Lecture 13
advertisement

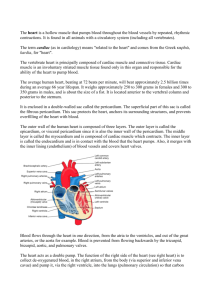
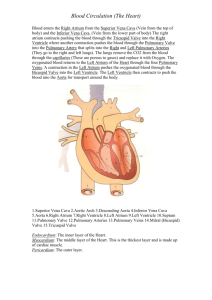
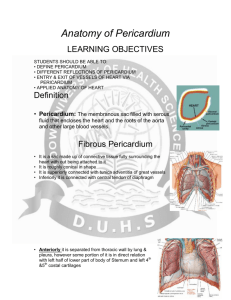
Lecture 13 : The Cardiovascular Pump - Heart I. General Anatomy of the Heart A. Location and Size 1. 2. 3. 4. primary 2/3 lie size of between organ of the mediastinum left of the sagittal plane a human fist the sternum and thoracic vertebrae 5. apex - tip of left ventricle 6. left border - left ventricle and atrium 7. superior border - site of great vessels, near atria 8. base - formed by the atria, mainly left atrium 9. right border - formed by right atrium 10. inferior border - right ventricle and part of left 11. sternocostal surface - ventricles and right atrium 12. diaphragmatic surface - mostly left ventricle B. Pericardium - connective tissue sac around heart 1. fibrous pericardium - outer thick fibrous layer a. tough bag that surrounds the heart b. attached to diaphragm c. continuous with great vessels 2. serous pericardium - inner, thin, double layer a. parietal layer - fused to fibrous pericardium i. pericardial fluid - reduces friction ii. pericardial cavity - space between layers b. visceral layer (epicardium) - on myocardium 3. pericarditis - inflammation of pericardium i. cardiac tamponade - compression on the heart C. The Wall of the Heart - 3 Layers 1. epicardium - visceral layer of pericardium (above) 2. myocardium - heart muscle itself 3. endocardium - thin endothelium lining inside D. Chambers of the Heart 1. right and left atria - upper chambers a. auricles – dog-ear like appendages b. pectinate muscles - bundles of parallel fibers 2. interatrial septum a. fossa ovalis - closed foramen ovale of fetus 3. right and left ventricles - lower chambers 4. coronary sulcus - exterior groove dividing chambers 5. anterior and posterior interventricular sulci E. Great Vessels of the Heart 1. Venous return of blood to the Right Atrium via: a. superior vena cava - from areas above heart b. inferior vena cava - from areas below heart c. coronary sinus - from heart muscle itself 2. Right Atrium -> Right Ventricle 3. Right Ventricle to the Lungs via: a. pulmonary trunk i. right and left pulmonary arteries ii. only arteries with unoxygenated blood 4. Lungs -> Left Atrium via: a. pulmonary veins i. only veins with oxygenated blood 5. Left Atrium -> Left Ventricle 6. Left Ventricle to entire body via: a. ascending aorta i. coronary arteries ii. arch of the aorta iii. thoracic aorta iv. abdominal aorta 7. ductus arteriosus - only in fetus; from pulmonary trunk to aorta 8. ligamentum arteriosum - remnant in adult F. Valves of the Heart 1. Atrioventricular Valves (AV) a. tricuspid valve - between right atrium & ventr. b. bicuspid valve - between left atrium & ventr. i. chordae tendinea - attach cusps to muscles ii. papillary muscles - pull on cusps 2. Semilunar Valves - between ventricles and vessels a. pulmonary semilunar valve - pulmonary trunk b. aortic semilunar valve - aorta II. Blood Supply of the Heart A. Arterial Supply 1. ascending aorta -> left coronary artery -> a. anterior interventricular branch b. circumflex branch 2. ascending aorta -> right coronary artery -> a. posterior interventricular branch b. marginal branch B. Venous return: Coronary Sinus -> Right Atrium 1. tributaries contributing to the coronary sinus: a. great cardiac vein (drains anterior) b. middle cardiac vein (drains posterior)