Psychology Midterm Review
advertisement

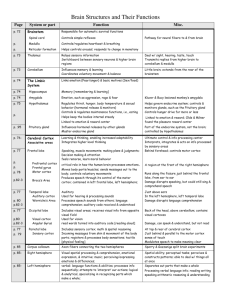
A.P Psychology Midterm Review Chapter 1 - Definition of Psychology -What is the difference between Behaviors and Mental Processes? - Why do we study psychology? - How did Psychology develop as a scientific study of behavior? - Pioneers of Psychology - study your timeline - What is the difference between Structuralism and Functionalism? - - Introspection - who pioneered it? - how do we use it? - what is it? How do the various schools of psychology differ? - be able to apply the approaches to Psychology to a case study o Behavioral Genetics o Neuroscience o Cognitive o Behavioral o Psychodynamic o Socio-Cultural o Evolutionary Chapter 2 - Differentiate between the different Research Methods o Field Experiment o Laboratory Experiment o Survey o Interview o Case Study o Naturalistic Observation o Longitudinal Study o Cross Sectional Study - pay particular attention to the following: o Placebo Effect o Control Group o Experimental Group o Single-Blind Study o Double-Blind Study o Independent Variable o Dependent Variable o Extraneous Variables o Confounding of Variables - when given a hypothesis, be able to determine independent and dependent as well as the controlled variables. - Organizing Data - What are Statistics? Why do we use them? Define: o Mean, Median & Mode o Correlation Be able to identify the correct graph as it applied to positive, negative and no correlation. Positive correlation Negative correlation o Standard Deviation o Variance - Psychological Evidence - What does it mean to be an Empirical Science? - What is the difference between Inference and Observation? - What Ethical Standards should a psychologist follow when conducting research on human subjects? - What are the two primary arguments presented by animal activists? think of any arguments to counter these? Chapter 3 Be able to identify the major parts of the neuron & explain their function. Explain the following: - action potential o all or none law - absolute refractory period - resting potential - reuptake process Can you Hemispheres of the Brain What are the functions of the right brain and left brains? What characteristics do people who are “left-brained” and “right-brained” possess? Neurotransmitters – name all of them and name 2 things they are responsible for. The Cortex – Lobes What are the functions of each: - Frontal Lobe o Motor Cortex o Broca’s Area o Frontal Lobotomy o Phineas Gage - Parietal Lobe o Somatosensory Cortex - Temporal Lobe o Primary Auditory Cortex o Auditory Association Area o Wernicke’s Area - Occipital Lobe o Primary Visual Cortex o Visual Association Area Major Parts of the Brain _______ Occipital Lobe _______ Broca’s Aphasia _______ Wernicke’s Area _______ Frontal Lobe _______ Somatosensory Cortex _______ Parietal Lobe _______ Broca’s Area _______ Temporal Lobe _______ Primary Auditory Cortex _______ Auditory Association Area _______ Neglect Syndrome _______ Visual Association Area _______ Primary Visual Cortex _______ Cortex _______ Frontal Lobotomy _______ Motor Cortex a. transforms signals from eyes into basic sensations b. lobe responsible for hearing and speaking coherently c. narrow strip at the front of the parietal lobe that processes sensory info d. lobe responsible for making decisions and executing plans e. the wrinkled area of the brain f. narrow strip at the back of the frontal lobe that initiates voluntary movement g. a surgical procedure where the frontal lobe is cut away from the rest of brain h. area of the brain that combines sound into words and sentences i. area of the brain that understands speech and allows you to speak coherently j. responsible for turning basic visual sensations into complete perceptions k. lobe responsible for seeing colors and recognizing objects l. transforms electrical signals from ears into meaningless sound sensations m. lobe responsible for processing sensory info like touching, feeling temperature and pain. n. disorder where the individual fails to see objects on the opposite side of the brain damage o. transforms noise and sounds into words and music p. disorder where a person can’t speak in sentences but can understand spoken and written words The __________________ is involved in performing timed motor responses such as those required in playing sports. The __________________ functions as a bridge between the spinal cord and the brain. The __________________ saves fleeting memories by putting them into permanent storage throughout the brain. The __________________ is the control center of the endocrine system. The __________________ gland regulates metabolism. The __________________ glands secrete adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine). The __________________ gland regulates growth and produces hormones. The __________________ receives sensory information and relays the information to areas of the cortex. The __________________ controls vital reflexes such as respiration, heart rate and blood pressure. Brain Scanning Techniques Explain each of the following: - Electroencephalograph: - CT Scan: - MRI Scan: - fMRI Scan: - PET Scan: - Lesioning: - ESB: Evolution of Psychology - be able to explain the major driving force behind Charles Darwin and his Evolutionary theory Genetics - Be aware of the basic genetic principles that we went over in class. Chapter 4 I. II. III. Sensation a. Thresholds b. Sensory Differences and Ratios c. Sensory Adaptation d. Motivation and Signal Detection Theory The Senses a. Vision b. Hearing c. Smell and Taste d. Touch e. Kinesthetic and Vestibular Systems Perception a. Principles of Perception b. Depth Perception c. Constancy d. Illusions e. Subliminal messages Review Questions: 1. Define Sensation and Perception. 2. What is Psychophysics? 3. Define Absolute Threshold. Give examples from notes. 4. What is a Just Noticable Difference? 5. What is Subliminal Advertising? Why was there a mass outcry over the use of Subliminal Messages? How do most psychologists view the technique today? 6. How does motivation affect a person’s ability to receive and perceive sensations? 7. Define and provide an example of the Signal Detection Theory. 8. Diagram the eye using the following parts: Cornea, Lens, Iris, Pupil, Retina, Fovea. What does each part do? 9. What is the difference in nearsightedness and farsightedness in the eye? 10. What is the Trichromatic Theory of Color Vision? The Opponent Process Theory? 11. What is an optical illusion? Impossible figures? 12. Explain the concept of the Ames Room. 13. Diagram the ear using the following parts: pinna, eardrum, hammer, anvil, stirrup, cochlea, outer ear, middle ear, inner ear. What do each of these parts do? 14. How do smell and taste work? 15. What factors can we attribute to taste preference? 16. What is the pathway involved in the feeling of pain? Explain. 17. What is Gate-Control Theory? 18. What are the Kinesthetic System and the Vestibular System? Why are they important to us? 19. Which of the senses is the only one in which impulses are NOT sent through the Thalamus? Chapter 7 – Memory Encoding: - Cocktail Party Phenomenon: Storage: Retrieval: Flashbulb memories: Sensory Memory: Short-Term Memory: - Chunking: - Rehearsal: Long-Term Memory: What are the two differing theories about Long-Term Memory? In order to commit something to memory you must pay _______ to it. Which means focusing awareness on a narrow range of stimuli. Elaboration: Dual-Coding Theory: Tip of the Tongue Phenomena: Clustering: Conceptual Hierarchy: Schema: Semantic Network: Why do we forget? Explain each of the following theories. 1. Ineffective Coding – (Psedoforgetting): 2. Decay: 3. Interference: a. Proactive b. Retroactive 4. Retrieval Failure: 5. Motivated Forgetting (Repression): Retrograde Amnesia: Anterograde Amnesia: Chapter 13 – Stress, Health & Coping The Nature of Stress - Biopsychosocial Model - Health Psychology - Types of Stress o Frustration o Conflict Kurt Lewin & Neal Miller Approach-approach conflict Avoidance-avoidance conflict Approach-avoidance conflict o Change Social-Readjustment Scale o Pressure Responding to Stress - Common emotional responses - Common physiological responses o Fight-or-flight response o General Adaptation Syndrome - Common behavioral responses o Coping Defense Mechanisms Constructive Coping o Learned Helplessness o Aggression o Catharsis Effects of Stress on Psychological Functioning - Burnout - Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder - Positive vs. Negative Effects of Stress Effects of Stress on Physical Health - Psychosomatic diseases - Type A vs. Type B Personalities - Diseases linked to stress Factors Impacting Stress - Social Support - Optimism - Conscientiousness Health-Impairing Behavior - Effects of Smoking - Effects of a poor diet - Alcohol and Drug Use - Lack of Exercise - AIDS Reactions to Illness - seeking treatment and communicating with health care professionals - listening to medical advice