work completely without use.
Since the lab work was fragmented into many groups distributed over two different lab
classes, it was sometimes difficult to manage it. Some groups didn’t know exactly what
to do, the architecture took time to its final version what influenced constant changes.
The final objectives should be well defined at start point in order to provide a fast lift off
to implementation phase. The architecture discussion phase is also extremely important,
but it should be shorter and at lab work starting.
In our opinion, the lab work should be executed brick by brick, in small steps, from a
very simple functional system, and then transform it to a more complex one, according
to time constrains. In this approach, we would always have a complete system
implemented for demonstration. The approach used in this lab work was a bit utopian,
what resulted in a delayed, very simple and incomplete system.
Finally, the main objectives were accomplished; however the final result was a bit away
from initial complex goals.
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 7 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
Conclusions
The main Content Editor module objectives were accomplished. The module provides
the necessary functionalities to create text content in a collaborative way between
professors. It was developed a locking mechanism to avoid problems in concurrent
editing: who wants to edit the file, locks it and avoids other remote edition; when
finishes, unlocks it and everyone else can see the changes made, and modify it again,
if they want. There is a known flaw for this module that happens when a user is editing a
file and, by mistake, closes the browser window. In this case, since the user didn’t
unlock the file, nobody else can afterwards edit that file. Once again, we assume a
correct behaviour by the user.
However, the module could provide other functionalities, such as text format, user
changes identification, insertion of images, or even, video edition, but due to delivery
time constrains it was not possible to implement.
Just to end, it was developed a simple, but working, Content Editor module for the
Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System supported by the eGroupWare
platform, regarding all the main objectives intended for it.
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 8 of 9
Lab Work Report - Computer Supported Collaborative Teaching System
Authors
Filipe Feijão – Nº. 16335
Gonçalo Cândido – Nº. 14056
«Pinipons. Making people successful in a changing world.»
References
BlackBoard Software, Inc.
http://www.blackboard.com
Php Freaks
http://www.phpfreaks.com/
Software in education revolution
http://br.news.yahoo.com/060605/25/15fkd.html
Wikipedia – BlackBoard Inc.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blackboard_%28software%29
Wikipedia – BlackBoard System
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blackboard_%28computing%29
Wikipedia – Virtual learning environment
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_learning_environment
Virtual Enterprises 2005/2006
Page 9 of 9