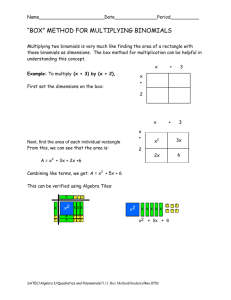
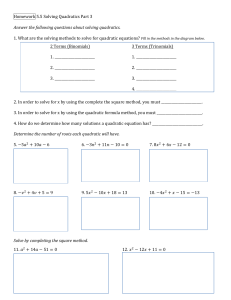
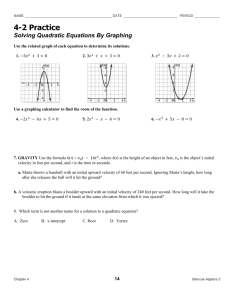
Mathematics
advertisement

Mathematics – Algebra 1 Unit 7: Polynomials CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Third Grading Period – Week 1- 4 (14 Days) Big Idea Unit Rationale All numerical operations with polynomials – adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing – including factoring and problem-solving applications. The geometric property of similarity for both 2-D and 3-D figures and the related concept of proportionality. Graphical representations of transformations – translations, reflections and dilations. Polynomial expressions easily lend themselves to modeling real-world situations and processes from ticket sales at a football game to energy levels in the nucleus of an atom. Students must learn to be comfortable working with these algebraic expressions to reveal many of the world’s secrets. Scale factors and the associated concept of similarity have wide usage in engineering, architecture and art. TEKS TEKS Specificity - Intended Outcome 8.3 Patterns, relationships, and algebraic thinking. The student identifies proportional or non-proportional linear relationships in problem situations and solves problems. The student is expected to: 8.3B estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percents and other proportional relationships such as similarity and rates. 8.6 Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses transformational geometry to develop spatial sense. The student is expected to: 8.6A generate similar figures using dilations including enlargements and reductions: and Concepts 8.6B graph dilations, reflections, and translations on a coordinate plane. 8.7 Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometry to model and describe the physical world. The student is expected to: 8.7B use geometric concepts and properties to solve problems in fields such as art and architecture: and 8.7D locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers. 8.9 Measurement. The student uses indirect measurement to solve problems. The student is expected to: ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. I can: estimate and find solutions to real-life problems involving percents and proportional relationships such as similarity and rates. (8.3B) generate similar figures through dilations which either enlarge or reduce the original shape (8.6A) graph dilations, reflections, and translations on a coordinate plane (8.6B) use geometric concepts and properties to solve real-world problems (8.7B) locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers (8.7D) use proportionality to find the missing measurements in two-dimensional or threedimensional figures. (8.9B) describe the changes on perimeter and area when the dimensions of a shape are altered proportionally (8.10A) evaluate polynomial expressions for a given value of the variable (A.4A) identify monomials, binomials, and trinomials (A.4A) add polynomials(A.4A) subtract polynomials (A.4A) multiply monomials (A.4A) use the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to simplify algebraic expressions (A.4B) multiply binomials using the F.O.I.L method (A.4A) multiply polynomials using laws of exponents (A.11A) divide polynomials using the laws of exponents (A.11A) understand the properties of exponents(A.11A) solve a polynomial equation using factoring (A.10A) 8.9B use proportional relationships in similar two-dimensional figures or similar three-dimensional figures to find missing measurements. 8.10 Measurement. The student describes how changes in dimensions affect linear, area, and volume measures. The student is expected to: SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 1 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. 8.10A describe the resulting effects on perimeter and area when dimensions of a shape are changed proportionally. A.4 Foundations for Functions. The student understands the importance of the skills to manipulate symbols in order to solve problems and uses the necessary algebraic skills required to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations and inequalities in problem situations. The student is expected to: A.4A. find specific function values, simplify polynomial expressions, transform and solve equations, and factor as necessary in problem situations; and A.4B. use the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to simplify algebraic expressions. A.10 Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands there is more than one way to solve a quadratic equation and solves them using appropriate methods. The student is expected to: A.10A solve quadratic equations using concrete models, tables, graphs, and algebraic methods. A.11 Quadratic and other nonlinear functions: The student understands there are situations modeled by functions that are neither linear nor quadratic and models the situation. The student is expected to: A.11A use patterns to generate the laws of exponents and apply them to problem-solving situations. Evidence of Learning At least 80% of the time, students will demonstrate on paper or use models to show they can estimate and solve application problems involving percents and other proportional relationships generate similar figures using dilations graph dilations, reflections, and translations on a coordinate plane solve problems using geometric concepts and properties locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of rational numbers use proportional relationships in similar two-dimensional figures or similar three-dimensional figures to find missing measurements describe the resulting effects on perimeter and area when dimensions of a shape are changed proportionally simplify a polynomial expression to transform and solve an equation use the commutative, associative and distributive properties to simplify a mathematical expression solve a polynomial equation by factorization express patterns of the variable with exponents for problem applications SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 2 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Unit 7: Polynomials CURRICULUM GUIDE Third Grading Period – Week 1-4 (14 Days) Essential Questions How do I add and subtract polynomials? How do I multiply and divide monomials? How do I factor multi-termed polynomials? What are the rules for multiplying and dividing mathematical expressions that contain exponents? How do I order rational numbers when expressed as integers, percents, decimals and fractions? What are the various procedures to transform a geometric figure on a coordinate plane? How do I use geometric properties and concepts to solve real-world problems? How do I use proportionality to solve for missing dimensions or other measures in geometric figures? Essential Pre-requisite Skills 7th Grade compare and order integers and positive rational numbers (7.1A) convert between fractions, decimals, whole numbers, and percents mentally, on paper, or with a calculator (7.1B) simplify numerical expressions involving order of operations and exponents (7.2E) estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percent (7.3A) estimate and find solutions to application problems involving proportional relationships such as similarity, scaling, unit costs, and related measurement units (7.3B) use critical attributes to define similarity (7.6D) locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of integers (7.7A) graph reflections across the horizontal or vertical axis and graph translations on a coordinate plane (7.7B) estimate measurements and solve application problems involving length and area of polygons and other shapes (7.9A) 8th Grade find and evaluate an algebraic expression to determine any term in an arithmetic sequence (with a constant rate of change) (8.5B) use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve real-life problems (8.9A) communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models (8.15A) make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and non-examples (8.16A) The Teaching Plan Instructional Model & Teacher Directions The teacher will… Jan 21 – Jan 23, 2009 These days are set aside for any or all of the following objectives: Set the stage for a focused approach to significantly improving all students’ TAKS performance Student awareness of the significance of improved scores for the campus accountability Student awareness of his/her specific math TAKS scores for the previous three years and need to develop a plan for improvement Review Jan 12-15 Benchmark results with students for teacher and students to know student’s individual TAKS strengths and weakness Review 2008 FMA results with students for teacher and students to know student’s individual course TEKS strengths and weakness Review campus/class 2008 TAKS results for teacher and students to know student’s individual previous strengths and weakness Re-teach any Unit 6 Systems of Equations unfinished lessons or areas needing emphasis Improve students graphing calculator skills Either assign or solicit volunteers (students) to become the class experts in one or two TAKS student expectations SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period So students can demonstrate competency, the students will … Jan 21 – Jan 23, 2009 These days are set aside for any or all of the following objectives: Set the stage for a focused approach to significantly improving all students’ TAKS performance Student awareness of the significance of improved scores for the campus accountability Student awareness of his/her specific math TAKS scores for the previous three years and need to develop a plan for improvement Review Jan 12-15 Benchmark results with students for teacher and students to know student’s individual TAKS strengths and weakness Review 2008 FMA results with students for teacher and students to know student’s individual course TEKS strengths and weakness Review campus/class 2008 TAKS results for teacher and students to know student’s individual previous strengths and weakness Re-teach any Unit 6 Systems of Equations unfinished lessons or areas needing emphasis Improve students graphing calculator skills Either assign or solicit volunteers (students) to become the class experts in one or two TAKS student expectations Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 3 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Ensure that a copy of Margaret Kilgo’s historical TAKS question material is made available to the student experts Day 1 TEA TAKS Study Guide Grade 9 Objective 9 SE 8.7B Engage/Explore (5-10 minutes) Ask students in pairs “What is the percent equivalent of ¼? of 7/8? of 4/7?” How do I answer these questions using proportionality? Explain (15 minutes) Explain the strategy to solve problems involving proportional relationships from page 168 with the example on page 169 Have the student pairs complete the Try It on page 170 for guided practice, as well as Questions 70, 71, and 72 on page 191. Evaluate (20 minutes) Assign problems 38-44 in McDougal Littell Algebra 1 on page 195 for in-class completion in pairs. Day 2 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.1 Engage/Explore (10 minutes) Collecting Like Objects (Terms) Make connections to prior knowledge – collecting like terms. From a deck of cards, give a different one to each student as they enter your classroom. When ready, have the students on their own group themselves by suit. Upon completion, then have them group themselves by card value – aces, twos,…, queens and kings. Conduct a discussion on grouping by “labels” Explain (20 minutes) Using Examples 1 and 2, define polynomials (monomial, binomial, and trinomial) and give examples. Ask the students to give examples. Have students take notes and generate the Frayer model for each of the above four terms. Explain that the coefficients of like terms (same variables and same degree) are added and subtracted like integers using Examples 3 and 4 Evaluate (10-15 minutes, as time allows) Using problems from the McDougal-Littell, Ch.9.1, pages 557, #17-26 have students practice how to add and subtract polynomials Monitor student activity for understanding throughout the class session. Consider the option of collecting the activity for either a grade or a completion check Alternate lesson: Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Notes and Adding or Subtracting Polynomials Assignment Day 3 Exponents, Multiplication/Division McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 8.1/8.2 Engage (5-7 minutes) KWL on Exponents KWL with students in groups of 3-4 on their knowledge of exponents with this question - What is the purpose of an exponent mathematically? SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Ensure that a copy of Margaret Kilgo’s historical TAKS question material is made available to the student experts Day 1 TEA TAKS Study Guide Grade 9 Objective 9 SE 8.7B Engage/Explore (5-10 minutes) What is the percent equivalent of ¼? of 7/8? of 4/7? How do I answer these questions using proportionality? Explain (15 minutes) Take notes on the strategy to solve problems involving proportional relationships from page 168 with the example on page 169 Complete with a partner the Try It on page 170 for guided practice, as well as Questions 70, 71, and 72 on page 191. Evaluate (20 minutes) Assign problems 38-44 in McDougal Littell Algebra 1 on page 195 for in-class completion in pairs. Day 2 Adding and Subtracting Polynomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.1 Engage/Explore Make connections to prior knowledge (collecting like terms) with playing cards sorted by suit or card value with other students. Explain Using the Frayer model, add the terms polynomial, monomial, binomial, and trinomial to your vocabulary Take notes on the teacher’s presentation on adding and subtracting polynomials (A.4A, A.4B) Evaluate Complete problems 17-26 on page 557 for a check on understanding. (A.4A, A.4B) Day 3 Exponents, Multiplication/Division McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 8.1/8.2 Engage Using a KWL activity, review your current knowledge of exponents. Put K’s and L’s on sticky notes (1 per sticky) and apply to class KWL chart. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 4 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Have students put there K and W on sticky notes - 1 per sticky note. Put on a previously prepared KWL chart paper. Explore (10 minutes) Exponent Rules for Products Have students in their groups do Activity 8.1 on page 488, “Product of Powers.” Explain (10 minutes) Exponent Rules for Products Confirm students’ conclusions about exponents by presenting the Key Concepts – Product of Powers Property on page 489 and Power of a Power Property on page 490. For guided practice, assign 9-12 on page 491. Elaborate (10 minutes) Exponent Rules for Quotients Present Key Concepts Quotient of Powers Property on page 495 and Power of a Quotient Property on page 496. For guided practice, assign 5-8 on page 497. Evaluate Monitor the students throughout the class for understanding (last 5 minutes of class) Have students add to W column on KWL chart paper Assign for homework Page 492 – 7, 12, 21, 23, 25, 31 Pages 498/499 – 9, 13, 17, 21, 27, 31, 33 Alternate Lesson: Multiplying Monomials Rules Notes, Multiplying Monomials Rules Assignment, Quotient of Powers Notes, Quotient of Powers Assignment Day 4 Exponents, Zero & Negative McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 8.3 Engage (10 minutes) Review homework assignment Explore (15 minutes) Have students do Activity 8.3, page 502 to gain an understanding and insight into Zero and Negative Exponents Explain (15 minutes) Present two Key Concepts – Definition of Zero and Negative Exponents on page 503 and Properties of Exponents on page 504. Present desired parts of examples 1-3 to model the use of the properties Assign for guided practice on pp 503/4/5: 1, 3, 6, 7, 9 Evaluate For homework , have students choose one of the following as a notebook entry: 1. make a flip chart for all the Laws of Exponents (page 504) with the rules and examples to each rule. 2. put all the Laws of Exponents (page 504) into your own words with examples of each. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Explore Complete “Product of Powers” activity on page 488 to draw conclusions from patterns recognized (A.11A) Explain/Elaborate Take notes on 4 Key Concepts presented by teacher – 2 on multiplying and 2 on dividing C Work guided practice problems to check for understanding (A.4A, A.4B, A.11A) Evaluate As a class learning summary, add “L” sticky notes to class KWL chart. Complete homework assignment. (A.4A, A.4B, A.11A) Day 4 Exponents, Zero & Negative McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 8.3 Engage Review homework assignment Explore Complete Activity 8.3, page 502 to gain an understanding of Zero and Negative Exponents(A.3.B, A.11.A) by drawing conclusions from recognized patterns (A.11A) Explain Take notes on the Key Concepts associated with zero and negative exponents (A.11A) Complete guided practice to check for understanding (A.11A) Evaluate For homework either (A.11A) 1. make a flip chart for all the Laws of Exponents with the rules and examples for each rule, or 2. put all the Laws of Exponents (page 504) into your own words with examples of each. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 5 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Days 5 & 6 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 1 – Coordinate Plane SEs 8.6B, 8.7D Engage (10 minutes) Ordering Rational Numbers in Different Forms Prepare and distribute Cruising the Number Line Cards and begin the activity Use the Facilitation Questions on page 4 to ensure depth of understanding Explore (20 minutes) Plotting and Transforming Ordered Pairs of Rational Numbers Distribute Part A and Part B to each student Divide students in group of 3-4 and complete activity in these groups Actively monitor each group’s progress Use the Facilitation Questions on pages 5 and 6 to ensure depth of understanding Explain (10 minutes) Class presentations (may continue over to Day 6) Distribute to each group either transparency of Part A or Part B for class presentation Chose 1 group to present Part A and another group to present Part B Use the Facilitation Questions on pages 7 and 8 to ensure depth of understanding Day 6 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Transformation Activity Distribute Bobby’s Transformation to each student Have students complete in their same groups as before. Use the Facilitation Questions on page 9 to ensure depth of understanding Evaluate (20 Minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Coordinate Plane to each student Have students complete individually showing all work on the pages Have student trade pages for grading Have students journal their strengths and weaknesses regarding plotting and transforming rational ordered pairs. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Day 7 Multiply Polynomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.2 Engage Review homework from Day 4 – flip charts or “own words.” Explore Have students in pairs review Example 1 on page 562 for multiplying a polynomial by a monomial using the distributive property. Have students in pairs review Example 2 on page 562 for multiplying a binomial by a binomial with the box or rectangle method. Assign for guided practice 1-3 on page 562. Have students use the box or rectangle method on the problem from Example 4. Explain Walk the students through the FOIL Method using Example #5 in textbook on page 563. Also have the students use the box or rectangle method on Example 5 to see the commonalities. Assign for guided practice 1-3 on page 563. Evaluate Assign for homework on pages 565/566: 1, 2, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 31, 35 SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Days 5 & 6 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 1 – Coordinate Plane SEs 8.6B, 8.7D Engage (10 minutes) Ordering Rational Numbers in Different Forms Order rational numbers via kinesthetic movement Answer questions related to the strategies of numerical ordering Explore (20 minutes) Plotting and Transforming Ordered Pairs of Rational Numbers Plot rational pairs on a coordinate plane in small groups (8.7D) Reflect and translate geometric figures on a coordinate plane (8.6B) Answer questions related to the details of the plotting process Explain (10 minutes) Class presentations (may continue over to Day 6) Present problem results via presentation to rest of class Answer questions related to the effects of reflection and translation (8.6B) Critique strategies for ordering rational numbers Day 6 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Transformation Activity Process analysis by a small group of how a student generated a reflection of a given geometric shape (8.6B) Evaluate (20 Minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.6B, 8.7D) Evaluate strengths and weaknesses related to highlighted TEKS SEs Day 7 Multiply Polynomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.2 Engage Review homework from Day 4 – flip charts or “own words.” (A.11A) Explore Review with a partner Example 1 on page 562 for multiplying a polynomial by a monomial using the distributive property. (A.4A, A.4B) Review with a partner Example 2 on page 562 for multiplying a binomial by a binomial with the box or rectangle method. (A.4A, A.4B) Complete guided practice 1-3 on page 562 as a check for understanding. (A.4A, A.4B) Use the box or rectangle method on the problem from Example 4. (A.4A, A.4B) Explain Take notes on the FOIL Method using Example #5 in textbook on page 563. (A.4A, A.4B) Use the box or rectangle method on Example 5 to see the commonalities. (A.4A, A.4B) Complete guided practice 1-3 on page 563. (A.4A, A.4B) Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 6 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Alternate lesson: Multiplying Using FOIL Method Notes , Multiplying Using FOIL Method Assignment , and Area Problems using FOIL Method Evaluate Complete homework on pages 565/566: 1, 2, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 31, 35 (A.4A, A.4B) Day 8 Special Products McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.3 Day 8 Special Products McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.3 Explain (10 minutes) Review homework Explore (10-15 minutes) Have the students individually solve the following problems with either the rectangle or FOIL methods: (a + b)(a – b) (a + b)(a + b) (x + 5)(x – 5) (x – 5)(x – 5) (2w + 3z)(2w – 3z) (2w + 3z)(2w + 3z) Ask students to identify any patterns noticed. Explain (10-15 minutes) Review the “rules” for special products – i.e., confirm the patterns that the students should have noticed above using Examples 1 and 2 on pages 569 and 570. Assign as guided practice on pages 569-571: 1, 3, 5, 7 Evaluate Assign for homework on page 572: 1, 2, 9, 11, 15, 23, 27, 33, 35, 37 Day 9 Factoring Simple Trinomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.5 Engage/Explore (15 minutes) Factoring as reverse of multiplication Ask the students – What are 2 factors of 15? ( 3 and 5) Ask them -Why or how this is true? (because 3 x 5 = 15) Have the students multiply (x + 3)(x + 5) – (to get x2 + 8x + 15). Then ask them what the factors of x2 + 8x + 15 are. ((x +3) and (x+ 5)) Develop the concept in the students’ minds that factoring is the reverse of multiplication. Review homework Explore (10 minutes) Zero-Product Property Present Key Concept on page 575 along with the immediately following Examples 1, 3 and 4 Explain (15 minutes) Deliver the Key Concept and table method of Example 1 on page 583 for factoring a simple trinomial. Use Examples 2 and 3 to show the impact of the signs on the various terms in a polynomial to be factored Present Example 4 stating as a goal to make one side of the equation zero. Assign for guided practice on pages 584 and 585 problems 4-8 Evaluate Assign as homework on pages 586 and 587: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 21, 23, 29, 37 Explain Review homework (A.4A, A.4B) Explore Solve the following problems with either the rectangle or FOIL methods: (A.4A, A.4B) (a + b)(a – b) (a + b)(a + b) (x + 5)(x – 5) (x – 5)(x – 5) (2w + 3z)(2w – 3z) (2w + 3z)(2w + 3z) Identify any patterns noticed. Explain Take notes on the “rules” for special products. (A.4A, A.4B) Complete for guided practice on pages 569-571: 1, 3, 5, 7 (A.4A, A.4B) Evaluate Complete homework on page 572: 1, 2, 9, 11, 15, 23, 27, 33, 35, 37 (A.4A, A.4B, A.11A) Day 9 Factoring Simple Trinomials McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.5 Engage/Explore Factoring as reverse of multiplication What are 2 factors of 15? Why or how? Multiply (x + 3)(x + 5). What the factors of x2 + 8x + 15 are? Review homework (A.4A, A.4B, A.11A) Explore Zero-Product Property Take notes on Key Concept on page 575 along with the immediately following Examples 1, 3 and 4 (A.10A) Explain Take notes on: (A.4A, A.4B) 1. Key Concept and table method of Example 1 on page 583 for factoring a simple trinomial. 2. Examples 2 and 3 to show the impact of the signs on the various terms in a polynomial to be factored 3. Example 4 stating as a goal to make one side of the equation zero. Complete for guided practice on pages 584 and 585 problems 4-8 (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A) Evaluate Complete homework on pages 586 and 587: 1, 2, 5, 7, 13, 19, 21, 23, 29, 37 (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A) SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 7 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Days 10 & 11 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 13 – Scale Factor and Similar Figures SEs 8.3B, 8.6 A/B, 8.9B, 8.10A Engage (10 minutes) Similarity of Baseball Diamonds Display the transparency of the two baseball diamonds Activate prior knowledge of similarity via facilitation questions on page 234 Explore (15 minutes) Scale Factor and Proportional Reasoning Distribute to each student What a Trip activity – interpreting a distance scale on a map Divide students into groups of 3-4 students for activity completion Provide each groups blank transparencies and markers for a class presentation on one of the four suggested methods used to solve the problem Use facilitation questions on pages 235-236 to assist students as needed as they work Explain (20 minutes) Class Presentations (may extend to Day 11) Assign the order of presentations to be given by which groups Use the questions and tips on page 237 to guide the students to a deeper understanding of similarity and proportional reasoning for problem solving Day 11 Elaborate (20 minutes) Similarity and Dilations Distribute the Similarity and Dilations activity to each student Complete the activity in original groups Use the facilitation questions to stimulate students to a deeper understanding of similarity and problem solving processes Evaluate Distribute Evaluate: Scale Factor and Similar Figures to each student Have students complete individually showing all work on the pages Have student trade pages for grading Have students journal their strengths and weaknesses regarding scale factors and similar figures. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach Day 12 Factoring Trinomials, a ≠ 1 McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.6 Engage/Explore (15 minutes) Ask students to multiply (3x + 1)( 5x + 2) (yields 15x2 + 11x + 2) Have the students work backwards from their answer to see if they can figure out how to uniquely get the original factors Go over Day 9 homework Explain (25 minutes) Present Examples 1, 2 and 3 on pages 593 and 594 Show check with graphing calculator after Example 3 Assign as guided practice 1-6 on page 594. Evaluate Assign for homework on pages 596 and 597: 1, 2, 5, 19, 25, 31, 39, 43, 49, 57 SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Days 10 & 11 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 13 – Scale Factor and Similar Figures SEs 8.3B, 8.6 A/B, 8.9B, 8.10A Engage Similarity of Baseball Diamonds Answer questions related to two similar baseball diamonds (8.3B) Explore Scale Factor and Proportional Reasoning In groups complete What a Trip activity on scale factors and problem solving methods (8.3B) Prepare with your group the assigned method for a class presentation Explain Class Presentations (may extend to Day 11) Present to class your assigned problem solving method Take notes on other three methods of problem solving Day 11 Elaborate Similarity and Dilations Complete in groups the Similarity and Dilations activity (8.3B, 8.6A, 8.6B, 8.9B, 8.10A) Answer teachers questions for a deeper understanding of similarity (8.3B, 8.6A, 8.6B, 8.9B, 8.10A) Evaluate Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.3B, 8.6A, 8.6B, 8.9B, 8.10A) Evaluate strengths and weaknesses related to highlighted TEKS SEs Day 12 Factoring Trinomials, a ≠ 1 McDougal Littell, Algebra 1, Section 9.6 Engage/Explore Multiply (3x + 1)( 5x + 2) Work backwards from your answer to see if you can figure out how to uniquely get the original factors Review Day 9 homework (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A) Explain Present Examples 1, 2 and 3 on pages 593 and 594 ((A.4A, A.4B) Show check with graphing calculator after Example 3 Assign as guided practice 1-6 on page 594. (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A) Evaluate Assign for homework on pages 596 and 597: 1, 2, 5, 19, 25, 31, 39, 43, 49, 57 (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A) Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 8 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Days 13 & 14 Review and Assessment Days 13 & 14 Review and Assessment Engage (10 minutes) Review homework Explain On pages 543 and 544, use the review of Vocabulary and sections 8.1, 8.2, and 8.3. On pages 616 through 619, use the review of Vocabulary and sections 9.1, 9.2, 9.3, 9.5 and 9.6. Skim 9.1-9.3 to concentrate on 9.5 and 9.6. Highlight the procedures for a vertically thrown object in 9.6. McDougall Littell TAKS Review and Practice Grade 9 – pp 68-74, 78-79, 92-95, 102103 for 8th Grade TEKS SEs Pick appropriate exercises for review. Evaluate Create a test from McDougal Littell Test Generator or use problems from above lessons for a Unit Test on Polynomials Teacher should include TAKS type problems that cover the TEKS from this unit Test questions should be aligned with the verbs and nouns in the unit TEKS student expectations. Evaluate Student will review concepts and then test on Unit 7-Polynomials (A.4A, A.4B, A.10A, A.11A, 8.3B, 8.6 A, 8.6B, 8.7B, 8.7D, 8.9B, 8.10A)) Vocabulary: Math Content Specific Polynomial Monomial Binomial Trinomial Exponent Product FOIL method Degree of polynomial Leading coefficient Constant Rational number Reflection Translation Dilation Scale factor Similarity Resources: McDougal Littell Algebra 1 Chapter 8 8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products 8.2 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Quotients 8.3 Define and Use Zero and Negative Exponents Chapter 9 9.1 Add and Subtract Polynomials 9.2 Multiply Polynomials 9.3 Find Special Products of polynomials 9.5 Factor x2 + bx + c 9.6 Factor ax2 + bx + c Vocabulary: TEKS Student Expectation Verbs (refer to Margaret Kilgo’s TEKS verb definitions) simplify transform solve factor apply estimate generate graph locate name Closing the Distance A Flexible Tutorial for TAKS Grade 9 Math (Region 4) Lesson 1 Coordinate Plane Lesson 13 Scale Factor and Similar Figures Problem Solving Checklist Frayer model KWL Alternate Lessons Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Notes Adding or Subtracting Polynomials Assignment Multiplying Monomials Rules Notes Multiplying Monomials Rules Assignment Quotient of Powers Notes Quotient of Powers Assignment Multiplying Using FOIL Method Notes Multiplying Using FOIL Method Assignment SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 9 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Area Problems using FOIL Method TEA TAKS Study Guide Grade 9 Math Objective 9 Evidence of Learning Differentiation McDougal Littell Algebra 1 TE Section Annotations (page bottom) Day 2 Section 9.1 pp 555-557 Day 3 Section 8.1 pg 490 Section 8.2 pp 496-498 Day 4 Section 8.3 pg 504 Day 7 Section 9.2 pg 563 Day 8 Section 9.3 pg 570 Day 9 Section 9.5 pp 584-585 Day 12 Section 9.6 pg 594 McDougal Littell Algebra 1 Best Practices Toolkit Differentiated Instruction Notes Day 2 Sections 9.1 pg 73 Day 3 Sections 8.1/8.2 pp 69/70 Day 4 Sections 8.3 pg 70 Day 7 Sections 9.2 pg 73 Day 8 Sections 9.3 pg 74 Day 9 Sections 9.5 pg 75 Day 12 Section 9.6 pg 75 Interims/TAKS/Benchmarks TAKS 2005 Grade 9 (8.3B) College-Readiness i.e., Anticipated Skills for SAT/ACT/AP/Career/Life SAT Prep If and x x 3 = x m , what is the value of m? (A) (B) (C) TAKS 2005 Grade 9 (8.6A) (D) English Language Learner Notes Day 2 Sections 9.1 pg 113 Day 3 Sections 8.1/8.2 pg 111 Day 4 Sections 8.3 pp 111/112 Day 7 Sections 9.2 pg 113 Day 8 Sections 9.3 pg 113 Day 9 Sections 9.5 pg 114 Day 12 Section 9.6 pg 114 (E) Inclusion Lesson Notes Day 2 Sections 9.1 pg 145 Day 3 Sections 8.1/8.2 pg 143 Day 4 Sections 8.3 pg 143 Day 7 Sections 9.2 pg 145 Day 8 Sections 9.3 pg 145 Day 9 Sections 9.5 pg 146 Day 12 Section 9.6 pg 146 PreAP Pacing and Assignment Guide Day 2 Sections 9.1 pg 268 SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 10 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 3 Sections 8.1/8.2 pg 266 Day 4 Sections 8.3 pg 266 Day 7 Sections 9.2 pg 268 Day 8 Sections 9.3 pg 268 Day 9 Sections 9.5 pg 268 Day 12 Section 9.6 pg 268 TAKS 2004 Grade 9 (A.4A) TAKS 2004 Grade 9 (A.4B) SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 11 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. TAKS 2004 Grade 9 (A.11A) SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 12 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratics Third Grading Period - Weeks 4- 10 (27 days) CURRICULUM OVERVIEW Big Idea The graph of a quadratic function is the first to be studied that has a continually changing slope or rate of change. There are many methods or strategies for solving a quadratic equation. 8th grade review: two dimensional representations and two-dimensional measures of three-dimensional figures. probability of dependent events and experimental probabilities appropriate representation and display of data application of appropriate models and strategies to solve everyday problems TEKS TEKS Specificity - Intended Outcome 8.7 Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student uses geometry to model and describe the physical world. The student is expected to: 8.7A draw three-dimensional figures from different perspectives: and 8.7C use pictures or models to demonstrate the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.8 Measurement. The student uses procedures to determine measures of threedimensional figures. The student is expected to: Concepts 8.8A find lateral and total surface area of prisms, pyramids, and cylinders using concrete models and nets (two-dimensional models); 8.8B connect models of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, spheres, and cones to formulas for volume of these objects: and 8.8C estimate measurements and use formulas to solve application problems involving lateral and total surface area and volume. 8.9 Measurement. The student uses indirect measurement to solve problems. The student is expected to: 8.9A use proportional relationships in similar two-dimensional figures or similar threedimensional figures to find missing measurements. 8.11 Probability and statistics. The student applies concepts of theoretical and experimental probability to make predictions. The student is expected to: 8.11A find the probabilities of dependent and independent events: and 8.11B use theoretical probabilities and experimental results to make predictions and decisions. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Unit Rationale The student should understand: when given a quadratic function y = ax2 + bx + c, a¹ 0, the emphasis is placed on certain attributes of the graphs - vertex, intercepts and the maximum/minimum. how to find the roots, the maximum value and minimum value, where the functions are increasing/decreasing. various motion problems are chosen so students see relationships to the real world in the area of physical and social science. Mathematics – Algebra 1 ” I CAN” statements highlighted in yellow should be displayed for students. I can: draw all the perspectives of a three dimensional object (8.7A) demonstrate the meaning and usage of the Pythagorean Theorem with pictures or models (8.7C) calculate the total surface area and lateral surface area of prisms, pyramids, and cylinders using concrete models and nets (two-dimensional models) (8.8A) relate the physical attributes of concrete models of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, spheres, and cones to the variables in the abstract formulas (8.8B) solve real-world problems involving lateral and total surface area by estimating measurements and using formulas (8.8C) determine the values of missing measurements of similar two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures by using proportional relationships (8.9A) determine the probability of events happening, whether the events are either dependent or independent (8.11A) make decisions and predictions based on either theoretical or experimental probabilities (8.11B) justify a choice of decision for a particular decision by selecting an appropriate measure of central tendency or range fr the related set of data (8.12A) present and display relationships among collected data by selecting and appropriately using one of several listed representations (8.12C) recognize misuses of graphical or numerical information (8.13B) evaluate predictions and conclusions based on data analysis (8.13B) Page 13 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. 8.12 Probability and statistics. The student uses statistical procedures to describe data. The student is expected to: 8.12A select the appropriate measure of central tendency or range to describe a set of data and justify the choice for a particular situation: and 8.12C select and use an appropriate representation for presenting and displaying relationships among collected data, including line plots, stem and leaf plots, circle graphs, bar graphs, box and whisker plots, histograms, and Venn diagrams, with and without the use of technology. 8.13 Probability and statistics. The student evaluates predictions and conclusions based on statistical data. The student is expected to: 8.13B recognize misuses of graphical or numerical information and evaluate predictions and conclusions based on data analysis. 8.14 Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student applies Grade 8 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school. The student is expected to: 8.14A identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics: apply mathematical procedures and concepts to everyday experiences (8.14A) use a problem solving model that at a minimum includes the following 4 steps – understanding the problem, making a plan to solve it, executing the plan, and checking the solution for reasonability (8.14B) select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy from a given list (8.14C) communicate mathematical ideas or concepts using language, efficient tools, appropriate units and mathematical models – graphical, numerical, physical or algebraic (8.15A) make conjectures or draw conclusions from patterns or sets of examples or non-examples (8.16A) validate conclusions sing mathematical properties and relationships (8.16B) identify and sketch the general form of quadratic parent functions (A.2A) determine domain and range for quadratic functions (A.9A) investigate, describe and predict the effects of changes in “a” on the graph of y = ax2 + c (A.9B) investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in “c” on the graph of y = ax2 + c (A.9C) analyze graphs of quadratic functions an draw conclusion (A.9D) solve quadratic equations using concrete models, tables, graphs and algebraic methods (A.10A) make connections among the solutions (roots) of quadratic equations, the zeros of their related functions, and horizontal intercepts (x-intercepts) of the graph of the function. (A.10B) 8.14B use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness; and 8.14C select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types, including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, acting it out, making a table, working a simpler problem, or working backwards to solve a problem. 8.15 Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student communicates about Grade 8 mathematics through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models. The student is expected to: 8.15A communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models. 8.16 Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student uses logical reasoning to make conjectures and verify conclusions. The student is expected to: 8.16A make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and non-examples; and 8.16B validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 14 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. A.2 Foundations for functions. The student uses the properties and attributes of functions. The student is expected to: A.2A identify and sketch the general forms of linear (y = x) and quadratic (y = x2 ) parent functions. A.9 Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands that the graphs of quadratic functions are affected by the parameters of the function and can interpret and describe the effects of changes in the parameters of quadratic functions. The student is expected to: A.9A determine the domain and range for quadratic functions in given situations; A.9B investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in a on the graph of y = ax2 + c; A.9C investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in c on the graph of y = ax2 + c; and A.9D analyze graphs of quadratic functions and draw conclusions. A.10 Quadratic and other nonlinear functions. The student understands there is more than one way to solve a quadratic equation and solves them using appropriate methods. The student is expected to: A.10A solve quadratic equations using concrete models, tables, graphs, and algebraic methods; and A.10B make connections among the solutions (roots) of quadratic equations, the zeros of their related functions, and the horizontal intercepts (x-intercepts) of the graph of the function. Evidence of Learning At least 80% of the time students will demonstrate on paper or use models to show they can draw three-dimensional figures from different perspectives use pictures or models to demonstrate the Pythagorean Theorem find the lateral or total surface area or prisms, pyramids and cylinders using concrete models and nets connect models of prisms, cylinders, pyramids, spheres, and cones to the formulas for their volumes estimate measurements and use formulas to solve application problems involving lateral and total surface area and volume use proportional relationships to determine the missing measurements of similar two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures find the probabilities of dependent and independent events occurring use theoretical probabilities and experimental results to make decisions and predictions select and use an appropriate representation for presenting and displaying relationships among collected data recognize the misuses of graphical or numerical information evaluate predictions and conclusions based on data analyses identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences use a problem solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, devising and then executing a plan and checking the results for reasonability select or develop an appropriate problem solving strategy from a supplied variety of types communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units and mathematical models – graphical, numerical, physical or algebraic make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples or non-examples validate conclusions drawn using mathematical properties and relationships SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 15 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. identify and sketch the general forms of the quadratic parent function determine domain and range values to fit a given situation investigate, describe and predict the effects of changes in “a” on the graph of y = ax2 + c investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in “c” on the graph of y = ax2 + c draw conclusions from analyzing graphs of quadratic functions solve quadratic equations using concrete models, tables, graphs, and algebraic methods make connections among the zeros, roots and horizontal intercepts of a quadratic function SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 16 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Unit 8: Quadratics Third Grading Period - Weeks 4- 10 (27 days) Essential Questions How do you graph a quadratic function? What determines which way a parabola opens? How can you tell how much a parabola’s vertex is shifted from the origin? How can you locate the maximum and minimum value of a quadratic function? Does every quadratic function have two zeros? CURRICULUM GUIDE Essential Pre-requisite Skills 7th Grade represent squares and square roots using geometric models (7.1C) estimate and find solutions to application problems involving proportional relationships such as similarity, scaling, unit costs, and related measurement units (7.3B) generate formulas involving unit conversions, perimeter, area, circumference, volume, and scaling (7.4A) use properties to classify three-dimensional figures, including pyramids, cones, prisms, and cylinders (7.6C) use critical attributes to define similarity (7.6D) sketch three-dimensional figures when given the top, side, and front views (7.8A) make a net (two-dimensional model) of the surface area of a three-dimensional figure (7.8B) estimate measurements and solve application problems involving length and area of polygons and other shapes (7.9A) connect models for volumes of prisms (triangular and rectangular) and cylinders to formulas of prisms (triangular and rectangular) and cylinders (7.9B) estimate measurements and solve application problems involving volume of prisms (triangular and rectangular) and cylinders (7.9C) find the probability of independent events (7.10B) select and use an appropriate representation for presenting and displaying relationships among collected data, including line plot, line graph, stem and leaf plot, circle graph, bar graph, and Venn diagrams, and justify the selection (7.11A) make inferences and convincing arguments based on an analysis of given or collected data (7.11B) describe a set of data using mean, median, mode, and range (7.12A) choose among mean, median, mode, or range to describe a set of data and justify the choice for a particular situation (7.12B) The Teaching Plan Instructional Model & Teacher Directions The teacher will… So students can … Days 1 and 2 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 10 – Modeling and Applying the Pythagorean Theorem SEs 8.7C, 8.9A Day 1 Engage (10 minutes) Divide students into groups of 3-4. Distribute the MacArthur Park activity to the students. Provide scissors to each student or student group. Display the transparency of MacArthur Park. Ask the students to read the problem and answer the questions in their small groups. Use the facilitation questions on p 182 to assist students as needed. Explore (15 Minutes) Distribute the Side, Side and the Problem Solving Checklist everywhere a side activity to the students. Ask the students to read the problems and answer the questions in their small groups. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Days 1 and 2 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 10 – Modeling and Applying the Pythagorean Theorem SEs 8.7C, 8.9A Day 1 Engage (10 minutes) Cut out the towers as instructed. Arrange the tower pieces so that there are no gaps or overlaps. Answer the question. Explore (15 Minutes) Read and solve the problems presented. (8.7C,8.9A) Use the Problem Solving Checklist to help solve the problem. Explain (15 Minutes) Present the problem solutions to the class. Fill in the “This is what I need to do” boxes on the summarizing the Pythagorean Theorem page. (8.7C,8.9A) Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 17 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Use the facilitation questions on p 183 to assist students as needed. Explain (15 Minutes) Have each student group share their responses to the class. Display the transparency: Summarizing the Pythagorean Theorem and distribute this page to the students. Have the students fill in the missing boxes on their own activity sheet. Use the facilitation questions on p 185 to guide a discussion with the students. Day 2 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Distribute Fences and Pastures and the Problem Solving Checklist to each student. Ask the students to work on the two problems in their groups. Use the facilitation questions on page 186 to assist students as needed. Evaluate (20 Minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Modeling and Applying the Pythagorean Theorem to each student Have students complete individually showing all work on the pages Have student trade pages for grading Have students journal a summary of solving Pythagorean Theorem problems (Use the Summarizing the Pythagorean Theorem page). Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Days 3 and 4 – Introduction to Quadratic Functions Engage: (15-20 minutes) Create a foldable using the vocabulary for Quadratics. See p. 628, 629, 630 of text for assistance. Note: the foldable should be interactive and include the word, the definition and graphic illustrations. Explore: (10 minutes) Direct the students in pairs to read the excerpt about a rare and precious metal from Quadratics - Day 1 Notes. Emphasize the domain (length of a side) and the range (area) as a table is developed from the different size rectangles. Explain: (15-20 minutes) Have students work through the notes as a class analyzing and drawing conclusions regarding the curve generated by plotting the different lengths versus the areas of the rectangles. Discuss the equation of the line of symmetry and its purpose. Point out the x-intercepts as they relate to the area of the rectangles and the length of a side. Identify the significant graphical points of the generated quadratic function. Elaborate: (20-30 minutes) Allow students to work in pairs to complete the Quadratics – Day 1 Assignment Study examples 1 and 2 pp 628-629 in the text, emphasizing the quadratic parent function. Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor the students as they work Have the students complete both handouts for submission at the beginning on the next class period SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Day 2 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Read and answer the Fences and Pastures handout. (8.7C,8.9A) Use the Problem Solving Checklist to help solve the problem Discuss your problem solving technique with the rest of the group Evaluate (20 Minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.7C, 8.9A) Discuss in your journal a summary of solving Pythagorean Theorem problems (Use the Summarizing the Pythagorean Theorem page if needed) Discuss how using the problem solving checklist helped you solve the problems. Days 3 and 4 - Intro to Quadratic Functions Engage: create a foldable using the vocabulary for Quadratics. The foldable should be interactive. It should include the word, the definition and a graphic illustration. Explore: read along with teacher on the Quadratics - Day 1 Notes about a rare and precious metal. develop a table and determine the domain (length of a side) and the range (area of the rectangle) for the quadratic function.(A.9A) Explain: analyze the graph of the quadratic function and draw conclusions about the length and width of the rectangles (A.9D) find an equation for the line of symmetry. make connections between the horizontal intercepts (x-intercepts) of the graph of the function and the physical reality of what the coordinates represent. (A.10B) identify the significant graphical points of the quadratic function and their interpretation related to the problem situation. (A.10B) Elaborate: work in pairs to complete the Quadratics – Day 1 Assignment (A.9A, A.9D, A.10B) study examples 1 and 2 on p. 628-629 in the text, emphasizing quadratic parent functions (A.2A) Evaluate: ask appropriate questions for understanding complete both handouts for homework Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 18 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Days 5 and 6 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 12 – Surface Area and Volume SEs 8.8A,B,C & 8.15A Day 5 Days 5 and 6 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 12 – Surface Area and Volume SEs 8.8A,B,C & 8.15A Day 5 Engage (10 Minutes) Divide students into groups of 3-4. Distribute a TAKS Mathematics Chart and a “What’s my formula?” card set to each student. Ask students to match each card with a formula, using the Mathematics chart as a guide. After students have completed the card match, have a brief discussion with the students using the facilitation questions on p. 214. Explore (15 Minutes) Distribute the Prism Net Activity, a TAKS Mathematics Chart, colored pencils and a graphing calculator to the students. Have the students complete the activity in their groups requested using the formula chart as a guide. Use the facilitation questions on p 215 to assist the student groups as needed. Explain (15 Minutes) Have the student groups discuss and display their work from the Prism Net activity to the rest of the class. Use one of the following methods: make a poster, make a transparency or fill in a copy of the teacher’s transparency. Use the facilitation questions on page 217 to check the students’ conceptual understanding. Make sure and connect the procedures to their understanding as they present their work. Engage (10 Minutes) Match each formula card to its drawing using the provided formula charts. Participate in a classroom discussion on formulas. Explore (15 Minutes) Complete the provided activity. Color the parts of the shape. Find the areas and volumes requested using the formula chart as a guide. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Answer question related to finding area and volume of 2 and 3 dimensional shapes. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Explain (15 Minutes) Make a group presentation on the prism net activity using one of the following methods: make a poster, make a transparency or fill in a copy of the teacher’s transparency. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Answer question related to finding area and volume of 2 and 3 dimensional shapes. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Day 6 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Complete the provided activity. Color the parts of the shape. Find the areas and volumes requested using the formula chart as a guide. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Answer question related to finding area and volume of 2 and 3 dimensional shapes. (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Evaluate (20 Minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.8A,B,C & 8.15A) Discuss in your journal probability and central tendency especially the difference between theoretical and experimental probability. Day 6 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Distribute the Cylinder Net activity, a TAKS Mathematics Chart, colored pencils and a graphing calculator to each student. Have the students complete the activity in their groups. Use the facilitation questions on p 218 to assist the student groups as needed. Evaluate (20 Minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Surface Area and Volume to each student Have students complete the questions individually showing all work on the pages Have student trade pages for grading Have the students write a summary of how to find surface area and volume in their journals. Make sure they know the importance of the formula chart. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Use the error analysis on page 220 to analyze the results for effective reteaching. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 19 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 7- Interpreting the Maximum or Minimum of a Quadratic Function Engage: (5 minutes) Ask students if they have ever seen a long fly ball in a baseball game. Show a clip of a baseball game (if readily available) to aid a discussion between partners of the flight of the fly ball off the bat. Have the students in pairs write down the main points of their discussion. Explore: (15-20 minutes) Have the students in pairs complete the Quadratics – Day 2 Notes Explain: (10 minutes) Have the students analyze the 1. maximum height of the path of the soccer ball; and 2. domain and range as Leslie kicked the soccer ball Discuss with the students the equation d = -16 t 2 + h as the stone is dropped Elaborate: (As time allows) Facilitate and monitor student as they work in groups to complete the 3 scenarios on Quadratics – Day 2 Assignment about Engineer Erik, Studious Stanley and Athletic Adam. Evaluate: Study the key concepts on pg 630 of text and describe the changes Direct the students to complete the handouts for homework Day 7- Interpreting the Maximum or Minimum of a Quadratic Function Engage: Discuss with a partner the flight of a long fly ball during a baseball game. Write down the major points of your discussion. Explore: complete with a partner the Quadratics – Day 2 Notes (A.9A, A.9D, A.10B) Explain: analyze the graph of the maximum height as Leslie kicks the ball. (A.9D) determine and make connections among the domain and range of the quadratic. (A.9A)(A.10B) investigate, describe and predict the effects of changes on “a” and “c” the equation d = -16 t 2 + h as the stone is dropped (A.9B) (A.9C) Elaborate: ask questions for understanding as they work in groups to complete the 3 scenarios on Quadratics – Day 2 Assignment about Engineer Erik, Studious Stanley and Athletic Adam. Evaluate: Study the key concepts on page 630 of text and explain their observations (A.9B, A.9C) Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Day 8- Writing Quadratic Functions Engage: (5 minutes) Have the students study examples 3, 4 and 5 pp 629-631 focusing on the change in the coordinates of the vertex Explore: (10-15 minutes) Distribute Quadratics – Day 3 Notes and investigate the equation h=16t2 +vt + s to discuss height, time in motion, initial height, and initial velocity as they relates to the table and the graph. Explain: (10-15 minutes) Have students solve for the maximum height, total time in motion, initial height, and initial velocity using the table and graph Elaborate: (As time allows) Have students answer the questions about the 3 different scenarios on Quadratics – Day 3 Assignment Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Have the students complete the handouts for homework Day 8- Writing Quadratic Functions Engage: study example 3, 4 and 5 p. 629-631 investigate, describe, and predict the effects of changes in “c” on the quadratic graph (A.9B, A.9C) Explore: work on Quadratics – Day 3 Notes (A.10B) investigate, describe the equation h = -16t2 +vt + s (A.9B, A.9C) Explain: solve for the maximum height, total time in motion, initial height, and initial velocity using the table and graph (A.10A) work through the notes as a class engaging in discussion (A.9D, A.10A, A.10B) Elaborate: answer the questions about the 3 different scenarios on Quadratics – Day 3 Assignment (A.9A, A.9D, A.10A, A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for understanding complete the handouts for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 20 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 9- Quadratics Quiz Evaluate: Have student complete the Quadratics – Day 4 Fireworks Assessment Elaborate: Have students read and work through example #6 pg 631 Facilitate and monitor student work Days 10 and 11 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 14 – Probability and Central Tendency SEs 8.11A & B, 8.12A & C & 8.13B\ Day 10 Day 5- Quadratics Quiz Evaluate: complete the Quadratics – Day 4 Fireworks Assessment (A.9A, A.9D) Elaborate: read and work through example #6 pg 631(A.9A) ask questions for understanding Days 10 and 11 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 14 – Probability and Central Tendency SEs 8.11A & B, 8.12A & C & 8.13B Day 10 Engage (10 Minutes) Display the Transparency: Movie Survey Have a student act as scribe to record the answers to the problems. Use the facilitation questions on p 252 to guide a brief discussion. Explore (15 Minutes) Distribute The Show Must Go On activity to each student. Distribute 1 set of Movie survey response slips to each group. Have the students read and complete the activity in their groups. Use the facilitation questions on p 253 to assist the student groups as needed. Explain (20 Minutes) Have the student groups display and present their work from the The Show Must Go On activity. Use the facilitation questions on page 255 to check the students’ conceptual understanding. Make sure and connect the procedures to their understanding as they present their work. Day 11 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Distribute the Displaying Data activity. Provide each student with a graphing calculator. Have the students complete the activity in their groups. Use the facilitation questions on p 256 to assist the student groups as needed. Evaluate (20 Minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Probability and Central Tendency to each student Have students complete the questions individually showing all work on the pages. Have student trade pages for grading Have the students write a summary of what they learned about probability and central tendency in their journals. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Use the error analysis on page 257 to analyze the results for effective reteaching. Day 12 - Exploring the Quadratic Parent Function-Changes in “a” and “c” Engage: Have the students in pairs study problem #23 p.632 to determine the error Distribute Quadratics – Day 5 Notes on graphing the quadratic parent function y = x2 Explain: SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Engage (10 Minutes) Discuss the Movie Survey activity. Discuss the question “How can probability be simulated?” Explore (15 Minutes) Complete The Show Must Go On activity. Find the experimental and theoretical probabilities. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Answer questions as needed. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Explain (20 Minutes) Make a group presentation on The Show Must Go On to the class. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Answer question related to probability and central tendency. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Day 11 Elaborate (20 Minutes) Complete the Displaying data activity using a graphing calculator. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Answer questions related to probability and central tendency. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Evaluate (20 Minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Discuss in your journal a summary of how to find areas and volumes using a formula chart. (8.11A,B; 8.12A,C; 8.13B) Day 12 - Exploring the Quadratic Parent Function-Changes in “a” and “c” Engage: study problem #23 p.632 to determine the error (A.2A) Explore: complete Quadratics – Day 5 Notes on the quadratic parent functions y = x2 (A.2A, A.9B, A.9C, A.9D) Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 21 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Discuss how to input the quadratic equations into the graphing calculator, observe the graph and find the values. Determine whether a quadratic opens up or down depending on the sign of a. Go over the Properties of the Graph of a Quadratic Function pg. 635 Elaborate: Plot the points on the graphs on the Quadratic Notes worksheets and describe the affects of “a” and “c” Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor students Have the students complete the handout for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Day 13 - Exploring the Quadratic Parent Function-Changes in “a” and “c” Engage: Have the students read and analyze example 4 pg 637 Suspension Bridges and discuss the lowest point of the cable above the water. Explore: Continue with problem #41 p.639 the Dallas Convention Center Explain: Pass out the Quadratics – Day 5 Assignment on Parent functions y = x2 Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor students Assign completion of the handout for homework Explain: input the quadratic equations into the graphing calculator, observe the graph and find solutions (A.10A) determine whether a quadratic opens up or down. Go over the properties of the graph of a quadratic function on pg.635.(A.9B) Elaborate: Plot the points on the graphs on the Quadratic Notes worksheets and describe the affects of “a” and “c” (A.9B, A.9C) Evaluate: ask questions for understanding complete the handout for homework Day 13 - Exploring the Quadratic Parent Function-Changes in “a” and “c” Engage: read example 4 p.637 Suspension Bridges and discuss the lowest point of the cable above the water.(A.9D, A.10B) Explore: Continue with problem #41 p.639 The Dallas Convention Center (A.9D)(A.10B) Explain: work on the Quadratics – Day 5 Assignment on Parent functions y = x2 (A.9B, A.9C, A.10A,A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for understanding complete the handout for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Days 14 and 15 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 15 – Discovering Patterns SEs 8.14C, 8.16A,B Day 14 Engage (15 minutes) Distribute the Toothpick Windows activity to each student. Distribute 50 toothpicks per group. Display the toothpick windows transparency. Ask the students to read and complete the activity. Use the facilitation questions on p 270 to assist the student groups as needed. Explore (15 minutes) Distribute one of the problem transparencies, either problem 1, problem 2 or problem 3 to each group. Also distribute to each group the activity debriefing questions for the problem the group was assigned. Ask each group to complete the activity and debriefing questions. Ask the groups to record their responses, so that the explain part of the lesson will SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Days 14 and 15 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 15 – Discovering Patterns SEs 8.14C, 8.16A,B Day 14 Engage (15 minutes) Complete the Toothpick Windows activity with the aid of the provided toothpicks. Answer the questions and participate in the teacher led discussion. Explore (15minutes) Complete the problem transparency and the activity debriefing questions. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Make sure and record my responses for future use. Explain (15 minutes) Present our problem transparency to the class. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Answer questions about our problem from the four debriefing questions. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Mathematics – Algebra 1 Day 15 Page 22 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. go smoothly. Use the facilitation questions on p 271-3 to assist the student groups as needed. Explain (15 minutes) Make sure each group has completed their activity debrief questions. Ask a group that explored problem 1 to display and present their transparency. Ask the group the 4 questions that correspond to their problem. Repeat this process for the other groups. Ask the students who are not presenting to complete the debriefing questions recording sheet for the other problems. Elaborate (20 minutes) Complete the analyzing error activity. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Answer the questions about the pattern activity. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Evaluate (20 minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Discuss in your journal a summary of finding patterns. (8.14C, 8.16A,B) Day 15 Elaborate (20 minutes) Distribute the analyzing errors activity to each student. Ask the students to complete the activity. Use the facilitation questions on p 276-8 to assist the student groups as needed. Evaluate (20 minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Discovering Patterns to each student Have students complete the questions individually showing all work on the pages. Have student trade pages for grading Have the students write a summary of what they learned about discovering patterns in their journals. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Use the error analysis on page 279 to analyze the results for effective reteaching. Day 16- Finding Solutions to a Quadratic Equation Using a Table Engage: Have the students analyze the table that models the function f(x) = 2x2 – 2x – 12 on the Quadratics – Day 6 Notes to determine the solutions to the equation. Explore: Have students complete the tables in problems 1-5 finding the solutions and the appropriate domain Have the students describe the zeros, or the roots as solutions Explain: Have students complete the tables with and without a calculator Continue by practicing on Quadratics – Day 6 Assignment problems 1-7 Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Complete the handouts for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Day 16- Finding Solutions to a Quadratic Equation Using a Table Engage: go over the table that models the function f(x) = 2x2 – 2x -12 on the Quadratics – Day 6 Notes to determine the solutions to the equation using tables and graphs (A.10A, A.10B) Explore: complete the tables making connections in problems 1-5 finding the solutions and determining the appropriate domain( A.9A, A.10A, A.10B) Explain: describe the zeros, or the roots as solutions (A.10A, A.10B) Elaborate: complete the table with and without a calculator practice on Quadratics – Day 6 Assignment problems 1-7 (A.9A, A.10A, A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for understanding complete the handouts for homework Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 23 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 17- Solving Quadratics in Factor Form Engage: Answer the question, Does every quadratic function have two zeros? Post the rules for the Number of Solutions of a Quadratic Equation found at the bottom of pg 644 Explore: Work out examples 1-4 p. 643-645 Explain: Distribute the Quadratics – Day 7 Notes and explain the steps to finding the roots of a quadratic function by factoring Elaborate: Have students practice factoring problems 1-6 on the Quadratic Notes Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Assign completion of the handout as homework Day 17- Solving Quadratics in Factor Form Engage: answer the question, Does every quadratic function have two zeros? take notes on the rules for the Number of Solutions of a Quadratic Equation found at the bottom of pg 644 (A.10A, A.10B) Explore: Work out examples 1-4 pp 643-645 (A.10A, A.10B) Explain: Take notes on the Quadratics – Day 7 Notes which explains the steps to finding the roots of a quadratic function by factoring (A.10A, A.10B) Elaborate: Practice factoring problems 1-6 on the Quadratic Notes (A.10A, A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for better understanding complete the handout for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Day 18 - Solving Quadratics in Factor Form Engage/Explore: Have students read and discuss Example 6 pg 646 on Sports - When an athlete throws a shot put. Have students find the equation and use the equation to find the time that the shot put is in the air. Explain: Have the students draw the situation on a poster and summarize their observations Elaborate: Have students continue practicing factoring skills using the Quadratics – Day 7 Assignment-, work problems 1-12 Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Assign completion of handouts for homework Day 18 - Solving Quadratics in Factor Form Engage/Explore: read and discuss with a partner Example 6 p. 646 on Sports - When an athlete throws a shot put. find the equation and use it to find the time that the shot put is in the air. (A.10A, A.10B) Explain: draw the situation on a poster and write a short summary on observations (A.9D, A.10A, A.10B) Elaborate: continue practicing factoring skills using the Quadratics – Day 7 Assignment, work problems 1-12 (A.10A, A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for better understanding Complete the handouts for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 24 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Days 19 and 20 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 9 – Solids and Planar Figures SEs 8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B Day 19 Engage (10 minutes) Display the John Hancock Transparency Show the students the preconstructed frustum of a rectangular pyramid model with the net on a transparency. Use the facilitation questions on p. 164 to lead a class discussion. Explore (15 minutes) Distribute the activity Angles Everywhere to each student. Provide each student with a ruler or a TAKS Mathematics Chart Ask the students to read and complete the activity in their groups. Use the facilitation questions on p. 165 to assist the students as necessary. Explain (15 minutes) Display the transparency Triangles Tree diagram Distribute a paper version of the above transparency to each student. Ask the students to complete the tree diagram graphic organizer to represent the relationships among the types of triangles. Ask a student volunteer to record the class’s responses on the teacher transparency. Use the facilitation questions on p. 166 to guide a class discussion. Display the transparency How Do You Know? Ask the students to use their graphic organizers to answer the questions. Allow a few minutes for class discussion. Use the facilitation questions on p. 167 to debrief student responses. Days 19 and 20 Closing the Distance Grade 9 Lesson 9 – Solids and Planar Figures SEs 8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B Day 19 Engage (10 minutes) Participate in the class discussion. Explore (15 minutes) Complete the activity by measuring the side lengths of the triangles. Find the measures of the angles not labeled. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Name the types of triangles seen in your diagram. Justify the answer. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Explain (15 minutes) Complete your own tree diagram graphic organizer. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Participate in the class discussion the types of triangles. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Answer the How do you know questions. Be able to justify your answer. Day 20 Elaborate (20 minutes) Complete the Quads, Quads Everywhere activity. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Create a Venn diagram representing the relationships among quadrilaterals. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Present the Venn diagram to the rest of the class. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Evaluate (20 minutes) Complete 4-question multiple choice assessment and grading (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Discuss in your journal a summary of the properties of solid and planar figures. (8.7A, 8.15A,8.16A,B) Day 20 Elaborate (20 minutes) Distribute the activity Quads, Quads Everywhere to each student. Be sure each student still has a ruler or a TAKS Mathematics Chart. Ask the students to complete the activity. Use the facilitation questions on p. 168 to assist students as necessary. Distribute a sheet of chart paper and markers (or a blank transparency and transparency pens) to each student group. Ask the students to create a Venn diagram representing the relationships among types of quadrilaterals. Use the facilitation questions on page 169 to assist struggling students. Evaluate (20 minutes) Distribute Evaluate: Solids and Planar Figures to each student Have students complete the questions individually showing all work on the pages. Have student trade pages for grading Have the students write a summary of what they learned about properties of solid and planar figures in their journals. Collect assessments for further analysis on need to re-teach. Use the error analysis on page 170 to analyze the results for effective reteaching. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 25 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Day 21- Writing and Solving Quadratics Engage: Have students complete the Challenge problem 55 on pg 649 Explore: Have students take notes on Quadratics – Day 8 Notes to define variables, write equations and solve using any method 1-8 Explain: Describe each of the problems by drawing a geometric sketch Elaborate: Have students practice what they have learned on the Quadratics – Day 8 Assignment by defining variables, writing equations and solving them using any method Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Assign handout completion for homework Day 21- Writing and Solving Quadratics Engage: complete the Challenge problem 55 on pg 649 to make connections among the solutions of a quadratic equation (A.10A, A.10B) Explore: take notes on the worksheet Quadratics – Day 8 Notes to define variables, write equations and solve using any method 1-8 (A.10A, A.10B) Explain: describe each of the problems by drawing a geometric sketch (A.10A, A.10B) Elaborate: Practice lessons learned on the Quadratics – Day 8 Assignment (A.10A, A.10B) Evaluate: ask questions for better understanding complete handouts for homework Alternative Textual Resources for the Quadratics Unit are listed in the Resource Section of this Curriculum Guide. This is not a day for day replacement, but a different complete unit for the specific Algebra 1 material. Day 22- Poster Project of Quadratics Explore: Have students demonstrate understanding of quadratics by solving selected problems on page 647 – see Quadratic Function Poster Have students create a table, graph, identify the zeros, and maximum and minimum values Elaborate: Answer the question: How can you use a graphing calculator to find models for data? Perform Regressions p. 692-693 Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Day 22- Poster Project of Quadratics Explore: demonstrate understanding of quadratics by solving selected problems on page 647 and create a table, graph, identify the zeros, and maximum and minimum values Elaborate: answer the question: How can you use a graphing calculator to find models for data? Perform Regressions p. 692-693 Evaluate: Facilitate and monitor student work Day 23- Review Unit 8 Quadratics Day 23- Review Unit 8 Quadratics Explain: Review p. 696-701 Explain: Review p. 696-701 Day 24 – Unit 8 Exam Evaluate Ensure assessment question alignment with TEKS verbs and nouns Day 24 – Unit 8 Exam Evaluate Take assessment Day 25 SE 8.14A Day 25 SE 8.14A Engage Use the McDougal Littell TAKS Objectives Review and Practice Grade 9 TAKS SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Engage Study the types of problems in this TEK. Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 26 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Test pp. 116-7. Read TEK 8.14A Explain to the students that many different items can be tested including Formulas, Central Tendency and the Pythagorean Theorem. Explore Distribute the graphing calculators, TAKS Mathematics Charts and the Problem Solving Checklist and p 117 to the students. With student input go over the example and the You Do It on p 116. with the students. Explain Have the students complete p 117 in their groups. Have each group present at least 1 of the problems to the rest of the class. Elaborate Have each students write their own problems for this TEK. Evaluate Have the students work other student problems. Explore Help the teacher solve the problems on p 116. Explain Complete p 117 in your groups using the provided materials for guidance. (8.14A) Elaborate Write at least 2 problems for TEK 8.14A. (8.14A) Evaluate Solve the problems from one of the other groups. (8.14A) Day 26 SE 8.14B Engage Use the McDougal Littell TAKS Objectives Review and Practice Grade 9 TAKS Test pp. 118-9. Read TEK 8.14B Explain to the students that many different items can be tested that use a plan to solve them. Explore Distribute the graphing calculators, TAKS Mathematics Charts and the Problem Solving Checklist and p 119 to the students. With student input go over the example and the You Do It on p 118. with the students. Explain Have the students complete p 119 in their groups. Have each group present at least 1 of the problems to the rest of the class. Elaborate Have each student write at least two of their own problems for this TEK. Evaluate Have the students work other student problems. Day 26 SE 8.14B Engage Study the types of problems in this TEK. Explore Help the teacher solve the problems on p 118. Explain Complete p 119 in your groups using the provided materials for guidance. (8.14B) Elaborate Write at least 2 problems for TEK 8.14B. (8.14B) Evaluate Solve the problems from one of the other groups. (8.14B) Day 27 Unit 8 Reteach/ Review SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Day 27 Unit 8 Reteach/ Review Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 27 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Vocabulary: Math Content Quadratic Function Roots Solution Maximum Value Minimum value Vertex Quadratic Equation Domain Range Height Time in motion Initial height Initial velocity x-intercepts y-intercept Axis of Symmetry Parabola Parent Quadratic Function Vocabulary: Verbs locate determine identify describe investigate estimate validate evaluate Resources: Quadratics - Day 1 Notes Quadratics – Day 1 Assignment Quadratics – Day 2 Notes Quadratics – Day 2 Assignment Quadratics – Day 3 Notes Quadratics – Day 3 Assignment Quadratics – Day 4 Fireworks Assessment Quadratics – Day 5 Notes Quadratics – Day 5 Assignment Quadratics – Day 6 Notes Quadratics – Day 6 Assignment Quadratics – Day 7 Notes Quadratics – Day 7 Assignment Quadratics – Day 8 Notes Quadratics – Day 8 Assignment Quadratic Function Poster Problem Solving Checklist McDougal Littell TAKS Objectives Review and Practice Grade 9 TAKS Test McDougal Littell Algebra 1 (MDL) Alternative Text Resources for Quadratics Unit: Day 3 – MDL 10.1 Graph y = ax2 + c Day 4 – MDL 10.2 Graph y = ax2 + bx + c Day 7 – Core 1A pp 142-144, Investigation 1 What Goes Up … Must Come Down Day 8–MDL 10.2 Extension pp 641-642, Graph Quadratic Functions in Intercept Form Day 12 – MDL 10.3 Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing Day 13 – MDL 10.8 Compare Linear, Exponential and Quadratic Models Day 16 – Core 1A pp 144-147, Investigation 2 The Shape of Rules Day 17 – MDL 9.4 Solve Polynomial Equations in Factored Form Day 18 - Review MDL 9.5-9.6 Day 21 - MDL 9.7 Factor Special Products SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 28 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. Evidence of Learning Differentiation Interims/TAKS/Benchmarks What do you do for students who need additional support? Look over the Teaching Tips on p.203 Best Practice Tool Kit Use the Idea Map and Concept Map p. 158159 for Vocabulary Strategies Best Practice Tool Kit Use Substitute Teacher Activities p. 573 Best Practice Toolkit. April 2006 TAKS Test, TEKS A.2A, #28 College-Readiness i.e., Anticipated Skills for SAT/ACT/AP/Career/Life 1. If one root of 4z2+bz-80=0 is 5, what is the other root? 2. f(x) = -x3 - 3x2 + 70x Is x + 10 a factor? What do you do for students who master the learning quickly? Choose from a variety of advanced activities on p. 425-452 in the Best Practice Tool Kit. Teacher Edition Page Notes: Section 10.1 pg 629 Section 10.2 pg 636 Section 10.3 pp 645/6 April 2003TAKS Test, TEKS A.9B, #49 Best Practices Toolkit (For Chapter 10) Differentiated Instruction pp 77-80 ELL pp115-116 Inclusion pp147-148 PreAP pp 269-271 Academic Mentoring: Grade 9 TAKS Study Guide: Interactive TEA website Mathematics April 2004TAKS Test, TEKS A.9C, #8 SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 29 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards. SAISD © 2008-09 – Third Grading Period Mathematics – Algebra 1 Page 30 of 30 Power Standards represent the essential knowledge and skills students need for success in high school and beyond. Power Standards must be mastered to successfully pass the required assessments at each grade level. All TAKS eligible knowledge and skills are identified as Power Standards.