Leadership styles activity guide and handout
advertisement

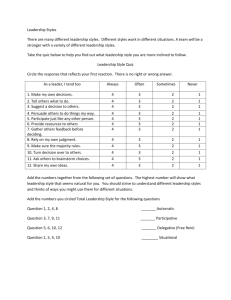
Unit 13: Leadership Skills Leadership styles activity guide and handout Developed by This project was funded by the Department of Sustainability and Environment. This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 Australia licence. A copy of this licence is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.5/au/ or by writing to info@creativecommons.org.au. However logos arePage protected 1 ofby 4 copyright. Unit 13: Leadership Skills Leadership styles activity guide and handout Estimated duration: 20 minutes Aim To provide a three clear examples of leadership styles Outcome By the end of this class, students will be able to: Identify the situations where one leadership style is more appropriate than another. Resources Handout: Leadership styles (included below) Activity description This is a group discussion facilitated by the teacher based on three types of leadership: authoritarian, participative and delegation. Students are asked to give examples, and tasks allocated for their project are reviewed and thought about in terms of the three styles. Styles of Leadership Quite a lot of research has been undertaken to examine leadership styles. Perhaps the most critical study was undertaken in 1939 by a group of researchers led by psychologist Kurt Lewin. This early study was very influential and established three major leadership styles: autocratic, democratic, or laissez-fair. Over time these terms have been developed to define the following leadership styles: authoritative, participative and delegative. Discuss these styles with the students, using the information in the handout as a guide. Ask students to give examples of each type of leadership they might have encountered, seen in a film, read about or heard about. Mixing it all together Leaders have many different styles. Depending on the situation, some styles may be more effective than others. Good leaders utilise all three styles depending upon the situation. For example, they: Use an authoritative style if a group member lacks knowledge about a certain procedure. Use a participative style with group members who understand the objectives and their role in the task. Page 2 of 4 Use a delegative style if the group member knows more than they do about the task. Refer back to some of the tasks that students have to complete in their project. You can use some of these examples of the tasks to demonstrate how students might think about applying the three leadership types. (Based on activity from the Centre for Multicultural Youth’s Short Burst Training) Student Roles and Responsibilities Contribute to class discussions Level of Teacher Support Facilitate discussion Organise materials and equipment Assessment To use these learning activities as assessment tasks, collect evidence such as: Teacher checklist and observation Student notes Page 3 of 4 Unit 13: Leadership Skills Leadership styles handout Authoritarian Leadership These leaders make all the decisions without consulting others. They provide clear expectations to group members on what should be done, when it should be completed, and how it should be accomplished. Positive: Authoritarian leadership is best used in situations when there is little time for group decision-making or when the leader is the one best equipped to solve the problem or give directions. Negative: Overuse of an authoritarian style can be construed as bossy and controlling. Worstcase examples of this style can be seen when leaders utilise bullying techniques such as yelling, abusing power, or demeaning group members. Participative Leadership Participative leaders accept input from one or more group members when making decisions and solving problems, but the leader has the final say when choices are made. Positive: Group members tend to be encouraged and motivated by this style of leadership. It often leads to more effective and accurate decisions, since no leader can be an expert in all areas. Negative: It can be problematic when there are a wide range of opinions and no clear way of reaching an equitable final decision. Delegative Leadership Delegative leaders allow group members to make decisions. These leaders often go with the flow. Positive: This style is best used in situations where the leader needs to rely on the expertise of group members. After all, the leader cannot be an expert in all situations, which is why it is important to delegate certain tasks out to knowledgeable and capable group members. Negative: There is potential for the leader to lose track of the decisions made by team members. Page 4 of 4